Eczema Treatments
Visualize and Compare Treatments
# Treatments per Category
Non-steroid Prescription Medication
-
 Rinvoq(Upadacitinib)If your child is 12+ years, needs rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedIf you need rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedOral once dailyHigh
Rinvoq(Upadacitinib)If your child is 12+ years, needs rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedIf you need rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedOral once dailyHigh⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Upper respiratory tract infection 23% Acne 10% Herpes simplex 4% Headache 6%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$396 per month($268 - $1,535)$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSUpadacitinib is highly effective at reducing itch and improving skin symptoms in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with benefits seen as early as 1-2 weeks of treatment and maintained through 52 weeksStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Upadacitinib, taken as a daily pill, significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo. After 16 weeks, 60-70% of patients taking upadacitinib 15mg and 73-80% of patients taking 30mg had their eczema improve by at least 75%, compared to only 13-16% of patients taking placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,683📄Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes Upadacitinib shows superior efficacy compared to dupilumab (another common treatment) in improving skin clearance and reducing itch, with faster onset of actionStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Upadacitinib was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in adults, including patients who didn't respond well to other treatments like dupilumab or baricitinib. About 73% of patients achieved significant improvement in their eczema, and 69% experienced reduced itching after 16 weeks of treatment.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 47Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 673The most common side effect is acne (occurring in 10-16% of patients), which is usually mild/moderate and manageable. Other potential side effects include increased risk of infections and elevated liver enzymesStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at the safety of upadacitinib across multiple conditions including atopic dermatitis by analyzing data from clinical trials. For atopic dermatitis patients, upadacitinib was generally well-tolerated, with acne being a notable side effect specific to AD patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 2,693Severity: not availableAge: not availableUpadacitinib significantly improves quality of life measures including sleep, daily activities, and emotional wellbeing in patients with atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes 📄Upadacitinib combined with topical steroids significantly improved itch, skin pain, sleep, and quality of life in patients with atopic dermatitis. The improvements were seen within 1-2 weeks and lasted for up to 52 weeks, with 62-84% of patients experiencing meaningful improvements depending on the dose.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 901Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adultsBoth doses showed sustained improvements across all patient-reported outcomes, with higher dose showing better results Upadacitinib is highly effective at reducing itch and improving skin symptoms in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with benefits seen as early as 1-2 weeks of treatment and maintained through 52 weeks
Summary:Upadacitinib, taken as a daily pill, significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo. After 16 weeks, 60-70% of patients taking upadacitinib 15mg and 73-80% of patients taking 30mg had their eczema improve by at least 75%, compared to only 13-16% of patients taking placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,683Results:
Summary:Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Results:Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes
Upadacitinib shows superior efficacy compared to dupilumab (another common treatment) in improving skin clearance and reducing itch, with faster onset of action
Summary:Upadacitinib was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in adults, including patients who didn't respond well to other treatments like dupilumab or baricitinib. About 73% of patients achieved significant improvement in their eczema, and 69% experienced reduced itching after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 47Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 673Results:
The most common side effect is acne (occurring in 10-16% of patients), which is usually mild/moderate and manageable. Other potential side effects include increased risk of infections and elevated liver enzymes
Summary:This study looked at the safety of upadacitinib across multiple conditions including atopic dermatitis by analyzing data from clinical trials. For atopic dermatitis patients, upadacitinib was generally well-tolerated, with acne being a notable side effect specific to AD patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,693Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:
Upadacitinib significantly improves quality of life measures including sleep, daily activities, and emotional wellbeing in patients with atopic dermatitis
Summary:Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Results:Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes
Summary:Upadacitinib combined with topical steroids significantly improved itch, skin pain, sleep, and quality of life in patients with atopic dermatitis. The improvements were seen within 1-2 weeks and lasted for up to 52 weeks, with 62-84% of patients experiencing meaningful improvements depending on the dose.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 901Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adultsResults:Both doses showed sustained improvements across all patient-reported outcomes, with higher dose showing better results
-
 Dupixent(Dupilumab)If your child is 6+ months and topical treatments don't work for your childIf topical treatments don't work for youInjection every 2 weeksMedium
Dupixent(Dupilumab)If your child is 6+ months and topical treatments don't work for your childIf topical treatments don't work for youInjection every 2 weeksMediumSide Effect Affected Injection site reaction 10% Conjunctivitis 10% Blepharitis 5% Oral herpes 4% $285 per month($158 - $1,035)$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSDupilumab significantly improves signs and symptoms of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, including skin lesions, itching, and quality of life compared to placebo. In clinical trials, 60-70% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Dupilumab significantly improved quality of life in adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The improvements were meaningful in daily life, particularly reducing pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression, and helping with usual activities.Total Patients: 1,379Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Both weekly and every 2 weeks dupilumab treatment led to significantly greater improvements in quality of life compared to placebo 📄Dupilumab combined with topical steroids was significantly more effective than steroids alone in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. After 16 weeks, about 39% of patients on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 12% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for the full year of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 740Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Dupilumab is an effective treatment for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children as young as 6 months. Clinical trials show that 60-70% of patients achieve significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, including reduction in itch and skin clearance.Comment Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months and olderDupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo The medication has an acceptable safety profile, with the most common side effects being injection site reactions and conjunctivitis (eye inflammation). Serious side effects are rare. Dupilumab actually reduces skin infections compared to placebo.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 673📄This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Comparative Study Dupilumab works by blocking two key inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) that drive atopic dermatitis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, with a higher initial loading dose.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Dupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms and skin healing over 16 weeks of treatment. The medication worked by reducing inflammation in the skin and helping restore normal skin barrier function.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 54Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableDupilumab improved skin healing at both molecular and cellular levels 📄Dupilumab is the first approved targeted biological therapy for atopic dermatitis in adults and children over 6 years with moderate-to-severe disease. It works by blocking specific inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) and helps improve skin barrier function.Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 years and olderThe medication is approved for patients 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis that is not well controlled with topical prescription treatments. Continuous treatment is needed to maintain response.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe eczema, dupilumab with low-strength steroid cream worked significantly better than placebo. After 16 weeks, 28% of children on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to only 4% on placebo, and 53% had major improvement in their eczema compared to 11% on placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 162Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months to <6 years📄This study showed that taking dupilumab every 2 weeks maintains improvements in eczema symptoms over 36 weeks. About 72% of patients maintained their improvement when taking dupilumab every 2 weeks, compared to only 30% of patients who stopped treatment. The study found that taking dupilumab less frequently (every 4 or 8 weeks) was not as effective as taking it every 2 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 422Dupilumab significantly improves signs and symptoms of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, including skin lesions, itching, and quality of life compared to placebo. In clinical trials, 60-70% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Dupilumab significantly improved quality of life in adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The improvements were meaningful in daily life, particularly reducing pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression, and helping with usual activities.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 1,379Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Both weekly and every 2 weeks dupilumab treatment led to significantly greater improvements in quality of life compared to placebo
Summary:Dupilumab combined with topical steroids was significantly more effective than steroids alone in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. After 16 weeks, about 39% of patients on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 12% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for the full year of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 740Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Dupilumab is an effective treatment for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children as young as 6 months. Clinical trials show that 60-70% of patients achieve significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, including reduction in itch and skin clearance.Study Type:CommentStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months and olderResults:Dupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo
The medication has an acceptable safety profile, with the most common side effects being injection site reactions and conjunctivitis (eye inflammation). Serious side effects are rare. Dupilumab actually reduces skin infections compared to placebo.
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 673Results:
Summary:This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
Dupilumab works by blocking two key inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) that drive atopic dermatitis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, with a higher initial loading dose.
Summary:Dupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms and skin healing over 16 weeks of treatment. The medication worked by reducing inflammation in the skin and helping restore normal skin barrier function.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 54Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableResults:Dupilumab improved skin healing at both molecular and cellular levels
Summary:Dupilumab is the first approved targeted biological therapy for atopic dermatitis in adults and children over 6 years with moderate-to-severe disease. It works by blocking specific inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) and helps improve skin barrier function.Study Type:Studied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 years and olderResults:
The medication is approved for patients 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis that is not well controlled with topical prescription treatments. Continuous treatment is needed to maintain response.
Summary:In children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe eczema, dupilumab with low-strength steroid cream worked significantly better than placebo. After 16 weeks, 28% of children on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to only 4% on placebo, and 53% had major improvement in their eczema compared to 11% on placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 162Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months to <6 yearsResults:
Summary:This study showed that taking dupilumab every 2 weeks maintains improvements in eczema symptoms over 36 weeks. About 72% of patients maintained their improvement when taking dupilumab every 2 weeks, compared to only 30% of patients who stopped treatment. The study found that taking dupilumab less frequently (every 4 or 8 weeks) was not as effective as taking it every 2 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 422Results:
-
 Anzupgo(Delgocitinib)If your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youIf your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youTopical dailyMedium
Anzupgo(Delgocitinib)If your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youIf your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Nasopharyngitis Contact dermatitis KEY TAKEAWAYSDelgocitinib ointment is effective at reducing eczema symptoms in both adults and children. In clinical trials, it significantly improved skin condition and reduced disease severity scores compared to placebo within 4 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment, a new topical treatment for eczema, reduced disease severity by 44.3% after 4 weeks of treatment, while the placebo group showed almost no improvement (1.7%). The medication remained effective for up to 28 weeks and was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema severity compared to vehicle 📄Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsDelgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse 📄Delgocitinib ointment (0.25% and 0.5%) significantly improved eczema symptoms in children aged 2-15 years compared to vehicle (placebo) ointment after 4 weeks of treatment. Both concentrations were safe to use and well-tolerated.Clinical Trial Both concentrations of delgocitinib significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle The medication is generally safe and well-tolerated for long-term use (up to 52 weeks in adults and 56 weeks in children). Most side effects were mild and not related to the medication. Common side effects included common cold symptoms and mild skin reactions.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsDelgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse 📄Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment was found to be safe and effective for treating atopic dermatitis in Japanese adults when used for up to one year. The improvement in eczema symptoms was maintained throughout the treatment period, and most side effects were mild.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 506Severity: not availableAge: 16+Delgocitinib starts working quickly to reduce itching, with improvements noticed as early as the first day of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A new ointment called JTE-052 was tested in Japanese adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The ointment significantly improved skin symptoms and reduced itching as early as the first night of treatment. All tested strengths (0.25%, 0.5%, 1%, and 3%) worked better than the vehicle (placebo) ointment, with the 3% strength showing the best results.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 327Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+All strengths of JTE-052 significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle, with 3% being most effective The medication comes in two strengths (0.25% and 0.5%). For children with mild eczema, the 0.5% strength may work better than the 0.25% strength, while both strengths work similarly for moderate to severe cases.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Delgocitinib ointment at 0.5% concentration worked better than 0.25% concentration for children with mild eczema, with 71.4% of patients seeing clear or almost clear skin compared to 46.2%. The medication was safe to use for up to 56 weeks, even when combined with other eczema treatments.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to severeAge: pediatric (specific range not provided)0.5% concentration was more effective for mild cases, while both concentrations showed similar efficacy in moderate-severe cases Delgocitinib ointment is effective at reducing eczema symptoms in both adults and children. In clinical trials, it significantly improved skin condition and reduced disease severity scores compared to placebo within 4 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment, a new topical treatment for eczema, reduced disease severity by 44.3% after 4 weeks of treatment, while the placebo group showed almost no improvement (1.7%). The medication remained effective for up to 28 weeks and was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Results:Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema severity compared to vehicle
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsResults:Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment (0.25% and 0.5%) significantly improved eczema symptoms in children aged 2-15 years compared to vehicle (placebo) ointment after 4 weeks of treatment. Both concentrations were safe to use and well-tolerated.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Results:Both concentrations of delgocitinib significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle
The medication is generally safe and well-tolerated for long-term use (up to 52 weeks in adults and 56 weeks in children). Most side effects were mild and not related to the medication. Common side effects included common cold symptoms and mild skin reactions.
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsResults:Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse
Summary:Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment was found to be safe and effective for treating atopic dermatitis in Japanese adults when used for up to one year. The improvement in eczema symptoms was maintained throughout the treatment period, and most side effects were mild.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 506Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:
Delgocitinib starts working quickly to reduce itching, with improvements noticed as early as the first day of treatment.
Summary:A new ointment called JTE-052 was tested in Japanese adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The ointment significantly improved skin symptoms and reduced itching as early as the first night of treatment. All tested strengths (0.25%, 0.5%, 1%, and 3%) worked better than the vehicle (placebo) ointment, with the 3% strength showing the best results.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 327Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:All strengths of JTE-052 significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle, with 3% being most effective
The medication comes in two strengths (0.25% and 0.5%). For children with mild eczema, the 0.5% strength may work better than the 0.25% strength, while both strengths work similarly for moderate to severe cases.
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment at 0.5% concentration worked better than 0.25% concentration for children with mild eczema, with 71.4% of patients seeing clear or almost clear skin compared to 46.2%. The medication was safe to use for up to 56 weeks, even when combined with other eczema treatments.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to severeAge: pediatric (specific range not provided)Results:0.5% concentration was more effective for mild cases, while both concentrations showed similar efficacy in moderate-severe cases
-
 Protopic(Tacrolimus)If your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasTopical twice weekly to twice dailyMedium
Protopic(Tacrolimus)If your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasTopical twice weekly to twice dailyMedium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Burning sensation at application site 38% Skin infections 26% conjunctivitis 16% paradoxical head and neck erythema 8%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$45/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSTacrolimus is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, showing significant improvement in symptoms and disease severity compared to standard treatments like hydrocortisone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children with eczema, both tacrolimus ointment and hydrocortisone cream improved quality of life. Tacrolimus was better at reducing certain inflammatory markers in the blood compared to hydrocortisone, though both treatments were effective.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Tacrolimus was more effective at reducing inflammatory markers compared to hydrocortisone 📄Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 years📄Tacrolimus 0.03% ointment was more effective than Hydrocortisone 1% in treating children with atopic dermatitis. After 3 weeks of treatment, Tacrolimus reduced disease severity by 56% compared to 27% with Hydrocortisone.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 60Severity: not availableAge: 2-10 yearsLong-term safety studies show no increased risk of cancer in children using topical tacrolimus for atopic dermatitis over a 10-year period.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This 10-year study found that children using tacrolimus cream (Protopic) for eczema did not have an increased risk of developing cancer compared to the general population. No cases of lymphoma were reported.Observational Study Total Patients: 7,954Severity: not availableAge: pediatricIn adults, there is no evidence of increased skin cancer risk (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with tacrolimus use compared to other treatments.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Observational Study Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Tacrolimus appears to be particularly beneficial for patients who show signs of early allergic sensitization, and it can improve quality of life measures for both patients and caregivers.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 years📄This study compared two eczema treatments (tacrolimus 0.03% and crisaborole) in children with mild to moderate eczema. While both medications improved eczema symptoms, tacrolimus showed better results in improving quality of life for both children and their caregivers.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 47Severity: mildAge: children (mean age 8.0 ± 3.9 years)Both treatments improved eczema severity, with slightly better improvement in the crisaborole group Tacrolimus is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, showing significant improvement in symptoms and disease severity compared to standard treatments like hydrocortisone.
Summary:In children with eczema, both tacrolimus ointment and hydrocortisone cream improved quality of life. Tacrolimus was better at reducing certain inflammatory markers in the blood compared to hydrocortisone, though both treatments were effective.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Tacrolimus was more effective at reducing inflammatory markers compared to hydrocortisone
Summary:Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 yearsResults:
Summary:Tacrolimus 0.03% ointment was more effective than Hydrocortisone 1% in treating children with atopic dermatitis. After 3 weeks of treatment, Tacrolimus reduced disease severity by 56% compared to 27% with Hydrocortisone.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 60Severity: not availableAge: 2-10 yearsResults:
Long-term safety studies show no increased risk of cancer in children using topical tacrolimus for atopic dermatitis over a 10-year period.
Summary:This 10-year study found that children using tacrolimus cream (Protopic) for eczema did not have an increased risk of developing cancer compared to the general population. No cases of lymphoma were reported.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 7,954Severity: not availableAge: pediatricResults:
In adults, there is no evidence of increased skin cancer risk (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with tacrolimus use compared to other treatments.
Summary:This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Results:
Tacrolimus appears to be particularly beneficial for patients who show signs of early allergic sensitization, and it can improve quality of life measures for both patients and caregivers.
Summary:Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 yearsResults:
Summary:This study compared two eczema treatments (tacrolimus 0.03% and crisaborole) in children with mild to moderate eczema. While both medications improved eczema symptoms, tacrolimus showed better results in improving quality of life for both children and their caregivers.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 47Severity: mildAge: children (mean age 8.0 ± 3.9 years)Results:Both treatments improved eczema severity, with slightly better improvement in the crisaborole group
-
 Elidel(Pimecrolimus)If your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasTopical twice dailyMedium
Elidel(Pimecrolimus)If your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasTopical twice dailyMedium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Application site burning 15% Headache 14% Nasopharyngitis 16% Cough 10%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$80/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSPimecrolimus appears to be similarly effective to topical corticosteroids for treating atopic dermatitis, with about 85-90% of patients achieving treatment success after long-term use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 months📄Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsBoth treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin Long-term safety studies show Pimecrolimus is generally safe, with no significant effects on the immune system. However, it may have slightly higher rates of minor infections like bronchitis and infected eczema compared to topical steroids.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 months📄Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsBoth treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin Pimecrolimus can help reduce the need for topical steroids (steroid-sparing effect), which may be beneficial for areas sensitive to steroid side effects like the face and eyelids.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis in Chinese infants. After 26 weeks, about 83% of infants treated with Pimecrolimus showed improvement, which was similar to the 89% improvement seen with corticosteroids.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 120Severity: not availableAge: 3 months-12 monthsTreatment success rates were similar between Pimecrolimus and topical corticosteroids 📄This is a commentary on a 5-year safety study of pimecrolimus in treating atopic dermatitis. The article discusses how despite pimecrolimus being available for over a decade, there's still uncertainty about when to use it versus topical steroids, particularly for sensitive areas like the face and eyelids.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: infants and childrenThere is no increased risk of skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with using Pimecrolimus, based on long-term safety studies.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Observational Study Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Pimecrolimus appears to be similarly effective to topical corticosteroids for treating atopic dermatitis, with about 85-90% of patients achieving treatment success after long-term use.
Summary:This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 monthsResults:
Summary:Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsResults:Both treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Long-term safety studies show Pimecrolimus is generally safe, with no significant effects on the immune system. However, it may have slightly higher rates of minor infections like bronchitis and infected eczema compared to topical steroids.
Summary:This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 monthsResults:
Summary:Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsResults:Both treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Pimecrolimus can help reduce the need for topical steroids (steroid-sparing effect), which may be beneficial for areas sensitive to steroid side effects like the face and eyelids.
Summary:Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis in Chinese infants. After 26 weeks, about 83% of infants treated with Pimecrolimus showed improvement, which was similar to the 89% improvement seen with corticosteroids.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Severity: not availableAge: 3 months-12 monthsResults:Treatment success rates were similar between Pimecrolimus and topical corticosteroids
Summary:This is a commentary on a 5-year safety study of pimecrolimus in treating atopic dermatitis. The article discusses how despite pimecrolimus being available for over a decade, there's still uncertainty about when to use it versus topical steroids, particularly for sensitive areas like the face and eyelids.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: infants and childrenResults:
There is no increased risk of skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with using Pimecrolimus, based on long-term safety studies.
Summary:This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Results:
-
 Ebglyss(Lebrikizumab)If you are 12+, need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youIf you need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youInjection every 2-4 weeksMedium
Ebglyss(Lebrikizumab)If you are 12+, need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youIf you need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youInjection every 2-4 weeksMediumSide Effect Affected Conjunctivitis 8% Injection Site Reactions 3% Herpes Zoster 1% Keratitis 1% $45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSLebrikizumab significantly improves moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms compared to placebo. In phase 3 trials, 58-72% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in two large clinical trials. After 16 weeks, about 33-43% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 11-13% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch, and while it caused some eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), most side effects were mild.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 851Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+ years (adolescents and adults)About 3 times more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with lebrikizumab compared to placebo 📄Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultThe medication helps reduce itching quickly, with some patients experiencing improvement as early as 2 days after starting treatment. It also helps improve sleep disruption caused by itch.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Lebrikizumab helped improve itching and sleep quality in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients who experienced less itching and better sleep also reported better quality of life after 16 weeks of treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Patients who responded to treatment with improved itch and sleep showed significant improvements in quality of life measures 📄Lebrikizumab, a medication that targets IL-13, significantly improved moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults. After 16 weeks, about 60% of patients taking lebrikizumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 16% taking placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 751Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Significantly more patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema symptoms with lebrikizumab Lebrikizumab has a favorable safety profile with most side effects being mild to moderate. The most common side effects include conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), injection site reactions, and upper respiratory infections. Serious side effects are rare.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This analysis looked at the safety of lebrikizumab across eight clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The medication was generally safe, with most side effects being mild or moderate. The most common side effect specific to lebrikizumab was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in about 8.5% of patients.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adults📄Lebrikizumab was found to be generally safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and adolescents. The most common side effect was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in 8.5% of treated patients compared to 2.5% in placebo. Most side effects were mild or moderate.JournalArticle Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adults and adolescentsThe medication can be given either every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks after initial loading doses, with both dosing schedules showing effectiveness. This flexibility in dosing may be beneficial for patients.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Lebrikizumab helped maintain clear or almost clear skin in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 2 years. About half of the patients achieved completely clear skin, and more than 55% reported having no or minimal itching after 2 years of treatment.JournalArticle Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableAbout half of patients maintained completely clear skin 📄Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultLebrikizumab significantly improves moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms compared to placebo. In phase 3 trials, 58-72% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in two large clinical trials. After 16 weeks, about 33-43% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 11-13% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch, and while it caused some eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), most side effects were mild.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 851Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+ years (adolescents and adults)Results:About 3 times more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with lebrikizumab compared to placebo
Summary:Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultResults:
The medication helps reduce itching quickly, with some patients experiencing improvement as early as 2 days after starting treatment. It also helps improve sleep disruption caused by itch.
Summary:Lebrikizumab helped improve itching and sleep quality in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients who experienced less itching and better sleep also reported better quality of life after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Results:Patients who responded to treatment with improved itch and sleep showed significant improvements in quality of life measures
Summary:Lebrikizumab, a medication that targets IL-13, significantly improved moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults. After 16 weeks, about 60% of patients taking lebrikizumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 16% taking placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 751Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Significantly more patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema symptoms with lebrikizumab
Lebrikizumab has a favorable safety profile with most side effects being mild to moderate. The most common side effects include conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), injection site reactions, and upper respiratory infections. Serious side effects are rare.
Summary:This analysis looked at the safety of lebrikizumab across eight clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The medication was generally safe, with most side effects being mild or moderate. The most common side effect specific to lebrikizumab was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in about 8.5% of patients.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adultsResults:
Summary:Lebrikizumab was found to be generally safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and adolescents. The most common side effect was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in 8.5% of treated patients compared to 2.5% in placebo. Most side effects were mild or moderate.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adults and adolescentsResults:
The medication can be given either every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks after initial loading doses, with both dosing schedules showing effectiveness. This flexibility in dosing may be beneficial for patients.
Summary:Lebrikizumab helped maintain clear or almost clear skin in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 2 years. About half of the patients achieved completely clear skin, and more than 55% reported having no or minimal itching after 2 years of treatment.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableResults:About half of patients maintained completely clear skin
Summary:Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultResults:
-
 Cibinqo(Abrocitinib)If your child is 12+ years and needs rapid relief of itch and other symptomsIf you need rapid relief of itch and other symptomsOral once dailyHigh
Cibinqo(Abrocitinib)If your child is 12+ years and needs rapid relief of itch and other symptomsIf you need rapid relief of itch and other symptomsOral once dailyHigh⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Nasopharyngitis 11% Nausea 10% Headache 7% Herpes simplex 4%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$362 per month($233 - $1,359)$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSAbrocitinib is effective at treating moderate-to-severe eczema, with higher doses (200mg) showing better results than lower doses (100mg). After 12 weeks of treatment, 61% of patients on 200mg and 45% on 100mg saw at least 75% improvement in their eczema symptoms, compared to only 10% on placebo.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results The medication can provide rapid relief from itch - patients noticed improvement within 24 hours of starting treatment. This quick relief from itching led to significant improvements in quality of life for patients.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results The medication is generally well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild. The most common side effects include nausea (14% with 200mg dose), headache (8%), and upper respiratory infections. Some patients experienced temporary decreases in blood platelet counts, which typically stabilized with continued treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results For patients who respond well to initial treatment, continuing the medication helps prevent flare-ups. In a long-term study, only 19% of patients on 200mg experienced a flare-up compared to 81% of those who stopped treatment. If flares occur, restarting treatment is effective at regaining control of symptoms.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Abrocitinib is effective at treating moderate-to-severe eczema, with higher doses (200mg) showing better results than lower doses (100mg). After 12 weeks of treatment, 61% of patients on 200mg and 45% on 100mg saw at least 75% improvement in their eczema symptoms, compared to only 10% on placebo.
The medication can provide rapid relief from itch - patients noticed improvement within 24 hours of starting treatment. This quick relief from itching led to significant improvements in quality of life for patients.
The medication is generally well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild. The most common side effects include nausea (14% with 200mg dose), headache (8%), and upper respiratory infections. Some patients experienced temporary decreases in blood platelet counts, which typically stabilized with continued treatment.
For patients who respond well to initial treatment, continuing the medication helps prevent flare-ups. In a long-term study, only 19% of patients on 200mg experienced a flare-up compared to 81% of those who stopped treatment. If flares occur, restarting treatment is effective at regaining control of symptoms.
-
 Opzelura(Ruxolitinib)If your child is 12+ years and looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedIf you are looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedTopical twice dailyMedium
Opzelura(Ruxolitinib)If your child is 12+ years and looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedIf you are looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedTopical twice dailyMedium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Nasopharyngitis 3% Bronchitis 1% Ear infection 1% Eosinophil count increased 1%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$212 per month($85 - $743)$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSRuxolitinib cream provides rapid and significant itch relief, with improvements seen within 12-36 hours of first application and sustained through 8 weeks of treatment. Over 50% of patients achieved significant itch reduction by week 8.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream showed significant improvement in eczema symptoms compared to vehicle (placebo cream). The highest dose (1.5% twice daily) reduced eczema severity by 71.6% after 4 weeks, and patients experienced itch relief within 36 hours of starting treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 307Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Ruxolitinib 1.5% BID reduced eczema severity by 71.6% compared to 15.5% with vehicle The cream is generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. Application site reactions are infrequent (2-6% of patients) and most side effects are mild to moderate. There were no serious safety concerns even with long-term use up to 52 weeks.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableOnly a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream 📄Ruxolitinib cream was effective in treating eczema in teenagers, with about 51% achieving clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks compared to 14% using a placebo cream. The medication started working quickly, reducing itch from day 2, and continued to work well for up to 52 weeks with few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 245Severity: mild to moderateAge: 12-17 yearsSignificantly more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with ruxolitinib 📄Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsAlmost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment The medication has very low systemic absorption when applied to the skin, meaning it mainly works locally where applied and is unlikely to cause whole-body side effects that can occur with oral JAK inhibitors.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableOnly a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream 📄Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsAlmost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment Ruxolitinib cream improves quality of life and ability to work/perform daily activities. Patients using the cream showed significant improvements in work productivity and daily activity compared to vehicle (placebo) cream.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream improved itch and skin pain within 12 hours of application in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also improved sleep and quality of life within 2 weeks, and these benefits lasted for up to 52 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,208Ruxolitinib cream improved skin pain within 12 hours of application 📄Ruxolitinib cream, applied twice daily, quickly reduced itch in people with mild to moderate eczema. The cream started working within 12 hours and continued to improve itch symptoms over 8 weeks. The stronger version (1.5%) worked better than the weaker version (0.75%) and both worked better than the placebo cream.Editor's Picks January 2023 (2022)Total Patients: 1,200Severity: mild to moderateAge: adolescents and adultsRuxolitinib cream provided rapid itch relief within 12 hours and continued improvement through 8 weeks Ruxolitinib cream provides rapid and significant itch relief, with improvements seen within 12-36 hours of first application and sustained through 8 weeks of treatment. Over 50% of patients achieved significant itch reduction by week 8.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream showed significant improvement in eczema symptoms compared to vehicle (placebo cream). The highest dose (1.5% twice daily) reduced eczema severity by 71.6% after 4 weeks, and patients experienced itch relief within 36 hours of starting treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 307Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Ruxolitinib 1.5% BID reduced eczema severity by 71.6% compared to 15.5% with vehicle
The cream is generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. Application site reactions are infrequent (2-6% of patients) and most side effects are mild to moderate. There were no serious safety concerns even with long-term use up to 52 weeks.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Only a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream was effective in treating eczema in teenagers, with about 51% achieving clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks compared to 14% using a placebo cream. The medication started working quickly, reducing itch from day 2, and continued to work well for up to 52 weeks with few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 245Severity: mild to moderateAge: 12-17 yearsResults:Significantly more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with ruxolitinib
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsResults:Almost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment
The medication has very low systemic absorption when applied to the skin, meaning it mainly works locally where applied and is unlikely to cause whole-body side effects that can occur with oral JAK inhibitors.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Only a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsResults:Almost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment
Ruxolitinib cream improves quality of life and ability to work/perform daily activities. Patients using the cream showed significant improvements in work productivity and daily activity compared to vehicle (placebo) cream.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream improved itch and skin pain within 12 hours of application in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also improved sleep and quality of life within 2 weeks, and these benefits lasted for up to 52 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,208Results:Ruxolitinib cream improved skin pain within 12 hours of application
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream, applied twice daily, quickly reduced itch in people with mild to moderate eczema. The cream started working within 12 hours and continued to improve itch symptoms over 8 weeks. The stronger version (1.5%) worked better than the weaker version (0.75%) and both worked better than the placebo cream.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 1,200Severity: mild to moderateAge: adolescents and adultsResults:Ruxolitinib cream provided rapid itch relief within 12 hours and continued improvement through 8 weeks
-
 Nemluvio(Nemolizumab)If you are 12 years or older with moderate-to-severe AD and intense itchingIf you have moderate-to-severe AD with intense itchingInjection Every 4-8 weeksMedium
Nemluvio(Nemolizumab)If you are 12 years or older with moderate-to-severe AD and intense itchingIf you have moderate-to-severe AD with intense itchingInjection Every 4-8 weeksMediumSide Effect Affected Headache 6% Dermatitis atopic 4% Eczema 4% Eczema nummular 3% $45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSNemolizumab significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. In clinical trials, patients saw 40-70% reduction in itch scores after 16 weeks of treatment, with improvements noticeable within the first few days.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,728📄Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, reduced itching by 43% compared to 21% with placebo after 16 weeks. The medication also improved eczema severity and sleep quality in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 215Nemolizumab reduced itching twice as much as placebo 📄Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication improves skin symptoms and quality of life, including better sleep. Studies showed 45-78% improvement in eczema severity scores over 16-68 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,728📄Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks along with topical treatments, helped reduce itching by 66% and eczema severity by 78% over 68 weeks in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The improvements lasted even after treatment ended, and the medication was generally safe to use.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 303Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥13 yearsSignificant reduction in itching maintained over more than a year The most common side effects are mild and include nasopharyngitis (common cold), upper respiratory tract infections, and worsening of atopic dermatitis. Serious side effects are rare but can include severe allergic reactions.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks 📄Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication is given as a subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. It works by blocking interleukin-31, a protein that triggers itching in atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab is a new drug that targets IL-31, which is involved in causing eczema symptoms. The drug shows good results in reducing itch quickly and improving skin condition, with mostly mild side effects.Review Severity: not availableAge: not availablenot available 📄Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks Taken every 4 weeksStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Itch relief in as soon as 48 hoursStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Unique mechanism of actionStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Nemolizumab significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. In clinical trials, patients saw 40-70% reduction in itch scores after 16 weeks of treatment, with improvements noticeable within the first few days.
Summary:Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,728Results:
Summary:Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, reduced itching by 43% compared to 21% with placebo after 16 weeks. The medication also improved eczema severity and sleep quality in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 215Results:Nemolizumab reduced itching twice as much as placebo
Summary:Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication improves skin symptoms and quality of life, including better sleep. Studies showed 45-78% improvement in eczema severity scores over 16-68 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,728Results:
Summary:Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks along with topical treatments, helped reduce itching by 66% and eczema severity by 78% over 68 weeks in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The improvements lasted even after treatment ended, and the medication was generally safe to use.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 303Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥13 yearsResults:Significant reduction in itching maintained over more than a year
The most common side effects are mild and include nasopharyngitis (common cold), upper respiratory tract infections, and worsening of atopic dermatitis. Serious side effects are rare but can include severe allergic reactions.
Summary:Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Results:Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks
Summary:Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication is given as a subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. It works by blocking interleukin-31, a protein that triggers itching in atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Nemolizumab is a new drug that targets IL-31, which is involved in causing eczema symptoms. The drug shows good results in reducing itch quickly and improving skin condition, with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:not available
Summary:Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Results:Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks
Taken every 4 weeks
Itch relief in as soon as 48 hours
Unique mechanism of action
-
 Adbry(Tralokinumab)If you are 12+ years and topical prescription therapies don't work for youIf topical prescription therapies don't work for youInjection every 2 weeksMedium
Adbry(Tralokinumab)If you are 12+ years and topical prescription therapies don't work for youIf topical prescription therapies don't work for youInjection every 2 weeksMediumSide Effect Affected Upper respiratory tract infections 25% Conjunctivitis 11% Injection site reactions 9% Eosinophilia 1% $281 per month($154 - $1,020)$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSTralokinumab is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with 39% of patients achieving clear/almost clear skin at 16 weeks when combined with topical corticosteroids. The treatment continues to show progressive improvement beyond 16 weeks, with 70% of patients achieving a 75% improvement in symptoms by week 32.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab, a medication given every 2 weeks, helped improve severe eczema in adults who didn't respond well to topical treatments. After 16 weeks, about 25-33% of patients saw a significant improvement in their eczema symptoms compared to 11-13% who received placebo. Most patients who responded well at 16 weeks maintained their improvement through 52 weeks of treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication is generally well-tolerated with a favorable safety profile. The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections (16%), conjunctivitis (5%), and injection site reactions (4%). Most side effects are mild to moderate and do not lead to treatment discontinuation.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab was found to be safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis based on data from five clinical trials. The most common side effects were upper respiratory infections and eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), but serious side effects were rare and similar to placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 2,285Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Tralokinumab can help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids - patients using tralokinumab used approximately 50% less topical corticosteroids compared to those on placebo by week 16.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity 📄Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication improves quality of life measures including itch severity, sleep quality, and overall disease burden. These improvements are seen within the first few weeks of treatment and are sustained over time.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity 📄Tralokinumab, either alone or with topical steroids, showed rapid improvement in itch and sleep quality for patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients started experiencing relief from itch as early as 1-2 weeks into treatment, and improvements in sleep were seen within 2 weeks.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 1,976Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Meaningful improvements in quality of life were observed from week 2 Tralokinumab is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with 39% of patients achieving clear/almost clear skin at 16 weeks when combined with topical corticosteroids. The treatment continues to show progressive improvement beyond 16 weeks, with 70% of patients achieving a 75% improvement in symptoms by week 32.
Summary:Tralokinumab, a medication given every 2 weeks, helped improve severe eczema in adults who didn't respond well to topical treatments. After 16 weeks, about 25-33% of patients saw a significant improvement in their eczema symptoms compared to 11-13% who received placebo. Most patients who responded well at 16 weeks maintained their improvement through 52 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication is generally well-tolerated with a favorable safety profile. The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections (16%), conjunctivitis (5%), and injection site reactions (4%). Most side effects are mild to moderate and do not lead to treatment discontinuation.
Summary:Tralokinumab was found to be safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis based on data from five clinical trials. The most common side effects were upper respiratory infections and eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), but serious side effects were rare and similar to placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,285Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Tralokinumab can help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids - patients using tralokinumab used approximately 50% less topical corticosteroids compared to those on placebo by week 16.
Summary:Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication improves quality of life measures including itch severity, sleep quality, and overall disease burden. These improvements are seen within the first few weeks of treatment and are sustained over time.
Summary:Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Tralokinumab, either alone or with topical steroids, showed rapid improvement in itch and sleep quality for patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients started experiencing relief from itch as early as 1-2 weeks into treatment, and improvements in sleep were seen within 2 weeks.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,976Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Meaningful improvements in quality of life were observed from week 2
-
 Vtama(Tapinarof)For children 2 years and older who need a non-steroid creamIf you are looking for a non-steroid creamTopical dailyMedium
Vtama(Tapinarof)For children 2 years and older who need a non-steroid creamIf you are looking for a non-steroid creamTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Upper respiratory tract infection 12% Folliculitis 9% Lower respiratory tract infection 5% Headache 4% $45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSTapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. In clinical trials, 45-46% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment compared to 14-18% with vehicle (placebo) cream.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 years📄Tapinarof cream 1%, applied once daily, was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin, compared to only about 16% using the vehicle cream.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin The medication provided rapid itch relief, with improvements seen as early as 24 hours after the first application. By week 8, about 31-33% of patients achieved minimal to no itch compared to 14-17% with vehicle cream.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily helped reduce itching and improve sleep in people with atopic dermatitis. About one-third of patients achieved minimal to no itching after 8 weeks of treatment, compared to only 14-17% of those using a placebo cream.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof significantly improved itch compared to vehicle 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily showed rapid improvement in itch symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with effects seen as early as 24 hours after first use. The improvement in itch continued to increase through 8 weeks of treatment.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof was well-tolerated across all age groups and skin types. The most common side effects were mild to moderate and included folliculitis (hair follicle inflammation), headache, and nasopharyngitis (common cold). Very few patients (less than 2%) had to stop treatment due to side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 years📄Tapinarof cream 1% was tested for skin safety in healthy adults. The cream was found to be safe, causing only very mild skin irritation, and did not cause allergic reactions or increased sensitivity to sunlight.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 376This was a safety study, not an efficacy study The medication worked consistently well across all racial groups and skin types, including patients with darker skin tones who made up about 50% of the study participants.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. The medication worked significantly better than the vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in clearing or almost clearing eczema symptoms.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin across all racial groups 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races, including children as young as 2 years old. About 40-50% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment, which was significantly better than the placebo group.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years+Tapinarof showed significantly higher rates of clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle across all populations Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. In clinical trials, 45-46% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment compared to 14-18% with vehicle (placebo) cream.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 yearsResults:
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1%, applied once daily, was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin, compared to only about 16% using the vehicle cream.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:Tapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
The medication provided rapid itch relief, with improvements seen as early as 24 hours after the first application. By week 8, about 31-33% of patients achieved minimal to no itch compared to 14-17% with vehicle cream.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily helped reduce itching and improve sleep in people with atopic dermatitis. About one-third of patients achieved minimal to no itching after 8 weeks of treatment, compared to only 14-17% of those using a placebo cream.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:Tapinarof significantly improved itch compared to vehicle
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily showed rapid improvement in itch symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with effects seen as early as 24 hours after first use. The improvement in itch continued to increase through 8 weeks of treatment.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:
Tapinarof was well-tolerated across all age groups and skin types. The most common side effects were mild to moderate and included folliculitis (hair follicle inflammation), headache, and nasopharyngitis (common cold). Very few patients (less than 2%) had to stop treatment due to side effects.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 yearsResults:
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% was tested for skin safety in healthy adults. The cream was found to be safe, causing only very mild skin irritation, and did not cause allergic reactions or increased sensitivity to sunlight.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 376Results:This was a safety study, not an efficacy study
The medication worked consistently well across all racial groups and skin types, including patients with darker skin tones who made up about 50% of the study participants.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. The medication worked significantly better than the vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in clearing or almost clearing eczema symptoms.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:Tapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin across all racial groups
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races, including children as young as 2 years old. About 40-50% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment, which was significantly better than the placebo group.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years+Results:Tapinarof showed significantly higher rates of clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle across all populations
-
 Zoryve(Roflumilast)If your child is 6+ years and looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityIf you are looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityTopical once dailyLow
Zoryve(Roflumilast)If your child is 6+ years and looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityIf you are looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityTopical once dailyLowSide Effect Affected rash application site pain $164 per month($37 - $550)$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSRoflumilast cream appears to be effective in treating mild to moderate eczema, with patients showing significant improvements in their eczema severity scores after 4 weeks of once-daily useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 136Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant The medication appears to be very safe, with very few side effects reported. Only 2 out of 91 patients experienced mild treatment-related side effects (a mild rash and moderate application site pain), and only one patient had to stop using the medication due to side effectsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 136Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant Roflumilast cream is a non-steroid treatment option, which may be beneficial for patients who are concerned about using steroid-based treatmentsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 136Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant Roflumilast cream appears to be effective in treating mild to moderate eczema, with patients showing significant improvements in their eczema severity scores after 4 weeks of once-daily use
Summary:Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 136Results:Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant
The medication appears to be very safe, with very few side effects reported. Only 2 out of 91 patients experienced mild treatment-related side effects (a mild rash and moderate application site pain), and only one patient had to stop using the medication due to side effects
Summary:Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 136Results:Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant
Roflumilast cream is a non-steroid treatment option, which may be beneficial for patients who are concerned about using steroid-based treatments
Summary:Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 136Results:Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant
-
 Eucrisa(Crisaborole)If your child needs a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasIf you need a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasTopical twice dailyLow
Eucrisa(Crisaborole)If your child needs a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasIf you need a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasTopical twice dailyLowSide Effect Affected Application site pain 4% Contact urticaria 1% Allergic contact dermatitis $152 per month($29 - $520)$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSCrisaborole is effective for treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in both children and adults, with significantly more patients achieving clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle (placebo) treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderCrisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin 📄Crisaborole ointment was more effective than placebo in treating mild to moderate eczema in patients aged 2 years and older. About 32% of patients using crisaborole achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 18-25% using placebo, and the medication showed a good safety profile.Clinical Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderSignificantly more patients using crisaborole achieved clear/almost clear skin with ≥2-grade improvement compared to vehicle The most common side effect is application site pain/discomfort, occurring in about 4-6% of patients. Most side effects are mild to moderate and treatment-related adverse events are infrequentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderCrisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin 📄Crisaborole ointment was tested in infants aged 3-24 months with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects, and about 30% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 28 days of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 137Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-24 monthsCrisaborole can be used as a long-term maintenance treatment, with studies showing sustained efficacy and safety over 48-52 weeks of useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Once-daily crisaborole ointment helped prevent eczema flares for longer compared to vehicle (placebo), with patients staying flare-free for about 111 days versus 30 days. Patients using crisaborole had fewer flares overall and more flare-free days during the year-long study.Total Patients: 270Crisaborole significantly delayed time to first flare compared to vehicle 📄Once-daily crisaborole ointment was tested as a long-term maintenance treatment for mild-to-moderate eczema. Patients using crisaborole stayed flare-free for longer (111 days vs 30 days) compared to those using a placebo ointment, and had fewer flares over the course of a year.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 497Severity: mild to moderateAge: ≥3 monthsThe medication works quickly, with improvements in itch and skin symptoms seen within the first week of treatment in many patientsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderCrisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin 📄Crisaborole ointment 2% was more effective than placebo in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in children and teenagers. Patients using crisaborole showed faster and greater improvements in both skin appearance and itch compared to those using vehicle (placebo), with benefits seen as early as 8 days after starting treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2-17 yearsSignificantly greater improvement in ISGA scores for crisaborole vs vehicle, particularly in patients with moderate baseline disease Crisaborole is effective for treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in both children and adults, with significantly more patients achieving clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle (placebo) treatment
Summary:Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Studied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Crisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Summary:Crisaborole ointment was more effective than placebo in treating mild to moderate eczema in patients aged 2 years and older. About 32% of patients using crisaborole achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 18-25% using placebo, and the medication showed a good safety profile.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Significantly more patients using crisaborole achieved clear/almost clear skin with ≥2-grade improvement compared to vehicle
The most common side effect is application site pain/discomfort, occurring in about 4-6% of patients. Most side effects are mild to moderate and treatment-related adverse events are infrequent
Summary:Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Studied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Crisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Summary:Crisaborole ointment was tested in infants aged 3-24 months with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects, and about 30% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 28 days of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 137Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-24 monthsResults:
Crisaborole can be used as a long-term maintenance treatment, with studies showing sustained efficacy and safety over 48-52 weeks of use
Summary:Once-daily crisaborole ointment helped prevent eczema flares for longer compared to vehicle (placebo), with patients staying flare-free for about 111 days versus 30 days. Patients using crisaborole had fewer flares overall and more flare-free days during the year-long study.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 270Results:Crisaborole significantly delayed time to first flare compared to vehicle
Summary:Once-daily crisaborole ointment was tested as a long-term maintenance treatment for mild-to-moderate eczema. Patients using crisaborole stayed flare-free for longer (111 days vs 30 days) compared to those using a placebo ointment, and had fewer flares over the course of a year.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 497Severity: mild to moderateAge: ≥3 monthsResults:
The medication works quickly, with improvements in itch and skin symptoms seen within the first week of treatment in many patients
Summary:Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Crisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Summary:Crisaborole ointment 2% was more effective than placebo in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in children and teenagers. Patients using crisaborole showed faster and greater improvements in both skin appearance and itch compared to those using vehicle (placebo), with benefits seen as early as 8 days after starting treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2-17 yearsResults:Significantly greater improvement in ISGA scores for crisaborole vs vehicle, particularly in patients with moderate baseline disease
-
 Rinvoq (Upadacitinib)Who is this for?:If you need rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedIf your child is 12+ years, needs rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedEffectiveness:Side Effects:High
Rinvoq (Upadacitinib)Who is this for?:If you need rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedIf your child is 12+ years, needs rapid and strong relief of itch and other treatments have failedEffectiveness:Side Effects:High⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$396 per monthDelivery:Oral once dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSUpadacitinib is highly effective at reducing itch and improving skin symptoms in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with benefits seen as early as 1-2 weeks of treatment and maintained through 52 weeksStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Upadacitinib, taken as a daily pill, significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo. After 16 weeks, 60-70% of patients taking upadacitinib 15mg and 73-80% of patients taking 30mg had their eczema improve by at least 75%, compared to only 13-16% of patients taking placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,683📄Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes Upadacitinib shows superior efficacy compared to dupilumab (another common treatment) in improving skin clearance and reducing itch, with faster onset of actionStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Upadacitinib was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in adults, including patients who didn't respond well to other treatments like dupilumab or baricitinib. About 73% of patients achieved significant improvement in their eczema, and 69% experienced reduced itching after 16 weeks of treatment.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 47Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 673The most common side effect is acne (occurring in 10-16% of patients), which is usually mild/moderate and manageable. Other potential side effects include increased risk of infections and elevated liver enzymesStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at the safety of upadacitinib across multiple conditions including atopic dermatitis by analyzing data from clinical trials. For atopic dermatitis patients, upadacitinib was generally well-tolerated, with acne being a notable side effect specific to AD patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 2,693Severity: not availableAge: not availableUpadacitinib significantly improves quality of life measures including sleep, daily activities, and emotional wellbeing in patients with atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes 📄Upadacitinib combined with topical steroids significantly improved itch, skin pain, sleep, and quality of life in patients with atopic dermatitis. The improvements were seen within 1-2 weeks and lasted for up to 52 weeks, with 62-84% of patients experiencing meaningful improvements depending on the dose.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 901Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adultsBoth doses showed sustained improvements across all patient-reported outcomes, with higher dose showing better results Upadacitinib is highly effective at reducing itch and improving skin symptoms in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with benefits seen as early as 1-2 weeks of treatment and maintained through 52 weeks
Summary:Upadacitinib, taken as a daily pill, significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo. After 16 weeks, 60-70% of patients taking upadacitinib 15mg and 73-80% of patients taking 30mg had their eczema improve by at least 75%, compared to only 13-16% of patients taking placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,683Results:
Summary:Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Results:Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes
Upadacitinib shows superior efficacy compared to dupilumab (another common treatment) in improving skin clearance and reducing itch, with faster onset of action
Summary:Upadacitinib was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in adults, including patients who didn't respond well to other treatments like dupilumab or baricitinib. About 73% of patients achieved significant improvement in their eczema, and 69% experienced reduced itching after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 47Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 673Results:
The most common side effect is acne (occurring in 10-16% of patients), which is usually mild/moderate and manageable. Other potential side effects include increased risk of infections and elevated liver enzymes
Summary:This study looked at the safety of upadacitinib across multiple conditions including atopic dermatitis by analyzing data from clinical trials. For atopic dermatitis patients, upadacitinib was generally well-tolerated, with acne being a notable side effect specific to AD patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,693Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:
Upadacitinib significantly improves quality of life measures including sleep, daily activities, and emotional wellbeing in patients with atopic dermatitis
Summary:Upadacitinib (15mg or 30mg daily) showed rapid improvements in itch, pain, and other eczema symptoms within the first week of treatment. These improvements were maintained for 52 weeks, with patients also experiencing better sleep, quality of life, and mental health.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,609Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+Results:Upadacitinib showed better results than placebo across all measured outcomes
Summary:Upadacitinib combined with topical steroids significantly improved itch, skin pain, sleep, and quality of life in patients with atopic dermatitis. The improvements were seen within 1-2 weeks and lasted for up to 52 weeks, with 62-84% of patients experiencing meaningful improvements depending on the dose.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 901Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adultsResults:Both doses showed sustained improvements across all patient-reported outcomes, with higher dose showing better results
-
 Dupixent (Dupilumab)Who is this for?:If topical treatments don't work for youIf your child is 6+ months and topical treatments don't work for your childEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$285 per monthDelivery:Injection None every 2 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSDupilumab significantly improves signs and symptoms of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, including skin lesions, itching, and quality of life compared to placebo. In clinical trials, 60-70% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.
Dupixent (Dupilumab)Who is this for?:If topical treatments don't work for youIf your child is 6+ months and topical treatments don't work for your childEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$285 per monthDelivery:Injection None every 2 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSDupilumab significantly improves signs and symptoms of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, including skin lesions, itching, and quality of life compared to placebo. In clinical trials, 60-70% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Dupilumab significantly improved quality of life in adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The improvements were meaningful in daily life, particularly reducing pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression, and helping with usual activities.Total Patients: 1,379Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Both weekly and every 2 weeks dupilumab treatment led to significantly greater improvements in quality of life compared to placebo 📄Dupilumab combined with topical steroids was significantly more effective than steroids alone in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. After 16 weeks, about 39% of patients on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 12% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for the full year of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 740Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Dupilumab is an effective treatment for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children as young as 6 months. Clinical trials show that 60-70% of patients achieve significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, including reduction in itch and skin clearance.Comment Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months and olderDupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo The medication has an acceptable safety profile, with the most common side effects being injection site reactions and conjunctivitis (eye inflammation). Serious side effects are rare. Dupilumab actually reduces skin infections compared to placebo.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 673📄This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Comparative Study Dupilumab works by blocking two key inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) that drive atopic dermatitis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, with a higher initial loading dose.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Dupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms and skin healing over 16 weeks of treatment. The medication worked by reducing inflammation in the skin and helping restore normal skin barrier function.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 54Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableDupilumab improved skin healing at both molecular and cellular levels 📄Dupilumab is the first approved targeted biological therapy for atopic dermatitis in adults and children over 6 years with moderate-to-severe disease. It works by blocking specific inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) and helps improve skin barrier function.Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 years and olderThe medication is approved for patients 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis that is not well controlled with topical prescription treatments. Continuous treatment is needed to maintain response.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe eczema, dupilumab with low-strength steroid cream worked significantly better than placebo. After 16 weeks, 28% of children on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to only 4% on placebo, and 53% had major improvement in their eczema compared to 11% on placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 162Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months to <6 years📄This study showed that taking dupilumab every 2 weeks maintains improvements in eczema symptoms over 36 weeks. About 72% of patients maintained their improvement when taking dupilumab every 2 weeks, compared to only 30% of patients who stopped treatment. The study found that taking dupilumab less frequently (every 4 or 8 weeks) was not as effective as taking it every 2 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 422Dupilumab significantly improves signs and symptoms of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, including skin lesions, itching, and quality of life compared to placebo. In clinical trials, 60-70% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Dupilumab significantly improved quality of life in adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The improvements were meaningful in daily life, particularly reducing pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression, and helping with usual activities.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 1,379Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Both weekly and every 2 weeks dupilumab treatment led to significantly greater improvements in quality of life compared to placebo
Summary:Dupilumab combined with topical steroids was significantly more effective than steroids alone in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. After 16 weeks, about 39% of patients on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 12% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for the full year of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 740Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Dupilumab is an effective treatment for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children as young as 6 months. Clinical trials show that 60-70% of patients achieve significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, including reduction in itch and skin clearance.Study Type:CommentStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months and olderResults:Dupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms compared to placebo
The medication has an acceptable safety profile, with the most common side effects being injection site reactions and conjunctivitis (eye inflammation). Serious side effects are rare. Dupilumab actually reduces skin infections compared to placebo.
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: oral upadacitinib and injectable dupilumab. Upadacitinib worked better and faster than dupilumab, with 72.4% of patients seeing major skin improvement after 16 weeks compared to 62.6% with dupilumab. However, upadacitinib had more side effects including acne and infections.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 673Results:
Summary:This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
Dupilumab works by blocking two key inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) that drive atopic dermatitis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, with a higher initial loading dose.
Summary:Dupilumab significantly improved eczema symptoms and skin healing over 16 weeks of treatment. The medication worked by reducing inflammation in the skin and helping restore normal skin barrier function.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 54Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableResults:Dupilumab improved skin healing at both molecular and cellular levels
Summary:Dupilumab is the first approved targeted biological therapy for atopic dermatitis in adults and children over 6 years with moderate-to-severe disease. It works by blocking specific inflammatory proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) and helps improve skin barrier function.Study Type:Studied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 years and olderResults:
The medication is approved for patients 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis that is not well controlled with topical prescription treatments. Continuous treatment is needed to maintain response.
Summary:In children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe eczema, dupilumab with low-strength steroid cream worked significantly better than placebo. After 16 weeks, 28% of children on dupilumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to only 4% on placebo, and 53% had major improvement in their eczema compared to 11% on placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 162Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months to <6 yearsResults:
Summary:This study showed that taking dupilumab every 2 weeks maintains improvements in eczema symptoms over 36 weeks. About 72% of patients maintained their improvement when taking dupilumab every 2 weeks, compared to only 30% of patients who stopped treatment. The study found that taking dupilumab less frequently (every 4 or 8 weeks) was not as effective as taking it every 2 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 422Results:
-
 Anzupgo (Delgocitinib)Who is this for?:If your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youIf your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSDelgocitinib ointment is effective at reducing eczema symptoms in both adults and children. In clinical trials, it significantly improved skin condition and reduced disease severity scores compared to placebo within 4 weeks of treatment.
Anzupgo (Delgocitinib)Who is this for?:If your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youIf your eczema is on your hands and topical steroids don't work for youEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSDelgocitinib ointment is effective at reducing eczema symptoms in both adults and children. In clinical trials, it significantly improved skin condition and reduced disease severity scores compared to placebo within 4 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment, a new topical treatment for eczema, reduced disease severity by 44.3% after 4 weeks of treatment, while the placebo group showed almost no improvement (1.7%). The medication remained effective for up to 28 weeks and was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema severity compared to vehicle 📄Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsDelgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse 📄Delgocitinib ointment (0.25% and 0.5%) significantly improved eczema symptoms in children aged 2-15 years compared to vehicle (placebo) ointment after 4 weeks of treatment. Both concentrations were safe to use and well-tolerated.Clinical Trial Both concentrations of delgocitinib significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle The medication is generally safe and well-tolerated for long-term use (up to 52 weeks in adults and 56 weeks in children). Most side effects were mild and not related to the medication. Common side effects included common cold symptoms and mild skin reactions.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsDelgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse 📄Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment was found to be safe and effective for treating atopic dermatitis in Japanese adults when used for up to one year. The improvement in eczema symptoms was maintained throughout the treatment period, and most side effects were mild.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 506Severity: not availableAge: 16+Delgocitinib starts working quickly to reduce itching, with improvements noticed as early as the first day of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A new ointment called JTE-052 was tested in Japanese adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The ointment significantly improved skin symptoms and reduced itching as early as the first night of treatment. All tested strengths (0.25%, 0.5%, 1%, and 3%) worked better than the vehicle (placebo) ointment, with the 3% strength showing the best results.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 327Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+All strengths of JTE-052 significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle, with 3% being most effective The medication comes in two strengths (0.25% and 0.5%). For children with mild eczema, the 0.5% strength may work better than the 0.25% strength, while both strengths work similarly for moderate to severe cases.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Delgocitinib ointment at 0.5% concentration worked better than 0.25% concentration for children with mild eczema, with 71.4% of patients seeing clear or almost clear skin compared to 46.2%. The medication was safe to use for up to 56 weeks, even when combined with other eczema treatments.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to severeAge: pediatric (specific range not provided)0.5% concentration was more effective for mild cases, while both concentrations showed similar efficacy in moderate-severe cases Delgocitinib ointment is effective at reducing eczema symptoms in both adults and children. In clinical trials, it significantly improved skin condition and reduced disease severity scores compared to placebo within 4 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment, a new topical treatment for eczema, reduced disease severity by 44.3% after 4 weeks of treatment, while the placebo group showed almost no improvement (1.7%). The medication remained effective for up to 28 weeks and was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Results:Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema severity compared to vehicle
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsResults:Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment (0.25% and 0.5%) significantly improved eczema symptoms in children aged 2-15 years compared to vehicle (placebo) ointment after 4 weeks of treatment. Both concentrations were safe to use and well-tolerated.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Results:Both concentrations of delgocitinib significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle
The medication is generally safe and well-tolerated for long-term use (up to 52 weeks in adults and 56 weeks in children). Most side effects were mild and not related to the medication. Common side effects included common cold symptoms and mild skin reactions.
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment was tested in Japanese children with eczema and found to reduce disease severity by about 39% after 4 weeks of treatment, while those using a placebo ointment got worse. The medication remained effective for up to 56 weeks and was generally safe to use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderateAge: 2-15 yearsResults:Delgocitinib significantly improved eczema symptoms while patients on vehicle got worse
Summary:Delgocitinib 0.5% ointment was found to be safe and effective for treating atopic dermatitis in Japanese adults when used for up to one year. The improvement in eczema symptoms was maintained throughout the treatment period, and most side effects were mild.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 506Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:
Delgocitinib starts working quickly to reduce itching, with improvements noticed as early as the first day of treatment.
Summary:A new ointment called JTE-052 was tested in Japanese adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. The ointment significantly improved skin symptoms and reduced itching as early as the first night of treatment. All tested strengths (0.25%, 0.5%, 1%, and 3%) worked better than the vehicle (placebo) ointment, with the 3% strength showing the best results.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 327Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:All strengths of JTE-052 significantly reduced eczema severity compared to vehicle, with 3% being most effective
The medication comes in two strengths (0.25% and 0.5%). For children with mild eczema, the 0.5% strength may work better than the 0.25% strength, while both strengths work similarly for moderate to severe cases.
Summary:Delgocitinib ointment at 0.5% concentration worked better than 0.25% concentration for children with mild eczema, with 71.4% of patients seeing clear or almost clear skin compared to 46.2%. The medication was safe to use for up to 56 weeks, even when combined with other eczema treatments.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to severeAge: pediatric (specific range not provided)Results:0.5% concentration was more effective for mild cases, while both concentrations showed similar efficacy in moderate-severe cases
-
 Protopic (Tacrolimus)Who is this for?:If you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium
Protopic (Tacrolimus)Who is this for?:If you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$45/monthDelivery:Topical None twice weekly to twice dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $45/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSTacrolimus is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, showing significant improvement in symptoms and disease severity compared to standard treatments like hydrocortisone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children with eczema, both tacrolimus ointment and hydrocortisone cream improved quality of life. Tacrolimus was better at reducing certain inflammatory markers in the blood compared to hydrocortisone, though both treatments were effective.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Tacrolimus was more effective at reducing inflammatory markers compared to hydrocortisone 📄Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 years📄Tacrolimus 0.03% ointment was more effective than Hydrocortisone 1% in treating children with atopic dermatitis. After 3 weeks of treatment, Tacrolimus reduced disease severity by 56% compared to 27% with Hydrocortisone.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 60Severity: not availableAge: 2-10 yearsLong-term safety studies show no increased risk of cancer in children using topical tacrolimus for atopic dermatitis over a 10-year period.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This 10-year study found that children using tacrolimus cream (Protopic) for eczema did not have an increased risk of developing cancer compared to the general population. No cases of lymphoma were reported.Observational Study Total Patients: 7,954Severity: not availableAge: pediatricIn adults, there is no evidence of increased skin cancer risk (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with tacrolimus use compared to other treatments.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Observational Study Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Tacrolimus appears to be particularly beneficial for patients who show signs of early allergic sensitization, and it can improve quality of life measures for both patients and caregivers.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 years📄This study compared two eczema treatments (tacrolimus 0.03% and crisaborole) in children with mild to moderate eczema. While both medications improved eczema symptoms, tacrolimus showed better results in improving quality of life for both children and their caregivers.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 47Severity: mildAge: children (mean age 8.0 ± 3.9 years)Both treatments improved eczema severity, with slightly better improvement in the crisaborole group Tacrolimus is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, showing significant improvement in symptoms and disease severity compared to standard treatments like hydrocortisone.
Summary:In children with eczema, both tacrolimus ointment and hydrocortisone cream improved quality of life. Tacrolimus was better at reducing certain inflammatory markers in the blood compared to hydrocortisone, though both treatments were effective.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Tacrolimus was more effective at reducing inflammatory markers compared to hydrocortisone
Summary:Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 yearsResults:
Summary:Tacrolimus 0.03% ointment was more effective than Hydrocortisone 1% in treating children with atopic dermatitis. After 3 weeks of treatment, Tacrolimus reduced disease severity by 56% compared to 27% with Hydrocortisone.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 60Severity: not availableAge: 2-10 yearsResults:
Long-term safety studies show no increased risk of cancer in children using topical tacrolimus for atopic dermatitis over a 10-year period.
Summary:This 10-year study found that children using tacrolimus cream (Protopic) for eczema did not have an increased risk of developing cancer compared to the general population. No cases of lymphoma were reported.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 7,954Severity: not availableAge: pediatricResults:
In adults, there is no evidence of increased skin cancer risk (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with tacrolimus use compared to other treatments.
Summary:This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Results:
Tacrolimus appears to be particularly beneficial for patients who show signs of early allergic sensitization, and it can improve quality of life measures for both patients and caregivers.
Summary:Both tacrolimus and mild corticosteroids were safe and effective in treating young children with moderate-to-severe eczema. Children who showed early signs of allergies (sensitization) had better results with tacrolimus than with corticosteroids after 12 months of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 75Severity: moderate to severeAge: 1-3 yearsResults:
Summary:This study compared two eczema treatments (tacrolimus 0.03% and crisaborole) in children with mild to moderate eczema. While both medications improved eczema symptoms, tacrolimus showed better results in improving quality of life for both children and their caregivers.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 47Severity: mildAge: children (mean age 8.0 ± 3.9 years)Results:Both treatments improved eczema severity, with slightly better improvement in the crisaborole group
-
 Elidel (Pimecrolimus)Who is this for?:If you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium
Elidel (Pimecrolimus)Who is this for?:If you need a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasIf your child needs a long-term, steroid-sparing option and for treatment in sensitive areasEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$80/monthDelivery:Topical twice dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $80/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSPimecrolimus appears to be similarly effective to topical corticosteroids for treating atopic dermatitis, with about 85-90% of patients achieving treatment success after long-term use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 months📄Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsBoth treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin Long-term safety studies show Pimecrolimus is generally safe, with no significant effects on the immune system. However, it may have slightly higher rates of minor infections like bronchitis and infected eczema compared to topical steroids.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 months📄Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsBoth treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin Pimecrolimus can help reduce the need for topical steroids (steroid-sparing effect), which may be beneficial for areas sensitive to steroid side effects like the face and eyelids.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis in Chinese infants. After 26 weeks, about 83% of infants treated with Pimecrolimus showed improvement, which was similar to the 89% improvement seen with corticosteroids.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 120Severity: not availableAge: 3 months-12 monthsTreatment success rates were similar between Pimecrolimus and topical corticosteroids 📄This is a commentary on a 5-year safety study of pimecrolimus in treating atopic dermatitis. The article discusses how despite pimecrolimus being available for over a decade, there's still uncertainty about when to use it versus topical steroids, particularly for sensitive areas like the face and eyelids.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: infants and childrenThere is no increased risk of skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with using Pimecrolimus, based on long-term safety studies.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Observational Study Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Pimecrolimus appears to be similarly effective to topical corticosteroids for treating atopic dermatitis, with about 85-90% of patients achieving treatment success after long-term use.
Summary:This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 monthsResults:
Summary:Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsResults:Both treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Long-term safety studies show Pimecrolimus is generally safe, with no significant effects on the immune system. However, it may have slightly higher rates of minor infections like bronchitis and infected eczema compared to topical steroids.
Summary:This 5-year study compared pimecrolimus cream with regular steroid creams in young children with mild-to-moderate eczema. While both treatments were generally safe, steroid creams worked slightly better, and children using pimecrolimus had more skin infections and respiratory issues.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-12 monthsResults:
Summary:Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical steroids in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in infants over a 5-year period. Both treatments helped more than 85% of patients achieve clear or almost clear skin, but pimecrolimus required much fewer steroid days (7 vs 178), making it a safer long-term option.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,418Severity: mild to moderateAge: infantsResults:Both treatments showed similar long-term effectiveness in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Pimecrolimus can help reduce the need for topical steroids (steroid-sparing effect), which may be beneficial for areas sensitive to steroid side effects like the face and eyelids.
Summary:Pimecrolimus cream was as effective as topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis in Chinese infants. After 26 weeks, about 83% of infants treated with Pimecrolimus showed improvement, which was similar to the 89% improvement seen with corticosteroids.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Severity: not availableAge: 3 months-12 monthsResults:Treatment success rates were similar between Pimecrolimus and topical corticosteroids
Summary:This is a commentary on a 5-year safety study of pimecrolimus in treating atopic dermatitis. The article discusses how despite pimecrolimus being available for over a decade, there's still uncertainty about when to use it versus topical steroids, particularly for sensitive areas like the face and eyelids.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: infants and childrenResults:
There is no increased risk of skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinoma) associated with using Pimecrolimus, based on long-term safety studies.
Summary:This study found that using topical calcineurin inhibitors (like Protopic) for treating atopic dermatitis does not increase the risk of skin cancer compared to using topical corticosteroids or using no treatment. This suggests that these medications are safe to use in terms of skin cancer risk in adults.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 93,746Severity: not availableAge: 40+Results:
-
 Ebglyss (Lebrikizumab)Who is this for?:If you need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youIf you are 12+, need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Injection every 2-4 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSLebrikizumab significantly improves moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms compared to placebo. In phase 3 trials, 58-72% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.
Ebglyss (Lebrikizumab)Who is this for?:If you need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youIf you are 12+, need strong relief and topical treatments don't work for youEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Injection every 2-4 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSLebrikizumab significantly improves moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms compared to placebo. In phase 3 trials, 58-72% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in two large clinical trials. After 16 weeks, about 33-43% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 11-13% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch, and while it caused some eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), most side effects were mild.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 851Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+ years (adolescents and adults)About 3 times more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with lebrikizumab compared to placebo 📄Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultThe medication helps reduce itching quickly, with some patients experiencing improvement as early as 2 days after starting treatment. It also helps improve sleep disruption caused by itch.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Lebrikizumab helped improve itching and sleep quality in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients who experienced less itching and better sleep also reported better quality of life after 16 weeks of treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Patients who responded to treatment with improved itch and sleep showed significant improvements in quality of life measures 📄Lebrikizumab, a medication that targets IL-13, significantly improved moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults. After 16 weeks, about 60% of patients taking lebrikizumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 16% taking placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 751Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Significantly more patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema symptoms with lebrikizumab Lebrikizumab has a favorable safety profile with most side effects being mild to moderate. The most common side effects include conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), injection site reactions, and upper respiratory infections. Serious side effects are rare.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This analysis looked at the safety of lebrikizumab across eight clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The medication was generally safe, with most side effects being mild or moderate. The most common side effect specific to lebrikizumab was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in about 8.5% of patients.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adults📄Lebrikizumab was found to be generally safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and adolescents. The most common side effect was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in 8.5% of treated patients compared to 2.5% in placebo. Most side effects were mild or moderate.JournalArticle Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adults and adolescentsThe medication can be given either every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks after initial loading doses, with both dosing schedules showing effectiveness. This flexibility in dosing may be beneficial for patients.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Lebrikizumab helped maintain clear or almost clear skin in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 2 years. About half of the patients achieved completely clear skin, and more than 55% reported having no or minimal itching after 2 years of treatment.JournalArticle Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableAbout half of patients maintained completely clear skin 📄Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultLebrikizumab significantly improves moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms compared to placebo. In phase 3 trials, 58-72% of patients achieved a 75% improvement in disease severity scores after 16 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in two large clinical trials. After 16 weeks, about 33-43% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 11-13% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch, and while it caused some eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), most side effects were mild.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 851Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12+ years (adolescents and adults)Results:About 3 times more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with lebrikizumab compared to placebo
Summary:Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultResults:
The medication helps reduce itching quickly, with some patients experiencing improvement as early as 2 days after starting treatment. It also helps improve sleep disruption caused by itch.
Summary:Lebrikizumab helped improve itching and sleep quality in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients who experienced less itching and better sleep also reported better quality of life after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 16+Results:Patients who responded to treatment with improved itch and sleep showed significant improvements in quality of life measures
Summary:Lebrikizumab, a medication that targets IL-13, significantly improved moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults. After 16 weeks, about 60% of patients taking lebrikizumab had clear or almost clear skin compared to 16% taking placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 751Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Significantly more patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema symptoms with lebrikizumab
Lebrikizumab has a favorable safety profile with most side effects being mild to moderate. The most common side effects include conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), injection site reactions, and upper respiratory infections. Serious side effects are rare.
Summary:This analysis looked at the safety of lebrikizumab across eight clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The medication was generally safe, with most side effects being mild or moderate. The most common side effect specific to lebrikizumab was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in about 8.5% of patients.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescents and adultsResults:
Summary:Lebrikizumab was found to be generally safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and adolescents. The most common side effect was conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), occurring in 8.5% of treated patients compared to 2.5% in placebo. Most side effects were mild or moderate.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,720Severity: moderate to severeAge: adults and adolescentsResults:
The medication can be given either every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks after initial loading doses, with both dosing schedules showing effectiveness. This flexibility in dosing may be beneficial for patients.
Summary:Lebrikizumab helped maintain clear or almost clear skin in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 2 years. About half of the patients achieved completely clear skin, and more than 55% reported having no or minimal itching after 2 years of treatment.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Severity: moderate-to-severeAge: not availableResults:About half of patients maintained completely clear skin
Summary:Lebrikizumab was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema over 52 weeks. After initial treatment, patients maintained good results whether they received the drug every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, with about 75-80% of patients maintaining clear or almost clear skin.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: adolescent and adultResults:
-
 Cibinqo (Abrocitinib)Who is this for?:If you need rapid relief of itch and other symptomsIf your child is 12+ years and needs rapid relief of itch and other symptomsEffectiveness:Side Effects:High
Cibinqo (Abrocitinib)Who is this for?:If you need rapid relief of itch and other symptomsIf your child is 12+ years and needs rapid relief of itch and other symptomsEffectiveness:Side Effects:High⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$362 per monthDelivery:Oral once dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSAbrocitinib is effective at treating moderate-to-severe eczema, with higher doses (200mg) showing better results than lower doses (100mg). After 12 weeks of treatment, 61% of patients on 200mg and 45% on 100mg saw at least 75% improvement in their eczema symptoms, compared to only 10% on placebo.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results The medication can provide rapid relief from itch - patients noticed improvement within 24 hours of starting treatment. This quick relief from itching led to significant improvements in quality of life for patients.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results The medication is generally well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild. The most common side effects include nausea (14% with 200mg dose), headache (8%), and upper respiratory infections. Some patients experienced temporary decreases in blood platelet counts, which typically stabilized with continued treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results For patients who respond well to initial treatment, continuing the medication helps prevent flare-ups. In a long-term study, only 19% of patients on 200mg experienced a flare-up compared to 81% of those who stopped treatment. If flares occur, restarting treatment is effective at regaining control of symptoms.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Abrocitinib is effective at treating moderate-to-severe eczema, with higher doses (200mg) showing better results than lower doses (100mg). After 12 weeks of treatment, 61% of patients on 200mg and 45% on 100mg saw at least 75% improvement in their eczema symptoms, compared to only 10% on placebo.
The medication can provide rapid relief from itch - patients noticed improvement within 24 hours of starting treatment. This quick relief from itching led to significant improvements in quality of life for patients.
The medication is generally well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild. The most common side effects include nausea (14% with 200mg dose), headache (8%), and upper respiratory infections. Some patients experienced temporary decreases in blood platelet counts, which typically stabilized with continued treatment.
For patients who respond well to initial treatment, continuing the medication helps prevent flare-ups. In a long-term study, only 19% of patients on 200mg experienced a flare-up compared to 81% of those who stopped treatment. If flares occur, restarting treatment is effective at regaining control of symptoms.
-
 Opzelura (Ruxolitinib)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedIf your child is 12+ years and looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium
Opzelura (Ruxolitinib)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedIf your child is 12+ years and looking for a short-term treatment with rapid relief of itch and inflammation, and other topical treatments have failedEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$212 per monthDelivery:Topical thin film to affected areas twice dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSRuxolitinib cream provides rapid and significant itch relief, with improvements seen within 12-36 hours of first application and sustained through 8 weeks of treatment. Over 50% of patients achieved significant itch reduction by week 8.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream showed significant improvement in eczema symptoms compared to vehicle (placebo cream). The highest dose (1.5% twice daily) reduced eczema severity by 71.6% after 4 weeks, and patients experienced itch relief within 36 hours of starting treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 307Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Ruxolitinib 1.5% BID reduced eczema severity by 71.6% compared to 15.5% with vehicle The cream is generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. Application site reactions are infrequent (2-6% of patients) and most side effects are mild to moderate. There were no serious safety concerns even with long-term use up to 52 weeks.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableOnly a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream 📄Ruxolitinib cream was effective in treating eczema in teenagers, with about 51% achieving clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks compared to 14% using a placebo cream. The medication started working quickly, reducing itch from day 2, and continued to work well for up to 52 weeks with few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 245Severity: mild to moderateAge: 12-17 yearsSignificantly more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with ruxolitinib 📄Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsAlmost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment The medication has very low systemic absorption when applied to the skin, meaning it mainly works locally where applied and is unlikely to cause whole-body side effects that can occur with oral JAK inhibitors.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableOnly a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream 📄Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsAlmost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment Ruxolitinib cream improves quality of life and ability to work/perform daily activities. Patients using the cream showed significant improvements in work productivity and daily activity compared to vehicle (placebo) cream.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ruxolitinib cream improved itch and skin pain within 12 hours of application in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also improved sleep and quality of life within 2 weeks, and these benefits lasted for up to 52 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,208Ruxolitinib cream improved skin pain within 12 hours of application 📄Ruxolitinib cream, applied twice daily, quickly reduced itch in people with mild to moderate eczema. The cream started working within 12 hours and continued to improve itch symptoms over 8 weeks. The stronger version (1.5%) worked better than the weaker version (0.75%) and both worked better than the placebo cream.Editor's Picks January 2023 (2022)Total Patients: 1,200Severity: mild to moderateAge: adolescents and adultsRuxolitinib cream provided rapid itch relief within 12 hours and continued improvement through 8 weeks Ruxolitinib cream provides rapid and significant itch relief, with improvements seen within 12-36 hours of first application and sustained through 8 weeks of treatment. Over 50% of patients achieved significant itch reduction by week 8.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream showed significant improvement in eczema symptoms compared to vehicle (placebo cream). The highest dose (1.5% twice daily) reduced eczema severity by 71.6% after 4 weeks, and patients experienced itch relief within 36 hours of starting treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 307Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Ruxolitinib 1.5% BID reduced eczema severity by 71.6% compared to 15.5% with vehicle
The cream is generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. Application site reactions are infrequent (2-6% of patients) and most side effects are mild to moderate. There were no serious safety concerns even with long-term use up to 52 weeks.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Only a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream was effective in treating eczema in teenagers, with about 51% achieving clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks compared to 14% using a placebo cream. The medication started working quickly, reducing itch from day 2, and continued to work well for up to 52 weeks with few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 245Severity: mild to moderateAge: 12-17 yearsResults:Significantly more patients achieved clear or almost clear skin with ruxolitinib
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsResults:Almost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment
The medication has very low systemic absorption when applied to the skin, meaning it mainly works locally where applied and is unlikely to cause whole-body side effects that can occur with oral JAK inhibitors.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream, when applied to the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, shows very low levels in the blood, suggesting it mainly works locally on the skin. This means it's less likely to cause the side effects typically seen with oral JAK inhibitor medications.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Only a small amount of the medication gets absorbed into the bloodstream
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream was tested in patients with moderate to severe eczema covering at least 25% of their body. After 56 days of treatment, about 95% of patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms. The cream was generally safe to use, with only a few patients experiencing treatment-related side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: moderate to severeAge: 12-65 yearsResults:Almost all patients (94.6%) achieved at least 75% improvement in their eczema severity after 56 days of treatment
Ruxolitinib cream improves quality of life and ability to work/perform daily activities. Patients using the cream showed significant improvements in work productivity and daily activity compared to vehicle (placebo) cream.
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream improved itch and skin pain within 12 hours of application in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also improved sleep and quality of life within 2 weeks, and these benefits lasted for up to 52 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,208Results:Ruxolitinib cream improved skin pain within 12 hours of application
Summary:Ruxolitinib cream, applied twice daily, quickly reduced itch in people with mild to moderate eczema. The cream started working within 12 hours and continued to improve itch symptoms over 8 weeks. The stronger version (1.5%) worked better than the weaker version (0.75%) and both worked better than the placebo cream.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 1,200Severity: mild to moderateAge: adolescents and adultsResults:Ruxolitinib cream provided rapid itch relief within 12 hours and continued improvement through 8 weeks
-
 Nemluvio (Nemolizumab)Who is this for?:If you have moderate-to-severe AD with intense itchingIf you are 12 years or older with moderate-to-severe AD and intense itchingEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Injection Every 4-8 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSNemolizumab significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. In clinical trials, patients saw 40-70% reduction in itch scores after 16 weeks of treatment, with improvements noticeable within the first few days.
Nemluvio (Nemolizumab)Who is this for?:If you have moderate-to-severe AD with intense itchingIf you are 12 years or older with moderate-to-severe AD and intense itchingEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Injection Every 4-8 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSNemolizumab significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. In clinical trials, patients saw 40-70% reduction in itch scores after 16 weeks of treatment, with improvements noticeable within the first few days.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,728📄Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, reduced itching by 43% compared to 21% with placebo after 16 weeks. The medication also improved eczema severity and sleep quality in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 215Nemolizumab reduced itching twice as much as placebo 📄Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication improves skin symptoms and quality of life, including better sleep. Studies showed 45-78% improvement in eczema severity scores over 16-68 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 1,728📄Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks along with topical treatments, helped reduce itching by 66% and eczema severity by 78% over 68 weeks in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The improvements lasted even after treatment ended, and the medication was generally safe to use.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 303Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥13 yearsSignificant reduction in itching maintained over more than a year The most common side effects are mild and include nasopharyngitis (common cold), upper respiratory tract infections, and worsening of atopic dermatitis. Serious side effects are rare but can include severe allergic reactions.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks 📄Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication is given as a subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. It works by blocking interleukin-31, a protein that triggers itching in atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Nemolizumab is a new drug that targets IL-31, which is involved in causing eczema symptoms. The drug shows good results in reducing itch quickly and improving skin condition, with mostly mild side effects.Review Severity: not availableAge: not availablenot available 📄Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks Taken every 4 weeksStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Itch relief in as soon as 48 hoursStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Unique mechanism of actionStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Nemolizumab significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. In clinical trials, patients saw 40-70% reduction in itch scores after 16 weeks of treatment, with improvements noticeable within the first few days.
Summary:Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,728Results:
Summary:Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, reduced itching by 43% compared to 21% with placebo after 16 weeks. The medication also improved eczema severity and sleep quality in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 215Results:Nemolizumab reduced itching twice as much as placebo
Summary:Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication improves skin symptoms and quality of life, including better sleep. Studies showed 45-78% improvement in eczema severity scores over 16-68 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Nemolizumab, when used with topical treatments, significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced itching in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The medication showed benefits as early as week 1 for itch reduction, and by week 16, 36-38% of patients had clear or almost clear skin compared to 25-26% on placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,728Results:
Summary:Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks along with topical treatments, helped reduce itching by 66% and eczema severity by 78% over 68 weeks in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The improvements lasted even after treatment ended, and the medication was generally safe to use.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 303Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥13 yearsResults:Significant reduction in itching maintained over more than a year
The most common side effects are mild and include nasopharyngitis (common cold), upper respiratory tract infections, and worsening of atopic dermatitis. Serious side effects are rare but can include severe allergic reactions.
Summary:Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Results:Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks
Summary:Nemolizumab, given as an injection every 4 weeks, significantly improved both skin inflammation and itch in patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. The 30mg dose worked best, with patients experiencing about 69% improvement in their eczema severity and 67% reduction in itch after 24 weeks.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 226Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication is given as a subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. It works by blocking interleukin-31, a protein that triggers itching in atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Nemolizumab is a new drug that targets IL-31, which is involved in causing eczema symptoms. The drug shows good results in reducing itch quickly and improving skin condition, with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:not available
Summary:Nemolizumab is a new medication approved in Japan that helps reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis when other treatments haven't worked well enough. The medication is given as an injection every 4 weeks and showed improvements in both itching and skin symptoms for up to 68 weeks.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 13+Results:Continuous improvement and/or maintenance of itching reduction up to 68 weeks
Taken every 4 weeks
Itch relief in as soon as 48 hours
Unique mechanism of action
-
 Adbry (Tralokinumab)Who is this for?:If topical prescription therapies don't work for youIf you are 12+ years and topical prescription therapies don't work for youEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$281 per monthDelivery:Injection 300mg every 2 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSTralokinumab is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with 39% of patients achieving clear/almost clear skin at 16 weeks when combined with topical corticosteroids. The treatment continues to show progressive improvement beyond 16 weeks, with 70% of patients achieving a 75% improvement in symptoms by week 32.
Adbry (Tralokinumab)Who is this for?:If topical prescription therapies don't work for youIf you are 12+ years and topical prescription therapies don't work for youEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$281 per monthDelivery:Injection 300mg every 2 weeksSee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSTralokinumab is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with 39% of patients achieving clear/almost clear skin at 16 weeks when combined with topical corticosteroids. The treatment continues to show progressive improvement beyond 16 weeks, with 70% of patients achieving a 75% improvement in symptoms by week 32.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab, a medication given every 2 weeks, helped improve severe eczema in adults who didn't respond well to topical treatments. After 16 weeks, about 25-33% of patients saw a significant improvement in their eczema symptoms compared to 11-13% who received placebo. Most patients who responded well at 16 weeks maintained their improvement through 52 weeks of treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication is generally well-tolerated with a favorable safety profile. The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections (16%), conjunctivitis (5%), and injection site reactions (4%). Most side effects are mild to moderate and do not lead to treatment discontinuation.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab was found to be safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis based on data from five clinical trials. The most common side effects were upper respiratory infections and eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), but serious side effects were rare and similar to placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 2,285Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Tralokinumab can help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids - patients using tralokinumab used approximately 50% less topical corticosteroids compared to those on placebo by week 16.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity 📄Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+The medication improves quality of life measures including itch severity, sleep quality, and overall disease burden. These improvements are seen within the first few weeks of treatment and are sustained over time.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity 📄Tralokinumab, either alone or with topical steroids, showed rapid improvement in itch and sleep quality for patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients started experiencing relief from itch as early as 1-2 weeks into treatment, and improvements in sleep were seen within 2 weeks.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 1,976Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Meaningful improvements in quality of life were observed from week 2 Tralokinumab is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with 39% of patients achieving clear/almost clear skin at 16 weeks when combined with topical corticosteroids. The treatment continues to show progressive improvement beyond 16 weeks, with 70% of patients achieving a 75% improvement in symptoms by week 32.
Summary:Tralokinumab, a medication given every 2 weeks, helped improve severe eczema in adults who didn't respond well to topical treatments. After 16 weeks, about 25-33% of patients saw a significant improvement in their eczema symptoms compared to 11-13% who received placebo. Most patients who responded well at 16 weeks maintained their improvement through 52 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication is generally well-tolerated with a favorable safety profile. The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections (16%), conjunctivitis (5%), and injection site reactions (4%). Most side effects are mild to moderate and do not lead to treatment discontinuation.
Summary:Tralokinumab was found to be safe for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis based on data from five clinical trials. The most common side effects were upper respiratory infections and eye inflammation (conjunctivitis), but serious side effects were rare and similar to placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 2,285Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Tralokinumab can help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids - patients using tralokinumab used approximately 50% less topical corticosteroids compared to those on placebo by week 16.
Summary:Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Tralokinumab effectively treated moderate-to-severe eczema in adults over 28 weeks, working well for both new patients and those who previously used dupilumab. About 76% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin, though some patients (27.4%) had to stop treatment due to side effects or lack of effectiveness.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 84Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication improves quality of life measures including itch severity, sleep quality, and overall disease burden. These improvements are seen within the first few weeks of treatment and are sustained over time.
Summary:Tralokinumab with topical steroids showed continuous improvement in eczema symptoms over 32 weeks. By week 32, about 70% of patients saw a 75% improvement in their eczema, and about 50% saw a 90% improvement. The treatment helped reduce sleep problems and improved quality of life.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 380Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:70.2% of patients achieved 75% improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Tralokinumab, either alone or with topical steroids, showed rapid improvement in itch and sleep quality for patients with moderate-to-severe eczema. Patients started experiencing relief from itch as early as 1-2 weeks into treatment, and improvements in sleep were seen within 2 weeks.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 1,976Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Meaningful improvements in quality of life were observed from week 2
-
 Vtama (Tapinarof)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a non-steroid creamFor children 2 years and older who need a non-steroid creamEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSTapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. In clinical trials, 45-46% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment compared to 14-18% with vehicle (placebo) cream.
Vtama (Tapinarof)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a non-steroid creamFor children 2 years and older who need a non-steroid creamEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSTapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. In clinical trials, 45-46% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment compared to 14-18% with vehicle (placebo) cream.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 years📄Tapinarof cream 1%, applied once daily, was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin, compared to only about 16% using the vehicle cream.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin The medication provided rapid itch relief, with improvements seen as early as 24 hours after the first application. By week 8, about 31-33% of patients achieved minimal to no itch compared to 14-17% with vehicle cream.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily helped reduce itching and improve sleep in people with atopic dermatitis. About one-third of patients achieved minimal to no itching after 8 weeks of treatment, compared to only 14-17% of those using a placebo cream.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof significantly improved itch compared to vehicle 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily showed rapid improvement in itch symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with effects seen as early as 24 hours after first use. The improvement in itch continued to increase through 8 weeks of treatment.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof was well-tolerated across all age groups and skin types. The most common side effects were mild to moderate and included folliculitis (hair follicle inflammation), headache, and nasopharyngitis (common cold). Very few patients (less than 2%) had to stop treatment due to side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 years📄Tapinarof cream 1% was tested for skin safety in healthy adults. The cream was found to be safe, causing only very mild skin irritation, and did not cause allergic reactions or increased sensitivity to sunlight.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 376This was a safety study, not an efficacy study The medication worked consistently well across all racial groups and skin types, including patients with darker skin tones who made up about 50% of the study participants.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. The medication worked significantly better than the vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in clearing or almost clearing eczema symptoms.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderTapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin across all racial groups 📄Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races, including children as young as 2 years old. About 40-50% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment, which was significantly better than the placebo group.JournalArticle Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years+Tapinarof showed significantly higher rates of clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle across all populations Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. In clinical trials, 45-46% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment compared to 14-18% with vehicle (placebo) cream.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 yearsResults:
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1%, applied once daily, was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin, compared to only about 16% using the vehicle cream.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:Tapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
The medication provided rapid itch relief, with improvements seen as early as 24 hours after the first application. By week 8, about 31-33% of patients achieved minimal to no itch compared to 14-17% with vehicle cream.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily helped reduce itching and improve sleep in people with atopic dermatitis. About one-third of patients achieved minimal to no itching after 8 weeks of treatment, compared to only 14-17% of those using a placebo cream.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:Tapinarof significantly improved itch compared to vehicle
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily showed rapid improvement in itch symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with effects seen as early as 24 hours after first use. The improvement in itch continued to increase through 8 weeks of treatment.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:
Tapinarof was well-tolerated across all age groups and skin types. The most common side effects were mild to moderate and included folliculitis (hair follicle inflammation), headache, and nasopharyngitis (common cold). Very few patients (less than 2%) had to stop treatment due to side effects.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating moderate to severe eczema in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. After 8 weeks, about 46% of patients using tapinarof had clear or almost clear skin compared to only about 16% using placebo cream. The medication was generally safe with mostly mild side effects.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-81 yearsResults:
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% was tested for skin safety in healthy adults. The cream was found to be safe, causing only very mild skin irritation, and did not cause allergic reactions or increased sensitivity to sunlight.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 376Results:This was a safety study, not an efficacy study
The medication worked consistently well across all racial groups and skin types, including patients with darker skin tones who made up about 50% of the study participants.
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races in both adults and children as young as 2 years old. The medication worked significantly better than the vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in clearing or almost clearing eczema symptoms.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years and olderResults:Tapinarof was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin across all racial groups
Summary:Tapinarof cream 1% applied once daily was effective in treating atopic dermatitis across all skin colors and races, including children as young as 2 years old. About 40-50% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 8 weeks of treatment, which was significantly better than the placebo group.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 813Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2 years+Results:Tapinarof showed significantly higher rates of clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle across all populations
-
 Zoryve (Roflumilast)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityIf your child is 6+ years and looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$164 per monthDelivery:Topical once dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSRoflumilast cream appears to be effective in treating mild to moderate eczema, with patients showing significant improvements in their eczema severity scores after 4 weeks of once-daily use
Zoryve (Roflumilast)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityIf your child is 6+ years and looking for a non-steroidal cream with good tolerabilityEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$164 per monthDelivery:Topical once dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSRoflumilast cream appears to be effective in treating mild to moderate eczema, with patients showing significant improvements in their eczema severity scores after 4 weeks of once-daily useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 136Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant The medication appears to be very safe, with very few side effects reported. Only 2 out of 91 patients experienced mild treatment-related side effects (a mild rash and moderate application site pain), and only one patient had to stop using the medication due to side effectsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 136Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant Roflumilast cream is a non-steroid treatment option, which may be beneficial for patients who are concerned about using steroid-based treatmentsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 136Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant Roflumilast cream appears to be effective in treating mild to moderate eczema, with patients showing significant improvements in their eczema severity scores after 4 weeks of once-daily use
Summary:Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 136Results:Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant
The medication appears to be very safe, with very few side effects reported. Only 2 out of 91 patients experienced mild treatment-related side effects (a mild rash and moderate application site pain), and only one patient had to stop using the medication due to side effects
Summary:Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 136Results:Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant
Roflumilast cream is a non-steroid treatment option, which may be beneficial for patients who are concerned about using steroid-based treatments
Summary:Roflumilast cream (0.15% and 0.05%) was tested as a once-daily treatment for mild to moderate eczema. While the primary goal wasn't met, the cream showed promising improvements in eczema symptoms with very few side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 136Results:Roflumilast showed greater improvement in eczema severity compared to vehicle, but the difference wasn't statistically significant
-
 Eucrisa (Crisaborole)Who is this for?:If you need a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasIf your child needs a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$152 per monthDelivery:Topical twice dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSCrisaborole is effective for treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in both children and adults, with significantly more patients achieving clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle (placebo) treatment
Eucrisa (Crisaborole)Who is this for?:If you need a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasIf your child needs a non-steroid topical treatment, especially in sensitive areasEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$152 per monthDelivery:Topical twice dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSCrisaborole is effective for treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in both children and adults, with significantly more patients achieving clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle (placebo) treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderCrisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin 📄Crisaborole ointment was more effective than placebo in treating mild to moderate eczema in patients aged 2 years and older. About 32% of patients using crisaborole achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 18-25% using placebo, and the medication showed a good safety profile.Clinical Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderSignificantly more patients using crisaborole achieved clear/almost clear skin with ≥2-grade improvement compared to vehicle The most common side effect is application site pain/discomfort, occurring in about 4-6% of patients. Most side effects are mild to moderate and treatment-related adverse events are infrequentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderCrisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin 📄Crisaborole ointment was tested in infants aged 3-24 months with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects, and about 30% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 28 days of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 137Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-24 monthsCrisaborole can be used as a long-term maintenance treatment, with studies showing sustained efficacy and safety over 48-52 weeks of useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Once-daily crisaborole ointment helped prevent eczema flares for longer compared to vehicle (placebo), with patients staying flare-free for about 111 days versus 30 days. Patients using crisaborole had fewer flares overall and more flare-free days during the year-long study.Total Patients: 270Crisaborole significantly delayed time to first flare compared to vehicle 📄Once-daily crisaborole ointment was tested as a long-term maintenance treatment for mild-to-moderate eczema. Patients using crisaborole stayed flare-free for longer (111 days vs 30 days) compared to those using a placebo ointment, and had fewer flares over the course of a year.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 497Severity: mild to moderateAge: ≥3 monthsThe medication works quickly, with improvements in itch and skin symptoms seen within the first week of treatment in many patientsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderCrisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin 📄Crisaborole ointment 2% was more effective than placebo in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in children and teenagers. Patients using crisaborole showed faster and greater improvements in both skin appearance and itch compared to those using vehicle (placebo), with benefits seen as early as 8 days after starting treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2-17 yearsSignificantly greater improvement in ISGA scores for crisaborole vs vehicle, particularly in patients with moderate baseline disease Crisaborole is effective for treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in both children and adults, with significantly more patients achieving clear/almost clear skin compared to vehicle (placebo) treatment
Summary:Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Studied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Crisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Summary:Crisaborole ointment was more effective than placebo in treating mild to moderate eczema in patients aged 2 years and older. About 32% of patients using crisaborole achieved clear or almost clear skin compared to 18-25% using placebo, and the medication showed a good safety profile.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Significantly more patients using crisaborole achieved clear/almost clear skin with ≥2-grade improvement compared to vehicle
The most common side effect is application site pain/discomfort, occurring in about 4-6% of patients. Most side effects are mild to moderate and treatment-related adverse events are infrequent
Summary:Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Studied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Crisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Summary:Crisaborole ointment was tested in infants aged 3-24 months with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment was well-tolerated with mostly mild side effects, and about 30% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after 28 days of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 137Severity: mild to moderateAge: 3-24 monthsResults:
Crisaborole can be used as a long-term maintenance treatment, with studies showing sustained efficacy and safety over 48-52 weeks of use
Summary:Once-daily crisaborole ointment helped prevent eczema flares for longer compared to vehicle (placebo), with patients staying flare-free for about 111 days versus 30 days. Patients using crisaborole had fewer flares overall and more flare-free days during the year-long study.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 270Results:Crisaborole significantly delayed time to first flare compared to vehicle
Summary:Once-daily crisaborole ointment was tested as a long-term maintenance treatment for mild-to-moderate eczema. Patients using crisaborole stayed flare-free for longer (111 days vs 30 days) compared to those using a placebo ointment, and had fewer flares over the course of a year.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 497Severity: mild to moderateAge: ≥3 monthsResults:
The medication works quickly, with improvements in itch and skin symptoms seen within the first week of treatment in many patients
Summary:Crisaborole 2% ointment is effective for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged 2 years and older. The medication works by reducing inflammation and itching, with about 30-50% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 4 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2 years and olderResults:Crisaborole showed better efficacy than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Summary:Crisaborole ointment 2% was more effective than placebo in treating mild-to-moderate eczema in children and teenagers. Patients using crisaborole showed faster and greater improvements in both skin appearance and itch compared to those using vehicle (placebo), with benefits seen as early as 8 days after starting treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: mild to moderateAge: 2-17 yearsResults:Significantly greater improvement in ISGA scores for crisaborole vs vehicle, particularly in patients with moderate baseline disease
Supplements and Natural Remedies
-
 Vitamin B12(Cobalamin)As an add-on alongside other therapiesAs an add-on alongside other therapiesOral dailyLow
Vitamin B12(Cobalamin)As an add-on alongside other therapiesAs an add-on alongside other therapiesOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($1.50 - $4)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTopical Vitamin B12 cream appears to be more effective than standard moisturizing creams for treating mild eczema, with studies showing a 78% improvement in symptoms compared to 33.5% with regular creamsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A vitamin B12 cream was compared to a standard moisturizing cream for treating mild eczema. The vitamin B12 cream reduced eczema severity by 77.6% compared to 33.5% with the standard cream after 12 weeks of use.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 22Severity: mildAge: not availableVitamin B12 cream was more than twice as effective as standard moisturizer in reducing eczema severity There may be a connection between Vitamin B12 blood levels and eczema severity - lower Vitamin B12 levels might be associated with worse eczema symptoms. Oral Vitamin B12 supplements might help improve severe eczema that's difficult to controlStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements Vitamin B12 has anti-inflammatory properties and can help regulate the immune system, which may explain why it helps with eczema symptomsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements Topical Vitamin B12 cream appears to be more effective than standard moisturizing creams for treating mild eczema, with studies showing a 78% improvement in symptoms compared to 33.5% with regular creams
Summary:A vitamin B12 cream was compared to a standard moisturizing cream for treating mild eczema. The vitamin B12 cream reduced eczema severity by 77.6% compared to 33.5% with the standard cream after 12 weeks of use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 22Severity: mildAge: not availableResults:Vitamin B12 cream was more than twice as effective as standard moisturizer in reducing eczema severity
There may be a connection between Vitamin B12 blood levels and eczema severity - lower Vitamin B12 levels might be associated with worse eczema symptoms. Oral Vitamin B12 supplements might help improve severe eczema that's difficult to control
Summary:In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Results:Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements
Vitamin B12 has anti-inflammatory properties and can help regulate the immune system, which may explain why it helps with eczema symptoms
Summary:In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Results:Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements
-
 Coconut Oil(Virgin Coconut Oil)If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer for your child that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationTopical dailyLow
Coconut Oil(Virgin Coconut Oil)If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer for your child that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationTopical dailyLowSide Effect Affected Skin irritation ($6.50 - $30)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSCoconut oil, when formulated with other ingredients (specifically isosorbide diesters), can significantly improve itching in people with mild-to-moderate eczema, showing about 66% improvement in itch symptomsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013) When used in a specialized formulation, coconut oil derivatives can help reduce the need for topical steroids in eczema treatment, particularly in the early weeks of treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013) Coconut oil-based treatments may help reduce harmful bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin of eczema patientsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013) Coconut oil is one of the most commonly used traditional home remedies for eczema treatment, particularly in Indian householdsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a study of 150 children in India, coconut oil was the most commonly used home remedy for treating eczema/atopic dermatitis, followed by olive oil and mustard oil. The study looked at various home remedies parents used before visiting a doctor.Observational Study Total Patients: 150Coconut oil, when formulated with other ingredients (specifically isosorbide diesters), can significantly improve itching in people with mild-to-moderate eczema, showing about 66% improvement in itch symptoms
Summary:A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013)
When used in a specialized formulation, coconut oil derivatives can help reduce the need for topical steroids in eczema treatment, particularly in the early weeks of treatment
Summary:A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013)
Coconut oil-based treatments may help reduce harmful bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin of eczema patients
Summary:A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013)
Coconut oil is one of the most commonly used traditional home remedies for eczema treatment, particularly in Indian households
Summary:In a study of 150 children in India, coconut oil was the most commonly used home remedy for treating eczema/atopic dermatitis, followed by olive oil and mustard oil. The study looked at various home remedies parents used before visiting a doctor.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 150Results:
-
 Probiotics(Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium)As a complementary treatment for children with moderate atopic dermatitisAs a complementary treatment alongside standard therapiesOral dailyLow
Probiotics(Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium)As a complementary treatment for children with moderate atopic dermatitisAs a complementary treatment alongside standard therapiesOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected No significant side effects reported ($20 - $30)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSProbiotics appear to be effective in reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis symptoms, with multiple studies showing significant improvements in SCORAD scores (a measure of eczema severity) compared to placeboStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsSignificant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment 📄An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Observational Study Total Patients: 320Significant improvement in eczema severity 📄A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsPatients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo Probiotics may help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis, potentially allowing for less steroid useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of probiotics taken by mouth significantly improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate atopic dermatitis. Children taking probiotics needed less topical steroids to manage their condition, with an 83% improvement in symptoms compared to 24% in the placebo group.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 50Severity: moderateAge: 4-17 yearsProbiotics led to a significantly greater improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo 📄A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsPatients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo Probiotics appear to be safe with very few reported side effects. Most studies reported similar adverse event rates between probiotic and placebo groupsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsSignificant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment 📄An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Observational Study Total Patients: 320Significant improvement in eczema severity Multi-strain probiotic combinations may be more effective than single strains, and treatment duration of 8-12 weeks appears to be optimal for seeing benefitsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Observational Study Total Patients: 320Significant improvement in eczema severity 📄Taking specific probiotics and prebiotics for 12 weeks helped improve mild eczema symptoms, including itching and skin lesions. The study suggests that these supplements might help maintain stable eczema and reduce flare-ups.Observational Study Total Patients: 144Severity: mildAge: not specified (mean age 25.1 ± 17.6 years)All measures of eczema severity showed significant improvement after 12 weeks of probiotic treatment Probiotics appear to be effective in reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis symptoms, with multiple studies showing significant improvements in SCORAD scores (a measure of eczema severity) compared to placebo
Summary:The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsResults:Significant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment
Summary:An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 320Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Summary:A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsResults:Patients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo
Probiotics may help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis, potentially allowing for less steroid use
Summary:A mixture of probiotics taken by mouth significantly improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate atopic dermatitis. Children taking probiotics needed less topical steroids to manage their condition, with an 83% improvement in symptoms compared to 24% in the placebo group.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderateAge: 4-17 yearsResults:Probiotics led to a significantly greater improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo
Summary:A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsResults:Patients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo
Probiotics appear to be safe with very few reported side effects. Most studies reported similar adverse event rates between probiotic and placebo groups
Summary:The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsResults:Significant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment
Summary:An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 320Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Multi-strain probiotic combinations may be more effective than single strains, and treatment duration of 8-12 weeks appears to be optimal for seeing benefits
Summary:An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 320Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Taking specific probiotics and prebiotics for 12 weeks helped improve mild eczema symptoms, including itching and skin lesions. The study suggests that these supplements might help maintain stable eczema and reduce flare-ups.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 144Severity: mildAge: not specified (mean age 25.1 ± 17.6 years)Results:All measures of eczema severity showed significant improvement after 12 weeks of probiotic treatment
-
 Shea butter(Shea butter)If you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerIf you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerTopical dailyLow
Shea butter(Shea butter)If you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerIf you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerTopical dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($4 - $10)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSShea butter-containing cream was well-received by most patients, with 74% of users rating it as 'very good' or 'good'Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Review Total Patients: 34Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable Patients who liked the shea butter cream experienced less itching and better quality of life after using it. Their itching scores improved from 6.7 to 6.0Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Review Total Patients: 34Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable The shea butter cream worked just as well as other moisturizers containing ceramides (another type of skin-protecting ingredient), suggesting it's an effective alternativeStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Review Total Patients: 34Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable Shea butter-containing cream was well-received by most patients, with 74% of users rating it as 'very good' or 'good'
Summary:A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Total Patients: 34Results:Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable
Patients who liked the shea butter cream experienced less itching and better quality of life after using it. Their itching scores improved from 6.7 to 6.0
Summary:A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Total Patients: 34Results:Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable
The shea butter cream worked just as well as other moisturizers containing ceramides (another type of skin-protecting ingredient), suggesting it's an effective alternative
Summary:A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Total Patients: 34Results:Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable
-
 Vitamin D3(Cholecalciferol)If your child's symptoms get worse during winter or your child has confirmed low Vitamin D levelsIf your symptoms get worse during winter or you have confirmed low Vitamin D levelsOral dailyLow
Vitamin D3(Cholecalciferol)If your child's symptoms get worse during winter or your child has confirmed low Vitamin D levelsIf your symptoms get worse during winter or you have confirmed low Vitamin D levelsOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected Allergic rash Idiosyncratic reactions No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSVitamin D supplementation appears to help reduce the severity of atopic dermatitis, particularly in patients with severe cases. Studies show that taking vitamin D along with standard treatments leads to greater improvement in eczema symptoms compared to standard treatment alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding vitamin D supplements (1600 IU/day) to standard treatment with hydrocortisone cream helped improve severe eczema symptoms in children more than using hydrocortisone cream alone. Patients taking vitamin D showed about 56% improvement in their eczema severity compared to 42% in those taking placebo.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 86Severity: severeAge: pediatric (not specified)Vitamin D supplementation led to significantly better improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo 📄People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Review Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms 📄Vitamin D supplements helped reduce the severity of eczema in children under 14. After 3 months of vitamin D supplementation, patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms.Observational Study Total Patients: 152Severity: mild to severeAge: 0-14 yearsSignificant improvement in eczema severity after vitamin D supplementation Pregnant women taking vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy may help reduce their baby's risk of developing eczema in the first year of life, particularly if they breastfeed for more than one month.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Pregnant women who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy had babies with a 45% lower chance of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This protective effect was stronger in babies who were breastfed for at least 1 month, but the effect became weaker as children got older.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsSignificant reduction in eczema at 12 months, effect weakens over time 📄Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.JournalArticle Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsPeople with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to those without the condition. This is especially true in children with atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Children with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to healthy children, especially those with severe eczema. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve eczema symptoms in children.Meta-Analysis Children with AD had significantly lower vitamin D levels than healthy children 📄People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Review Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms The effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation may vary based on factors like body weight - people with higher body mass index (BMI) may need higher doses to see benefits.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.JournalArticle Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsVitamin D supplementation appears to help reduce the severity of atopic dermatitis, particularly in patients with severe cases. Studies show that taking vitamin D along with standard treatments leads to greater improvement in eczema symptoms compared to standard treatment alone.
Summary:Adding vitamin D supplements (1600 IU/day) to standard treatment with hydrocortisone cream helped improve severe eczema symptoms in children more than using hydrocortisone cream alone. Patients taking vitamin D showed about 56% improvement in their eczema severity compared to 42% in those taking placebo.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 86Severity: severeAge: pediatric (not specified)Results:Vitamin D supplementation led to significantly better improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo
Summary:People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Results:Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms
Summary:Vitamin D supplements helped reduce the severity of eczema in children under 14. After 3 months of vitamin D supplementation, patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 152Severity: mild to severeAge: 0-14 yearsResults:Significant improvement in eczema severity after vitamin D supplementation
Pregnant women taking vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy may help reduce their baby's risk of developing eczema in the first year of life, particularly if they breastfeed for more than one month.
Summary:Pregnant women who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy had babies with a 45% lower chance of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This protective effect was stronger in babies who were breastfed for at least 1 month, but the effect became weaker as children got older.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsResults:Significant reduction in eczema at 12 months, effect weakens over time
Summary:Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsResults:
People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to those without the condition. This is especially true in children with atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Children with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to healthy children, especially those with severe eczema. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve eczema symptoms in children.Study Type:Meta-AnalysisStudied Population:Results:Children with AD had significantly lower vitamin D levels than healthy children
Summary:People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Results:Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms
The effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation may vary based on factors like body weight - people with higher body mass index (BMI) may need higher doses to see benefits.
Summary:Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsResults:
-
 Turmeric(Curcumin)If you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyIf you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyTopical dailyLow
Turmeric(Curcumin)If you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyIf you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyTopical dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($2 - $15)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTurmeric can be effective for treating eczema symptoms when applied topically (on the skin) in different forms like micro emulsion, gel, and ointment. Each form works better for different symptoms - micro emulsions help reduce redness and swelling, gels help with itching, and ointments work better for scaling and thickened skin.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 360All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms Turmeric-based treatments performed significantly better than placebo (dummy treatments), suggesting it's a promising natural alternative for eczema treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 360All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms Turmeric can be effective for treating eczema symptoms when applied topically (on the skin) in different forms like micro emulsion, gel, and ointment. Each form works better for different symptoms - micro emulsions help reduce redness and swelling, gels help with itching, and ointments work better for scaling and thickened skin.
Summary:Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 360Results:All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms
Turmeric-based treatments performed significantly better than placebo (dummy treatments), suggesting it's a promising natural alternative for eczema treatment.
Summary:Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 360Results:All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms
-
 Honey(Manuka honey)If you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentIf you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentTopical dailyLow
Honey(Manuka honey)If you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentIf you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentTopical dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($14 - $24)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSHoney appears to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, with clinical studies showing significant improvement in skin severity scores after treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not available80% of patients improved with honey mixture Honey works through multiple mechanisms including reducing inflammation, inhibiting certain bacterial toxins, and preventing mast cells from releasing histamine (which causes itching)Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results When combined with conventional corticosteroid treatments, honey mixtures allowed patients to reduce their steroid dose by 75% while maintaining improvementStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not available80% of patients improved with honey mixture Honey appears to be safe for topical use, with studies showing it can actually increase skin cell growth at certain concentrationsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Honey appears to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, with clinical studies showing significant improvement in skin severity scores after treatment
Summary:A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:80% of patients improved with honey mixture
Honey works through multiple mechanisms including reducing inflammation, inhibiting certain bacterial toxins, and preventing mast cells from releasing histamine (which causes itching)
When combined with conventional corticosteroid treatments, honey mixtures allowed patients to reduce their steroid dose by 75% while maintaining improvement
Summary:A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:80% of patients improved with honey mixture
Honey appears to be safe for topical use, with studies showing it can actually increase skin cell growth at certain concentrations
-
 Zinc(Zinc)If your baby is experiencing a rashTo treat minor skin irritationsTopical dailyLow
Zinc(Zinc)If your baby is experiencing a rashTo treat minor skin irritationsTopical dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($1 - $8)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSZinc levels are often lower in people with atopic dermatitis, and oral zinc supplements may help improve symptoms in patients who have low zinc levels. Improvements were seen in skin condition, itching, and sleep.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Children with atopic dermatitis had lower zinc levels in their hair compared to healthy children. When children with low zinc levels were given zinc supplements, their eczema symptoms, skin barrier function, and itching improved more than those who didn't receive supplements.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 58Zinc supplementation successfully increased hair zinc levels A cream containing zinc oxide along with other ingredients (starch, glycyrretinic acid, and bisabolol) was effective in treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in children, reducing symptoms by 74% after 6 weeks of use. This cream is steroid-free and was well-tolerated.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Not all studies show benefits of oral zinc supplements. One study found no improvement in eczema symptoms when children took zinc sulphate supplements for 8 weeks.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results When combined with a steroid cream (Clobetasol), adding zinc sulphate improved the treatment's effectiveness for hand eczema and reduced the chance of the condition returning after treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A combination cream containing Clobetasol and zinc sulphate was more effective in treating chronic hand eczema compared to Clobetasol alone. The combination treatment also showed lower recurrence rates of eczema after treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 47Combination cream showed significantly better improvement in all measured symptoms and lower recurrence rates compared to Clobetasol alone Zinc levels are often lower in people with atopic dermatitis, and oral zinc supplements may help improve symptoms in patients who have low zinc levels. Improvements were seen in skin condition, itching, and sleep.
Summary:Children with atopic dermatitis had lower zinc levels in their hair compared to healthy children. When children with low zinc levels were given zinc supplements, their eczema symptoms, skin barrier function, and itching improved more than those who didn't receive supplements.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 58Results:Zinc supplementation successfully increased hair zinc levels
A cream containing zinc oxide along with other ingredients (starch, glycyrretinic acid, and bisabolol) was effective in treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in children, reducing symptoms by 74% after 6 weeks of use. This cream is steroid-free and was well-tolerated.
Not all studies show benefits of oral zinc supplements. One study found no improvement in eczema symptoms when children took zinc sulphate supplements for 8 weeks.
When combined with a steroid cream (Clobetasol), adding zinc sulphate improved the treatment's effectiveness for hand eczema and reduced the chance of the condition returning after treatment.
Summary:A combination cream containing Clobetasol and zinc sulphate was more effective in treating chronic hand eczema compared to Clobetasol alone. The combination treatment also showed lower recurrence rates of eczema after treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 47Results:Combination cream showed significantly better improvement in all measured symptoms and lower recurrence rates compared to Clobetasol alone
-
 Omega-6(Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA))As a supplement to medicinal treatmentsAs a supplement to medicinal treatmentsOral dailyLow
Omega-6(Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA))As a supplement to medicinal treatmentsAs a supplement to medicinal treatmentsOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($3 - $9)KEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) for treating eczema shows mixed results. Some studies found it helped reduce symptoms like itching, redness, and oozing, while others found no significant improvement.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery GLA appears to be safe for both adults and children, with no significant side effects reported in multiple studies.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery When used preventively in infants at high risk for eczema, GLA supplementation didn't prevent eczema from developing, but it might help reduce the severity of symptoms when they do occur.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Early supplementation with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) in high-risk infants showed a trend toward reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis, though it didn't prevent the development of allergies. Infants receiving GLA had slightly less severe eczema symptoms compared to those receiving placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 118Severity: not availableAge: 0-12 monthsTrend toward lower disease severity with GLA supplementation (p=0.09) 📄Supplementing infants' diet with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) did not prevent atopic dermatitis. However, in infants who did develop atopic dermatitis, GLA supplementation appeared to reduce levels of IgE (an antibody associated with allergic responses) during their first year.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 131Severity: not availableAge: infants (newborn to 1 year)GLA supplementation did not prevent AD development The effectiveness of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) for treating eczema shows mixed results. Some studies found it helped reduce symptoms like itching, redness, and oozing, while others found no significant improvement.
Summary:Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Results:Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery
GLA appears to be safe for both adults and children, with no significant side effects reported in multiple studies.
Summary:Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Results:Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery
When used preventively in infants at high risk for eczema, GLA supplementation didn't prevent eczema from developing, but it might help reduce the severity of symptoms when they do occur.
Summary:Early supplementation with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) in high-risk infants showed a trend toward reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis, though it didn't prevent the development of allergies. Infants receiving GLA had slightly less severe eczema symptoms compared to those receiving placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 118Severity: not availableAge: 0-12 monthsResults:Trend toward lower disease severity with GLA supplementation (p=0.09)
Summary:Supplementing infants' diet with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) did not prevent atopic dermatitis. However, in infants who did develop atopic dermatitis, GLA supplementation appeared to reduce levels of IgE (an antibody associated with allergic responses) during their first year.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 131Severity: not availableAge: infants (newborn to 1 year)Results:GLA supplementation did not prevent AD development
-
 Omega-3(Polyunsaturated fatty acid)As a supplement to other treatmentsAs a supplement to other treatments, especially during pregnancy and breastfeedingOral dailyLow
Omega-3(Polyunsaturated fatty acid)As a supplement to other treatmentsAs a supplement to other treatments, especially during pregnancy and breastfeedingOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected Eructation 4% Dyspepsia 3% Taste perversion 4% Constipation ($4.50 - $10)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of fish oil supplements for eczema may depend on genetics. In pregnant women with a specific genetic type (TT genotype), taking fish oil during pregnancy reduced their children's risk of developing eczema. However, for women with different genetic types, it either had no effect or could increase the risk.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at whether taking fish oil supplements during pregnancy could prevent eczema in children. The effectiveness depended on the mother's genes - it helped prevent eczema in children whose mothers had a specific genetic type (TT genotype) but increased the risk in mothers with a different genetic type (CC genotype).Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-10 yearsNo overall effect on AD risk when not considering genetic differences When combined with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) and vitamin D, fish oil supplements showed promising results in children with eczema, reducing symptom severity, itching, and the need for steroid creams. It also improved sleep quality and overall quality of life.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Children with eczema who took omega-3 supplements combined with GLA from blackcurrant seed oil showed significant improvement in their symptoms after 4 months. The treatment reduced skin inflammation, itching, and the need for steroid creams by about half.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 52Severity: moderate to severeAge: childrenTaking fish oil supplements during pregnancy and early breastfeeding (up to 6 months after birth) did not show clear benefits in preventing allergic conditions, including eczema, in children up to age 2.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Taking fish oil and/or probiotics during pregnancy and up to 6 months after giving birth did not reduce the risk of atopic eczema or food allergies in children up to 2 years of age. Probiotics alone did reduce the risk of recurring wheezing in 2-year-olds.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 439Severity: not availableAge: 0-2 yearsNo benefit of fish oil and/or probiotics in preventing atopic eczema The effectiveness of fish oil supplements for eczema may depend on genetics. In pregnant women with a specific genetic type (TT genotype), taking fish oil during pregnancy reduced their children's risk of developing eczema. However, for women with different genetic types, it either had no effect or could increase the risk.
Summary:This study looked at whether taking fish oil supplements during pregnancy could prevent eczema in children. The effectiveness depended on the mother's genes - it helped prevent eczema in children whose mothers had a specific genetic type (TT genotype) but increased the risk in mothers with a different genetic type (CC genotype).Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-10 yearsResults:No overall effect on AD risk when not considering genetic differences
When combined with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) and vitamin D, fish oil supplements showed promising results in children with eczema, reducing symptom severity, itching, and the need for steroid creams. It also improved sleep quality and overall quality of life.
Summary:Children with eczema who took omega-3 supplements combined with GLA from blackcurrant seed oil showed significant improvement in their symptoms after 4 months. The treatment reduced skin inflammation, itching, and the need for steroid creams by about half.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 52Severity: moderate to severeAge: childrenResults:
Taking fish oil supplements during pregnancy and early breastfeeding (up to 6 months after birth) did not show clear benefits in preventing allergic conditions, including eczema, in children up to age 2.
Summary:Taking fish oil and/or probiotics during pregnancy and up to 6 months after giving birth did not reduce the risk of atopic eczema or food allergies in children up to 2 years of age. Probiotics alone did reduce the risk of recurring wheezing in 2-year-olds.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 439Severity: not availableAge: 0-2 yearsResults:No benefit of fish oil and/or probiotics in preventing atopic eczema
-
 Olive oil(Olive oil)If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerTopical dailyLow
Olive oil(Olive oil)If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerTopical dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($2 - $8)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSOlive oil, when combined with honey and beeswax in equal parts, can help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis. In one study, 80% of patients showed significant improvement after 2 weeks of use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableThe honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis Virgin olive oil can help moisturize dry skin in atopic dermatitis patients, though it may not be as effective as some other natural oils like coconut oil.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement When used alongside prescription steroid medications, a mixture containing olive oil allowed patients to reduce their steroid use by 75% while maintaining skin improvement.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableThe honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis While olive oil has some antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus aureus (a bacteria commonly found on eczema skin), studies suggest it may be less effective than alternatives like coconut oil for this purpose.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement Olive oil, when combined with honey and beeswax in equal parts, can help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis. In one study, 80% of patients showed significant improvement after 2 weeks of use.
Summary:A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:The honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis
Virgin olive oil can help moisturize dry skin in atopic dermatitis patients, though it may not be as effective as some other natural oils like coconut oil.
Summary:Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement
When used alongside prescription steroid medications, a mixture containing olive oil allowed patients to reduce their steroid use by 75% while maintaining skin improvement.
Summary:A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:The honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis
While olive oil has some antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus aureus (a bacteria commonly found on eczema skin), studies suggest it may be less effective than alternatives like coconut oil for this purpose.
Summary:Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement
-
 Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)Who is this for?:As an add-on alongside other therapiesAs an add-on alongside other therapiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy Vitamin B12No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTopical Vitamin B12 cream appears to be more effective than standard moisturizing creams for treating mild eczema, with studies showing a 78% improvement in symptoms compared to 33.5% with regular creams
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)Who is this for?:As an add-on alongside other therapiesAs an add-on alongside other therapiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy Vitamin B12No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTopical Vitamin B12 cream appears to be more effective than standard moisturizing creams for treating mild eczema, with studies showing a 78% improvement in symptoms compared to 33.5% with regular creamsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A vitamin B12 cream was compared to a standard moisturizing cream for treating mild eczema. The vitamin B12 cream reduced eczema severity by 77.6% compared to 33.5% with the standard cream after 12 weeks of use.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 22Severity: mildAge: not availableVitamin B12 cream was more than twice as effective as standard moisturizer in reducing eczema severity There may be a connection between Vitamin B12 blood levels and eczema severity - lower Vitamin B12 levels might be associated with worse eczema symptoms. Oral Vitamin B12 supplements might help improve severe eczema that's difficult to controlStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements Vitamin B12 has anti-inflammatory properties and can help regulate the immune system, which may explain why it helps with eczema symptomsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements Topical Vitamin B12 cream appears to be more effective than standard moisturizing creams for treating mild eczema, with studies showing a 78% improvement in symptoms compared to 33.5% with regular creams
Summary:A vitamin B12 cream was compared to a standard moisturizing cream for treating mild eczema. The vitamin B12 cream reduced eczema severity by 77.6% compared to 33.5% with the standard cream after 12 weeks of use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 22Severity: mildAge: not availableResults:Vitamin B12 cream was more than twice as effective as standard moisturizer in reducing eczema severity
There may be a connection between Vitamin B12 blood levels and eczema severity - lower Vitamin B12 levels might be associated with worse eczema symptoms. Oral Vitamin B12 supplements might help improve severe eczema that's difficult to control
Summary:In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Results:Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements
Vitamin B12 has anti-inflammatory properties and can help regulate the immune system, which may explain why it helps with eczema symptoms
Summary:In a case study of one patient with severe eczema, researchers found that low vitamin B12 levels were associated with worse eczema symptoms. When the patient took vitamin B12 supplements, their eczema improved significantly.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 18Results:Patient showed meaningful improvement in eczema severity score when taking vitamin B12 supplements
-
 Coconut Oil (Virgin Coconut Oil)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer for your child that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical as needed dailySee EvidenceBuy Coconut OilNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSCoconut oil, when formulated with other ingredients (specifically isosorbide diesters), can significantly improve itching in people with mild-to-moderate eczema, showing about 66% improvement in itch symptoms
Coconut Oil (Virgin Coconut Oil)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizer for your child that may help reduce inflammation and bacterial colonizationEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical as needed dailySee EvidenceBuy Coconut OilNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSCoconut oil, when formulated with other ingredients (specifically isosorbide diesters), can significantly improve itching in people with mild-to-moderate eczema, showing about 66% improvement in itch symptomsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013) When used in a specialized formulation, coconut oil derivatives can help reduce the need for topical steroids in eczema treatment, particularly in the early weeks of treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013) Coconut oil-based treatments may help reduce harmful bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin of eczema patientsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013) Coconut oil is one of the most commonly used traditional home remedies for eczema treatment, particularly in Indian householdsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a study of 150 children in India, coconut oil was the most commonly used home remedy for treating eczema/atopic dermatitis, followed by olive oil and mustard oil. The study looked at various home remedies parents used before visiting a doctor.Observational Study Total Patients: 150Coconut oil, when formulated with other ingredients (specifically isosorbide diesters), can significantly improve itching in people with mild-to-moderate eczema, showing about 66% improvement in itch symptoms
Summary:A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013)
When used in a specialized formulation, coconut oil derivatives can help reduce the need for topical steroids in eczema treatment, particularly in the early weeks of treatment
Summary:A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013)
Coconut oil-based treatments may help reduce harmful bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin of eczema patients
Summary:A cream containing coconut and sunflower seed oil derivatives improved itch by 65.6% compared to 43.8% with the control cream in people with mild-to-moderate eczema. The treatment also reduced the need for steroid creams and decreased harmful bacteria on the skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: mild to moderateAge: 18+Results:Significantly better itch relief in treatment group (p=0.013)
Coconut oil is one of the most commonly used traditional home remedies for eczema treatment, particularly in Indian households
Summary:In a study of 150 children in India, coconut oil was the most commonly used home remedy for treating eczema/atopic dermatitis, followed by olive oil and mustard oil. The study looked at various home remedies parents used before visiting a doctor.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 150Results:
-
 Probiotics (Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium)Who is this for?:As a complementary treatment alongside standard therapiesAs a complementary treatment for children with moderate atopic dermatitisEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy ProbioticsNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSProbiotics appear to be effective in reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis symptoms, with multiple studies showing significant improvements in SCORAD scores (a measure of eczema severity) compared to placebo
Probiotics (Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium)Who is this for?:As a complementary treatment alongside standard therapiesAs a complementary treatment for children with moderate atopic dermatitisEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy ProbioticsNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSProbiotics appear to be effective in reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis symptoms, with multiple studies showing significant improvements in SCORAD scores (a measure of eczema severity) compared to placeboStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsSignificant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment 📄An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Observational Study Total Patients: 320Significant improvement in eczema severity 📄A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsPatients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo Probiotics may help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis, potentially allowing for less steroid useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of probiotics taken by mouth significantly improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate atopic dermatitis. Children taking probiotics needed less topical steroids to manage their condition, with an 83% improvement in symptoms compared to 24% in the placebo group.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 50Severity: moderateAge: 4-17 yearsProbiotics led to a significantly greater improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo 📄A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsPatients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo Probiotics appear to be safe with very few reported side effects. Most studies reported similar adverse event rates between probiotic and placebo groupsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsSignificant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment 📄An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Observational Study Total Patients: 320Significant improvement in eczema severity Multi-strain probiotic combinations may be more effective than single strains, and treatment duration of 8-12 weeks appears to be optimal for seeing benefitsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Observational Study Total Patients: 320Significant improvement in eczema severity 📄Taking specific probiotics and prebiotics for 12 weeks helped improve mild eczema symptoms, including itching and skin lesions. The study suggests that these supplements might help maintain stable eczema and reduce flare-ups.Observational Study Total Patients: 144Severity: mildAge: not specified (mean age 25.1 ± 17.6 years)All measures of eczema severity showed significant improvement after 12 weeks of probiotic treatment Probiotics appear to be effective in reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis symptoms, with multiple studies showing significant improvements in SCORAD scores (a measure of eczema severity) compared to placebo
Summary:The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsResults:Significant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment
Summary:An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 320Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Summary:A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsResults:Patients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo
Probiotics may help reduce the need for topical corticosteroids in treating atopic dermatitis, potentially allowing for less steroid use
Summary:A mixture of probiotics taken by mouth significantly improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate atopic dermatitis. Children taking probiotics needed less topical steroids to manage their condition, with an 83% improvement in symptoms compared to 24% in the placebo group.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderateAge: 4-17 yearsResults:Probiotics led to a significantly greater improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo
Summary:A probiotic mixture helped improve eczema symptoms in children and teenagers after 12 weeks of treatment. Patients taking probiotics needed less topical steroids between weeks 6-12 of treatment compared to those taking placebo.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 61Severity: not availableAge: 4-17 yearsResults:Patients taking probiotics had significantly better SCORAD scores compared to placebo
Probiotics appear to be safe with very few reported side effects. Most studies reported similar adverse event rates between probiotic and placebo groups
Summary:The probiotic LGG helped improve eczema symptoms in young children when taken daily for 12 weeks. Children who took the probiotic needed less rescue medication and had better quality of life. The benefits were linked to positive changes in both gut and skin bacteria.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: not availableAge: 6-36 monthsResults:Significant improvement in eczema severity that was maintained after treatment
Summary:An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 320Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Multi-strain probiotic combinations may be more effective than single strains, and treatment duration of 8-12 weeks appears to be optimal for seeing benefits
Summary:An 8-week treatment with probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics improved eczema symptoms in children. The severity of eczema decreased significantly, with the percentage of children having moderate-severe disease dropping from 92.4% to 28.1%.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 320Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Taking specific probiotics and prebiotics for 12 weeks helped improve mild eczema symptoms, including itching and skin lesions. The study suggests that these supplements might help maintain stable eczema and reduce flare-ups.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 144Severity: mildAge: not specified (mean age 25.1 ± 17.6 years)Results:All measures of eczema severity showed significant improvement after 12 weeks of probiotic treatment
-
 Shea butter (Shea butter)Who is this for?:If you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerIf you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical 1-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Shea butterNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSShea butter-containing cream was well-received by most patients, with 74% of users rating it as 'very good' or 'good'
Shea butter (Shea butter)Who is this for?:If you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerIf you have mild to moderate atopic dermatitis with dry, irritated skin and are looking for a natural moisturizerEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical 1-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Shea butterNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSShea butter-containing cream was well-received by most patients, with 74% of users rating it as 'very good' or 'good'Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Review Total Patients: 34Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable Patients who liked the shea butter cream experienced less itching and better quality of life after using it. Their itching scores improved from 6.7 to 6.0Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Review Total Patients: 34Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable The shea butter cream worked just as well as other moisturizers containing ceramides (another type of skin-protecting ingredient), suggesting it's an effective alternativeStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Review Total Patients: 34Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable Shea butter-containing cream was well-received by most patients, with 74% of users rating it as 'very good' or 'good'
Summary:A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Total Patients: 34Results:Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable
Patients who liked the shea butter cream experienced less itching and better quality of life after using it. Their itching scores improved from 6.7 to 6.0
Summary:A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Total Patients: 34Results:Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable
The shea butter cream worked just as well as other moisturizers containing ceramides (another type of skin-protecting ingredient), suggesting it's an effective alternative
Summary:A cream containing shea butter was found to be acceptable by 74% of patients with atopic dermatitis. In patients who liked the cream, it reduced itching and improved quality of life. The shea butter cream worked similarly to another cream containing ceramides.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Total Patients: 34Results:Three quarters of patients found the products acceptable
-
 Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)Who is this for?:If your symptoms get worse during winter or you have confirmed low Vitamin D levelsIf your child's symptoms get worse during winter or your child has confirmed low Vitamin D levelsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral 1000-4000 IU dailySee EvidenceBuy Vitamin D3No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSVitamin D supplementation appears to help reduce the severity of atopic dermatitis, particularly in patients with severe cases. Studies show that taking vitamin D along with standard treatments leads to greater improvement in eczema symptoms compared to standard treatment alone.
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)Who is this for?:If your symptoms get worse during winter or you have confirmed low Vitamin D levelsIf your child's symptoms get worse during winter or your child has confirmed low Vitamin D levelsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral 1000-4000 IU dailySee EvidenceBuy Vitamin D3No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSVitamin D supplementation appears to help reduce the severity of atopic dermatitis, particularly in patients with severe cases. Studies show that taking vitamin D along with standard treatments leads to greater improvement in eczema symptoms compared to standard treatment alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding vitamin D supplements (1600 IU/day) to standard treatment with hydrocortisone cream helped improve severe eczema symptoms in children more than using hydrocortisone cream alone. Patients taking vitamin D showed about 56% improvement in their eczema severity compared to 42% in those taking placebo.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 86Severity: severeAge: pediatric (not specified)Vitamin D supplementation led to significantly better improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo 📄People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Review Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms 📄Vitamin D supplements helped reduce the severity of eczema in children under 14. After 3 months of vitamin D supplementation, patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms.Observational Study Total Patients: 152Severity: mild to severeAge: 0-14 yearsSignificant improvement in eczema severity after vitamin D supplementation Pregnant women taking vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy may help reduce their baby's risk of developing eczema in the first year of life, particularly if they breastfeed for more than one month.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Pregnant women who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy had babies with a 45% lower chance of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This protective effect was stronger in babies who were breastfed for at least 1 month, but the effect became weaker as children got older.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsSignificant reduction in eczema at 12 months, effect weakens over time 📄Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.JournalArticle Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsPeople with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to those without the condition. This is especially true in children with atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Children with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to healthy children, especially those with severe eczema. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve eczema symptoms in children.Meta-Analysis Children with AD had significantly lower vitamin D levels than healthy children 📄People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Review Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms The effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation may vary based on factors like body weight - people with higher body mass index (BMI) may need higher doses to see benefits.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.JournalArticle Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsVitamin D supplementation appears to help reduce the severity of atopic dermatitis, particularly in patients with severe cases. Studies show that taking vitamin D along with standard treatments leads to greater improvement in eczema symptoms compared to standard treatment alone.
Summary:Adding vitamin D supplements (1600 IU/day) to standard treatment with hydrocortisone cream helped improve severe eczema symptoms in children more than using hydrocortisone cream alone. Patients taking vitamin D showed about 56% improvement in their eczema severity compared to 42% in those taking placebo.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 86Severity: severeAge: pediatric (not specified)Results:Vitamin D supplementation led to significantly better improvement in eczema severity compared to placebo
Summary:People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Results:Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms
Summary:Vitamin D supplements helped reduce the severity of eczema in children under 14. After 3 months of vitamin D supplementation, patients showed significant improvement in their eczema symptoms.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 152Severity: mild to severeAge: 0-14 yearsResults:Significant improvement in eczema severity after vitamin D supplementation
Pregnant women taking vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy may help reduce their baby's risk of developing eczema in the first year of life, particularly if they breastfeed for more than one month.
Summary:Pregnant women who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) during pregnancy had babies with a 45% lower chance of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This protective effect was stronger in babies who were breastfed for at least 1 month, but the effect became weaker as children got older.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsResults:Significant reduction in eczema at 12 months, effect weakens over time
Summary:Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsResults:
People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to those without the condition. This is especially true in children with atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Children with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to healthy children, especially those with severe eczema. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve eczema symptoms in children.Study Type:Meta-AnalysisStudied Population:Results:Children with AD had significantly lower vitamin D levels than healthy children
Summary:People with atopic dermatitis tend to have lower vitamin D levels compared to people without the condition. Taking vitamin D supplements appears to help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Results:Vitamin D supplementation improved atopic dermatitis symptoms
The effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation may vary based on factors like body weight - people with higher body mass index (BMI) may need higher doses to see benefits.
Summary:Pregnant mothers who took vitamin D supplements (1000 IU daily) had babies with lower risk of developing eczema at 12 months of age. This effect was stronger in mothers with normal or slightly overweight BMI, but didn't work as well in mothers with obesity.Study Type:JournalArticleStudied Population:Total Patients: 636Severity: not availableAge: 0-48 monthsResults:
-
 Turmeric (Curcumin)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyIf you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy TurmericNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTurmeric can be effective for treating eczema symptoms when applied topically (on the skin) in different forms like micro emulsion, gel, and ointment. Each form works better for different symptoms - micro emulsions help reduce redness and swelling, gels help with itching, and ointments work better for scaling and thickened skin.
Turmeric (Curcumin)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyIf you are looking for a natural, anti-inflammatory remedyEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy TurmericNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTurmeric can be effective for treating eczema symptoms when applied topically (on the skin) in different forms like micro emulsion, gel, and ointment. Each form works better for different symptoms - micro emulsions help reduce redness and swelling, gels help with itching, and ointments work better for scaling and thickened skin.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 360All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms Turmeric-based treatments performed significantly better than placebo (dummy treatments), suggesting it's a promising natural alternative for eczema treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 360All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms Turmeric can be effective for treating eczema symptoms when applied topically (on the skin) in different forms like micro emulsion, gel, and ointment. Each form works better for different symptoms - micro emulsions help reduce redness and swelling, gels help with itching, and ointments work better for scaling and thickened skin.
Summary:Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 360Results:All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms
Turmeric-based treatments performed significantly better than placebo (dummy treatments), suggesting it's a promising natural alternative for eczema treatment.
Summary:Different formulations (micro emulsion, gel, and ointment) containing turmeric and other herbs were tested in eczema patients. The micro emulsion was best for reducing redness and swelling, the gel was best for itching, and the ointment was most effective for scaling and thickened skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 360Results:All formulations showed significant improvement compared to placebo for various symptoms
-
 Honey (Manuka honey)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentIf you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy HoneyNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSHoney appears to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, with clinical studies showing significant improvement in skin severity scores after treatment
Honey (Manuka honey)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentIf you are looking for a natural add-on treatmentEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy HoneyNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSHoney appears to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, with clinical studies showing significant improvement in skin severity scores after treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not available80% of patients improved with honey mixture Honey works through multiple mechanisms including reducing inflammation, inhibiting certain bacterial toxins, and preventing mast cells from releasing histamine (which causes itching)Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results When combined with conventional corticosteroid treatments, honey mixtures allowed patients to reduce their steroid dose by 75% while maintaining improvementStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not available80% of patients improved with honey mixture Honey appears to be safe for topical use, with studies showing it can actually increase skin cell growth at certain concentrationsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Honey appears to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, with clinical studies showing significant improvement in skin severity scores after treatment
Summary:A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:80% of patients improved with honey mixture
Honey works through multiple mechanisms including reducing inflammation, inhibiting certain bacterial toxins, and preventing mast cells from releasing histamine (which causes itching)
When combined with conventional corticosteroid treatments, honey mixtures allowed patients to reduce their steroid dose by 75% while maintaining improvement
Summary:A mixture of honey, beeswax, and olive oil helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:80% of patients improved with honey mixture
Honey appears to be safe for topical use, with studies showing it can actually increase skin cell growth at certain concentrations
-
 Zinc (Zinc)Who is this for?:To treat minor skin irritationsIf your baby is experiencing a rashEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical 1-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy ZincNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSZinc levels are often lower in people with atopic dermatitis, and oral zinc supplements may help improve symptoms in patients who have low zinc levels. Improvements were seen in skin condition, itching, and sleep.
Zinc (Zinc)Who is this for?:To treat minor skin irritationsIf your baby is experiencing a rashEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical 1-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy ZincNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSZinc levels are often lower in people with atopic dermatitis, and oral zinc supplements may help improve symptoms in patients who have low zinc levels. Improvements were seen in skin condition, itching, and sleep.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Children with atopic dermatitis had lower zinc levels in their hair compared to healthy children. When children with low zinc levels were given zinc supplements, their eczema symptoms, skin barrier function, and itching improved more than those who didn't receive supplements.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 58Zinc supplementation successfully increased hair zinc levels A cream containing zinc oxide along with other ingredients (starch, glycyrretinic acid, and bisabolol) was effective in treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in children, reducing symptoms by 74% after 6 weeks of use. This cream is steroid-free and was well-tolerated.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Not all studies show benefits of oral zinc supplements. One study found no improvement in eczema symptoms when children took zinc sulphate supplements for 8 weeks.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results When combined with a steroid cream (Clobetasol), adding zinc sulphate improved the treatment's effectiveness for hand eczema and reduced the chance of the condition returning after treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A combination cream containing Clobetasol and zinc sulphate was more effective in treating chronic hand eczema compared to Clobetasol alone. The combination treatment also showed lower recurrence rates of eczema after treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 47Combination cream showed significantly better improvement in all measured symptoms and lower recurrence rates compared to Clobetasol alone Zinc levels are often lower in people with atopic dermatitis, and oral zinc supplements may help improve symptoms in patients who have low zinc levels. Improvements were seen in skin condition, itching, and sleep.
Summary:Children with atopic dermatitis had lower zinc levels in their hair compared to healthy children. When children with low zinc levels were given zinc supplements, their eczema symptoms, skin barrier function, and itching improved more than those who didn't receive supplements.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 58Results:Zinc supplementation successfully increased hair zinc levels
A cream containing zinc oxide along with other ingredients (starch, glycyrretinic acid, and bisabolol) was effective in treating mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in children, reducing symptoms by 74% after 6 weeks of use. This cream is steroid-free and was well-tolerated.
Not all studies show benefits of oral zinc supplements. One study found no improvement in eczema symptoms when children took zinc sulphate supplements for 8 weeks.
When combined with a steroid cream (Clobetasol), adding zinc sulphate improved the treatment's effectiveness for hand eczema and reduced the chance of the condition returning after treatment.
Summary:A combination cream containing Clobetasol and zinc sulphate was more effective in treating chronic hand eczema compared to Clobetasol alone. The combination treatment also showed lower recurrence rates of eczema after treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 47Results:Combination cream showed significantly better improvement in all measured symptoms and lower recurrence rates compared to Clobetasol alone
-
 Omega-6 (Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA))Who is this for?:As a supplement to medicinal treatmentsAs a supplement to medicinal treatmentsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) for treating eczema shows mixed results. Some studies found it helped reduce symptoms like itching, redness, and oozing, while others found no significant improvement.
Omega-6 (Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA))Who is this for?:As a supplement to medicinal treatmentsAs a supplement to medicinal treatmentsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) for treating eczema shows mixed results. Some studies found it helped reduce symptoms like itching, redness, and oozing, while others found no significant improvement.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery GLA appears to be safe for both adults and children, with no significant side effects reported in multiple studies.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery When used preventively in infants at high risk for eczema, GLA supplementation didn't prevent eczema from developing, but it might help reduce the severity of symptoms when they do occur.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Early supplementation with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) in high-risk infants showed a trend toward reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis, though it didn't prevent the development of allergies. Infants receiving GLA had slightly less severe eczema symptoms compared to those receiving placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 118Severity: not availableAge: 0-12 monthsTrend toward lower disease severity with GLA supplementation (p=0.09) 📄Supplementing infants' diet with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) did not prevent atopic dermatitis. However, in infants who did develop atopic dermatitis, GLA supplementation appeared to reduce levels of IgE (an antibody associated with allergic responses) during their first year.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 131Severity: not availableAge: infants (newborn to 1 year)GLA supplementation did not prevent AD development The effectiveness of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) for treating eczema shows mixed results. Some studies found it helped reduce symptoms like itching, redness, and oozing, while others found no significant improvement.
Summary:Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Results:Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery
GLA appears to be safe for both adults and children, with no significant side effects reported in multiple studies.
Summary:Gamma-linolenic acid treatment showed some improvement in itch symptoms and reduced the need for antihistamines in infants with atopic dermatitis. While none of the children showed complete recovery, the treatment was found to be safe with no side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: infants (mean age 11.4 months)Results:Partial improvement in skin symptoms but no complete recovery
When used preventively in infants at high risk for eczema, GLA supplementation didn't prevent eczema from developing, but it might help reduce the severity of symptoms when they do occur.
Summary:Early supplementation with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) in high-risk infants showed a trend toward reducing the severity of atopic dermatitis, though it didn't prevent the development of allergies. Infants receiving GLA had slightly less severe eczema symptoms compared to those receiving placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 118Severity: not availableAge: 0-12 monthsResults:Trend toward lower disease severity with GLA supplementation (p=0.09)
Summary:Supplementing infants' diet with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) did not prevent atopic dermatitis. However, in infants who did develop atopic dermatitis, GLA supplementation appeared to reduce levels of IgE (an antibody associated with allergic responses) during their first year.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 131Severity: not availableAge: infants (newborn to 1 year)Results:GLA supplementation did not prevent AD development
-
 Omega-3 (Polyunsaturated fatty acid)Who is this for?:As a supplement to other treatments, especially during pregnancy and breastfeedingAs a supplement to other treatmentsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral None dailySee EvidenceBuy Omega-3No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of fish oil supplements for eczema may depend on genetics. In pregnant women with a specific genetic type (TT genotype), taking fish oil during pregnancy reduced their children's risk of developing eczema. However, for women with different genetic types, it either had no effect or could increase the risk.
Omega-3 (Polyunsaturated fatty acid)Who is this for?:As a supplement to other treatments, especially during pregnancy and breastfeedingAs a supplement to other treatmentsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral None dailySee EvidenceBuy Omega-3No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of fish oil supplements for eczema may depend on genetics. In pregnant women with a specific genetic type (TT genotype), taking fish oil during pregnancy reduced their children's risk of developing eczema. However, for women with different genetic types, it either had no effect or could increase the risk.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at whether taking fish oil supplements during pregnancy could prevent eczema in children. The effectiveness depended on the mother's genes - it helped prevent eczema in children whose mothers had a specific genetic type (TT genotype) but increased the risk in mothers with a different genetic type (CC genotype).Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-10 yearsNo overall effect on AD risk when not considering genetic differences When combined with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) and vitamin D, fish oil supplements showed promising results in children with eczema, reducing symptom severity, itching, and the need for steroid creams. It also improved sleep quality and overall quality of life.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Children with eczema who took omega-3 supplements combined with GLA from blackcurrant seed oil showed significant improvement in their symptoms after 4 months. The treatment reduced skin inflammation, itching, and the need for steroid creams by about half.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 52Severity: moderate to severeAge: childrenTaking fish oil supplements during pregnancy and early breastfeeding (up to 6 months after birth) did not show clear benefits in preventing allergic conditions, including eczema, in children up to age 2.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Taking fish oil and/or probiotics during pregnancy and up to 6 months after giving birth did not reduce the risk of atopic eczema or food allergies in children up to 2 years of age. Probiotics alone did reduce the risk of recurring wheezing in 2-year-olds.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 439Severity: not availableAge: 0-2 yearsNo benefit of fish oil and/or probiotics in preventing atopic eczema The effectiveness of fish oil supplements for eczema may depend on genetics. In pregnant women with a specific genetic type (TT genotype), taking fish oil during pregnancy reduced their children's risk of developing eczema. However, for women with different genetic types, it either had no effect or could increase the risk.
Summary:This study looked at whether taking fish oil supplements during pregnancy could prevent eczema in children. The effectiveness depended on the mother's genes - it helped prevent eczema in children whose mothers had a specific genetic type (TT genotype) but increased the risk in mothers with a different genetic type (CC genotype).Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 635Severity: not availableAge: 0-10 yearsResults:No overall effect on AD risk when not considering genetic differences
When combined with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) and vitamin D, fish oil supplements showed promising results in children with eczema, reducing symptom severity, itching, and the need for steroid creams. It also improved sleep quality and overall quality of life.
Summary:Children with eczema who took omega-3 supplements combined with GLA from blackcurrant seed oil showed significant improvement in their symptoms after 4 months. The treatment reduced skin inflammation, itching, and the need for steroid creams by about half.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 52Severity: moderate to severeAge: childrenResults:
Taking fish oil supplements during pregnancy and early breastfeeding (up to 6 months after birth) did not show clear benefits in preventing allergic conditions, including eczema, in children up to age 2.
Summary:Taking fish oil and/or probiotics during pregnancy and up to 6 months after giving birth did not reduce the risk of atopic eczema or food allergies in children up to 2 years of age. Probiotics alone did reduce the risk of recurring wheezing in 2-year-olds.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 439Severity: not availableAge: 0-2 yearsResults:No benefit of fish oil and/or probiotics in preventing atopic eczema
-
 Olive oil (Olive oil)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy Olive oilNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSOlive oil, when combined with honey and beeswax in equal parts, can help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis. In one study, 80% of patients showed significant improvement after 2 weeks of use.
Olive oil (Olive oil)Who is this for?:If you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerIf you are looking for a gentle and natural moisturizerEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy Olive oilNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSOlive oil, when combined with honey and beeswax in equal parts, can help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis. In one study, 80% of patients showed significant improvement after 2 weeks of use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableThe honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis Virgin olive oil can help moisturize dry skin in atopic dermatitis patients, though it may not be as effective as some other natural oils like coconut oil.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement When used alongside prescription steroid medications, a mixture containing olive oil allowed patients to reduce their steroid use by 75% while maintaining skin improvement.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableThe honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis While olive oil has some antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus aureus (a bacteria commonly found on eczema skin), studies suggest it may be less effective than alternatives like coconut oil for this purpose.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement Olive oil, when combined with honey and beeswax in equal parts, can help improve symptoms of atopic dermatitis. In one study, 80% of patients showed significant improvement after 2 weeks of use.
Summary:A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:The honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis
Virgin olive oil can help moisturize dry skin in atopic dermatitis patients, though it may not be as effective as some other natural oils like coconut oil.
Summary:Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement
When used alongside prescription steroid medications, a mixture containing olive oil allowed patients to reduce their steroid use by 75% while maintaining skin improvement.
Summary:A mixture of honey, olive oil, and beeswax helped improve symptoms in 8 out of 10 patients with atopic dermatitis after 2 weeks. The mixture also allowed some patients to reduce their steroid medication use by 75% without their condition getting worse.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:The honey-olive oil-beeswax mixture showed effectiveness in treating atopic dermatitis
While olive oil has some antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus aureus (a bacteria commonly found on eczema skin), studies suggest it may be less effective than alternatives like coconut oil for this purpose.
Summary:Virgin olive oil helped moisturize dry skin and reduce severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. However, it was less effective than coconut oil at removing bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) from the skin, with 50% of olive oil users still having bacteria after treatment compared to 5% in the coconut oil group.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 52Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Both oils reduced disease severity, but coconut oil showed greater improvement
Steroids
-
 Halobetasol(Halobetasol propionate)If you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidIf you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidTopical dailyMedium
Halobetasol(Halobetasol propionate)If you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidIf you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Application site reactions 3% Skin dryness Itching at application site $40/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSHalobetasol is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates between 88-94% across multiple studies. Most patients see significant improvement or complete healing of their eczema.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedAll three treatments showed similar high success rates 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate The medication works quickly, with many patients seeing improvements within the first 3 days of treatment. This fast action makes it particularly useful for quick relief of symptoms.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate 📄Halobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment was significantly more effective than vehicle (placebo) in treating eczema. After 2 weeks of treatment, 83% of patients using halobetasol showed complete or marked improvement compared to 28% using vehicle. The medication was well-tolerated with no skin thinning reported.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 224Halobetasol was significantly more effective than vehicle in treating chronic eczema Halobetasol is generally safe and well-tolerated. Side effects are uncommon (occurring in only 2-5% of patients) and usually mild, mainly including skin dryness, itching, or burning sensations at the application site.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedAll three treatments showed similar high success rates 📄Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The cream improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 111Severity: ChronicAge: Not specifiedSignificant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle (p<0.001) The medication is available in both cream and ointment forms, and can be effective in both adults and children. In pediatric patients, it showed excellent results with 100% success rate for eczema treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedAll three treatments showed similar high success rates Halobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates (defined as 'healed' or 'marked improvement') ranging from 88% to 94% in various studies. It starts working quickly, with many patients seeing improvement within 3 days of starting treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableAll three treatments showed similar high effectiveness 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate The medication is generally well-tolerated with a low rate of side effects (2-5% of patients). The most common side effects are skin dryness, itching, or burning at the application site.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableAll three treatments showed similar high effectiveness 📄Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The medication improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 111Significant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle by day 7 and day 14 (p<0.001) In children with severe eczema, the combination of halobetasol propionate cream during the day and ointment at night was extremely effective, with a 100% success rate. However, careful monitoring is needed as one case of mild skin thinning was reported.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results The medication performs as well as or better than other strong topical steroids like clobetasol propionate and betamethasone dipropionate, making it a reliable option for treating severe eczema.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableAll three treatments showed similar high effectiveness 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate Halobetasol is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates between 88-94% across multiple studies. Most patients see significant improvement or complete healing of their eczema.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedResults:All three treatments showed similar high success rates
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
The medication works quickly, with many patients seeing improvements within the first 3 days of treatment. This fast action makes it particularly useful for quick relief of symptoms.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
Summary:Halobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment was significantly more effective than vehicle (placebo) in treating eczema. After 2 weeks of treatment, 83% of patients using halobetasol showed complete or marked improvement compared to 28% using vehicle. The medication was well-tolerated with no skin thinning reported.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 224Results:Halobetasol was significantly more effective than vehicle in treating chronic eczema
Halobetasol is generally safe and well-tolerated. Side effects are uncommon (occurring in only 2-5% of patients) and usually mild, mainly including skin dryness, itching, or burning sensations at the application site.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedResults:All three treatments showed similar high success rates
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The cream improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 111Severity: ChronicAge: Not specifiedResults:Significant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle (p<0.001)
The medication is available in both cream and ointment forms, and can be effective in both adults and children. In pediatric patients, it showed excellent results with 100% success rate for eczema treatment.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedResults:All three treatments showed similar high success rates
Halobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates (defined as 'healed' or 'marked improvement') ranging from 88% to 94% in various studies. It starts working quickly, with many patients seeing improvement within 3 days of starting treatment.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableResults:All three treatments showed similar high effectiveness
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
The medication is generally well-tolerated with a low rate of side effects (2-5% of patients). The most common side effects are skin dryness, itching, or burning at the application site.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableResults:All three treatments showed similar high effectiveness
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The medication improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 111Results:Significant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle by day 7 and day 14 (p<0.001)
In children with severe eczema, the combination of halobetasol propionate cream during the day and ointment at night was extremely effective, with a 100% success rate. However, careful monitoring is needed as one case of mild skin thinning was reported.
The medication performs as well as or better than other strong topical steroids like clobetasol propionate and betamethasone dipropionate, making it a reliable option for treating severe eczema.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableResults:All three treatments showed similar high effectiveness
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
-
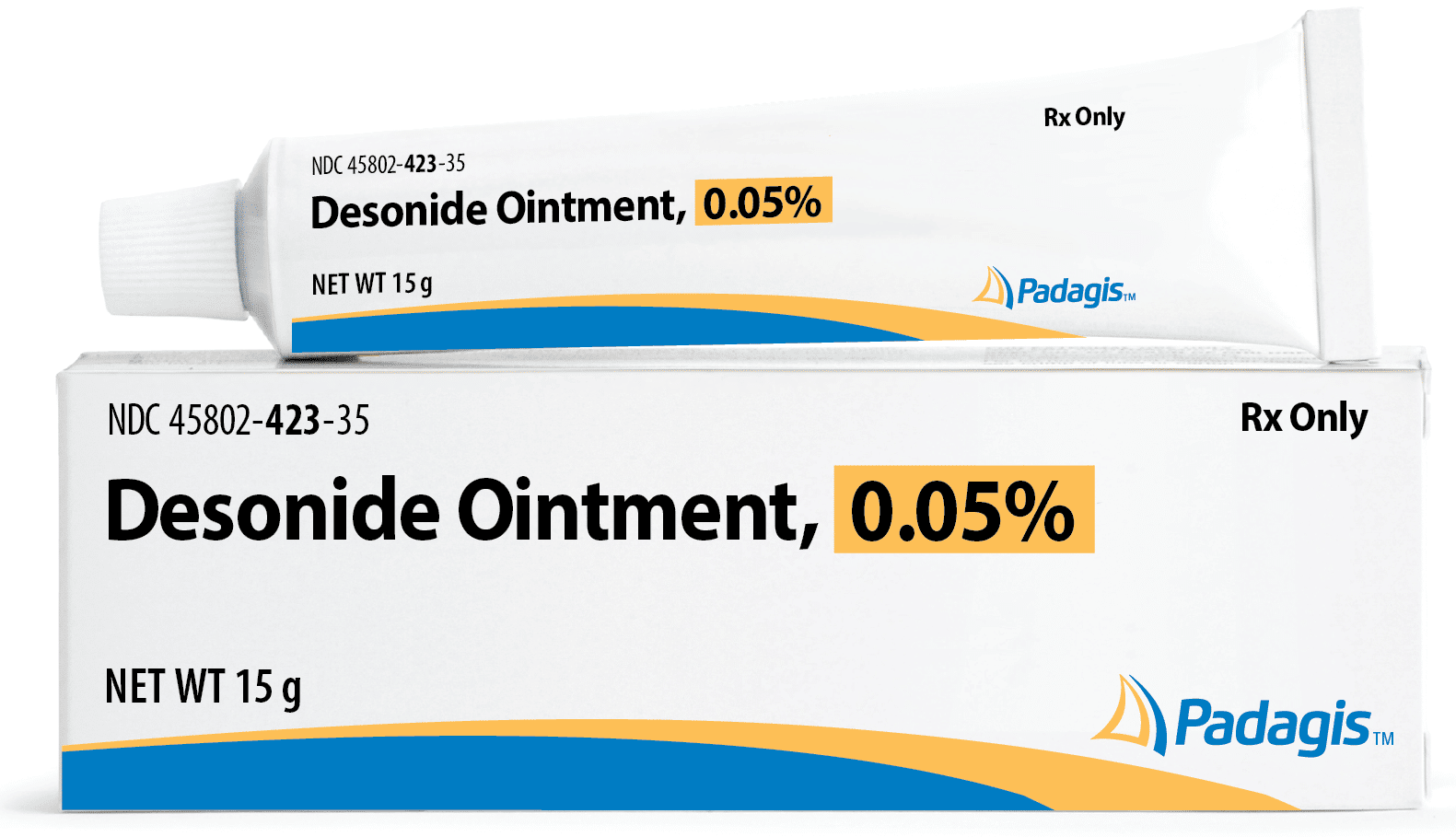 Desonide(Desonide)If you need a low-potency steroid treatmentIf you need a low-potency steroid treatmentTopical dailyLow
Desonide(Desonide)If you need a low-potency steroid treatmentIf you need a low-potency steroid treatmentTopical dailyLowSide Effect Affected Cortisol suppression $35/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSDesonide is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvements in symptoms like itching and inflammation. When combined with moisturizers, it shows even better results with up to 100% effectiveness compared to 60% with desonide alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Desonide is particularly safe for children, including infants. Studies show it rarely affects the body's natural hormone (cortisol) production, making it safer than stronger steroids like betamethasone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both desonide 0.05% ointment and hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment were found to be safe for children with atopic dermatitis when used for 4 weeks. Neither medication affected the body's natural cortisol production system.Clinical Trial Both medications were safe for use in children and did not affect their natural cortisol production system 📄Desonide hydrogel 0.05%, a low-potency steroid, was found to be safe and effective in treating children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The treatment showed good results in improving symptoms while having minimal impact on the body's hormone system.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-6 yearsTreatment was generally safe with minimal impact on the body's hormone system 📄Both desonide cream 0.1% and betamethasone cream were equally effective in treating childhood atopic dermatitis. However, desonide had less impact on the body's cortisol levels, making it potentially safer for children.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 29Severity: Not specifiedAge: mean 13.8 monthsBoth treatments showed similar clinical effectiveness The hydrogel form of desonide helps improve skin moisture and barrier function, with significant improvements seen in as little as 1-2 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Desonide hydrogel 0.05% was found to be safe and effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children aged 3 months to 18 years. The treatment was well-tolerated and showed significant improvements compared to the vehicle (gel without medication).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 582The medication showed significant improvement compared to the vehicle alone When used with moisturizers, desonide can help prevent disease recurrence. Studies show this combination can extend the time before symptoms return to about 69 days compared to 49 days with desonide alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Desonide is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvements in symptoms like itching and inflammation. When combined with moisturizers, it shows even better results with up to 100% effectiveness compared to 60% with desonide alone.
Desonide is particularly safe for children, including infants. Studies show it rarely affects the body's natural hormone (cortisol) production, making it safer than stronger steroids like betamethasone.
Summary:Both desonide 0.05% ointment and hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment were found to be safe for children with atopic dermatitis when used for 4 weeks. Neither medication affected the body's natural cortisol production system.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Results:Both medications were safe for use in children and did not affect their natural cortisol production system
Summary:Desonide hydrogel 0.05%, a low-potency steroid, was found to be safe and effective in treating children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The treatment showed good results in improving symptoms while having minimal impact on the body's hormone system.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-6 yearsResults:Treatment was generally safe with minimal impact on the body's hormone system
Summary:Both desonide cream 0.1% and betamethasone cream were equally effective in treating childhood atopic dermatitis. However, desonide had less impact on the body's cortisol levels, making it potentially safer for children.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 29Severity: Not specifiedAge: mean 13.8 monthsResults:Both treatments showed similar clinical effectiveness
The hydrogel form of desonide helps improve skin moisture and barrier function, with significant improvements seen in as little as 1-2 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Desonide hydrogel 0.05% was found to be safe and effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children aged 3 months to 18 years. The treatment was well-tolerated and showed significant improvements compared to the vehicle (gel without medication).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 582Results:The medication showed significant improvement compared to the vehicle alone
When used with moisturizers, desonide can help prevent disease recurrence. Studies show this combination can extend the time before symptoms return to about 69 days compared to 49 days with desonide alone.
-
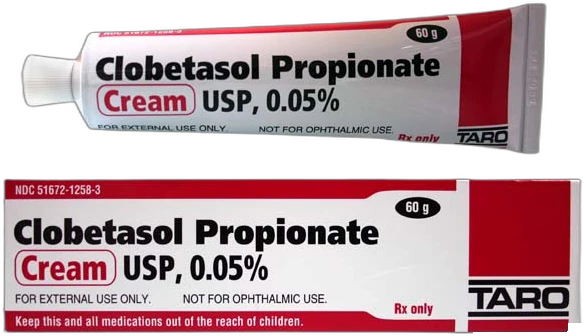 Clobetasol(Clobetasol propionate)If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)Topical dailyMedium
Clobetasol(Clobetasol propionate)If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)Topical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Morning plasma cortisol reductions 6% $25/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSClobetasol propionate is a highly effective treatment for eczema, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like redness, itching, and inflammation within 2-4 weeks of treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultClobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week 📄Clobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was tested against a vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 81The medication can be safely used with minimal side effects when used as directed. Side effects, when they occur, are generally mild and affect about 4% of patientsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultClobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week 📄Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 55Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden Using clobetasol propionate twice weekly as maintenance therapy can help prevent relapses in chronic eczema, with studies showing it kept 70% of patients free from relapses during the observation periodStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 55Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden The medication comes in different forms (cream, lotion, ointment) with similar effectiveness, though the lotion form may provide better long-term results after stopping treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Clobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates of over 90% in multiple studies. It typically starts working within a few days and can clear symptoms within 2-4 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsnot available When used twice weekly for maintenance therapy, clobetasol can help prevent eczema from coming back. In one study, 70% of patients remained free from relapses using this approach.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol propionate (a very strong steroid) was more effective than flupredniden acetate (a medium-strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 55Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses when used twice weekly While generally safe for short-term use, side effects can occur in about 4% of patients. These are usually mild but can include skin thinning and temporary changes in cortisol levels. Regular monitoring by a doctor is recommended for long-term use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultClobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week 📄Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsnot available Different formulations (cream, lotion, emollient) appear to be similarly effective, though some studies suggest the lotion form may provide better long-term results than the cream version.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Clobetasol propionate is a highly effective treatment for eczema, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like redness, itching, and inflammation within 2-4 weeks of treatment
Summary:Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultResults:Clobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week
Summary:Clobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was tested against a vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 81Results:
The medication can be safely used with minimal side effects when used as directed. Side effects, when they occur, are generally mild and affect about 4% of patients
Summary:Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultResults:Clobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week
Summary:Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 55Results:Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden
Using clobetasol propionate twice weekly as maintenance therapy can help prevent relapses in chronic eczema, with studies showing it kept 70% of patients free from relapses during the observation period
Summary:Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 55Results:Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden
The medication comes in different forms (cream, lotion, ointment) with similar effectiveness, though the lotion form may provide better long-term results after stopping treatment
Clobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates of over 90% in multiple studies. It typically starts working within a few days and can clear symptoms within 2-4 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsResults:not available
When used twice weekly for maintenance therapy, clobetasol can help prevent eczema from coming back. In one study, 70% of patients remained free from relapses using this approach.
Summary:Clobetasol propionate (a very strong steroid) was more effective than flupredniden acetate (a medium-strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 55Results:Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses when used twice weekly
While generally safe for short-term use, side effects can occur in about 4% of patients. These are usually mild but can include skin thinning and temporary changes in cortisol levels. Regular monitoring by a doctor is recommended for long-term use.
Summary:Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultResults:Clobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week
Summary:Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsResults:not available
Different formulations (cream, lotion, emollient) appear to be similarly effective, though some studies suggest the lotion form may provide better long-term results than the cream version.
-
 Betamethasone(Betamethasone)If you are 13 or older and responds to corticosteroidsIf you respond to corticosteroidsTopical dailyMedium
Betamethasone(Betamethasone)If you are 13 or older and responds to corticosteroidsIf you respond to corticosteroidsTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Skin thinning (atrophy) $35/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSBetamethasone is effective at reducing inflammation and symptoms of eczema, with studies showing 76-94% of patients experiencing significant improvement within 2-3 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both betamethasone and tacrolimus treatments effectively reduced eczema severity and inflammation. Betamethasone was better at reducing inflammation, while tacrolimus was better at improving skin hydration.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 36Severity: moderateAge: 18+Both treatments effectively reduced disease severity While betamethasone provides quick relief, long-term use may damage the skin barrier and cause skin thinning. It's better suited for short-term treatment of severe flares rather than long-term maintenance therapy.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Betamethasone was more effective at reducing inflammation compared to pimecrolimus in atopic dermatitis skin samples. However, betamethasone may impair skin barrier repair, while pimecrolimus helps maintain it, suggesting pimecrolimus might be better for long-term treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not available📄Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableBetamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms 📄In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health When combined with antibacterial agents like fusidic acid, betamethasone is more effective at treating infected eczema, eliminating 67% of bacteria compared to 51% with betamethasone alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A new cream containing fusidic acid and betamethasone (Fucicort Lipid cream) was found to be as effective as the existing cream formulation in treating infected atopic dermatitis. Both creams reduced severity scores by about 83% and cleared bacterial infection in about 90% of patients after 2 weeks of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 629Severity: Not specifiedAge: Not specifiedBoth Fucicort formulations showed similar effectiveness, significantly better than vehicle Alternative treatments like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be better for long-term use as they improve skin barrier function without causing the skin thinning associated with betamethasone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both tacrolimus and betamethasone improved skin barrier function during treatment. However, after stopping treatment, the benefits lasted longer with tacrolimus while the improvement from betamethasone partially wore off.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: moderateAge: not availableBoth treatments improved skin barrier function, but tacrolimus benefits lasted longer after stopping treatment 📄Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableBetamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms 📄In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health Betamethasone is effective at reducing inflammation and symptoms of eczema, with studies showing 76-94% of patients experiencing significant improvement within 2-3 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Both betamethasone and tacrolimus treatments effectively reduced eczema severity and inflammation. Betamethasone was better at reducing inflammation, while tacrolimus was better at improving skin hydration.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 36Severity: moderateAge: 18+Results:Both treatments effectively reduced disease severity
While betamethasone provides quick relief, long-term use may damage the skin barrier and cause skin thinning. It's better suited for short-term treatment of severe flares rather than long-term maintenance therapy.
Summary:Betamethasone was more effective at reducing inflammation compared to pimecrolimus in atopic dermatitis skin samples. However, betamethasone may impair skin barrier repair, while pimecrolimus helps maintain it, suggesting pimecrolimus might be better for long-term treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:
Summary:Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Betamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms
Summary:In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health
When combined with antibacterial agents like fusidic acid, betamethasone is more effective at treating infected eczema, eliminating 67% of bacteria compared to 51% with betamethasone alone.
Summary:A new cream containing fusidic acid and betamethasone (Fucicort Lipid cream) was found to be as effective as the existing cream formulation in treating infected atopic dermatitis. Both creams reduced severity scores by about 83% and cleared bacterial infection in about 90% of patients after 2 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 629Severity: Not specifiedAge: Not specifiedResults:Both Fucicort formulations showed similar effectiveness, significantly better than vehicle
Alternative treatments like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be better for long-term use as they improve skin barrier function without causing the skin thinning associated with betamethasone.
Summary:Both tacrolimus and betamethasone improved skin barrier function during treatment. However, after stopping treatment, the benefits lasted longer with tacrolimus while the improvement from betamethasone partially wore off.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: moderateAge: not availableResults:Both treatments improved skin barrier function, but tacrolimus benefits lasted longer after stopping treatment
Summary:Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Betamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms
Summary:In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health
-
 Mometasone(Mometasone furoate)If you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidIf you respond to corticosteroidsTopical dailyMedium
Mometasone(Mometasone furoate)If you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidIf you respond to corticosteroidsTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected $35/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSMometasone furoate cream is effective in treating atopic dermatitis, with success rates ranging from 80% to 90%. It can be used once daily, making it convenient for patients.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsCombination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores The treatment is generally safe, especially in children. In studies, it showed minimal side effects and didn't affect children's growth when used as directed. Morning cortisol levels remained normal in most cases, indicating minimal impact on the body's hormone system.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children with mild to moderate eczema, neither mometasone furoate 0.1% nor tacrolimus 0.1% affected their short-term growth rates. This suggests these treatments are safe to use in children without concerns about growth suppression.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to moderateAge: 5-12 yearsNo statistically significant effect on growth rate was observed with either treatment Long-term intermittent use (2-3 times per week) can help prevent disease recurrence. In one study, 83% of patients using it three times per week had no recurrences, compared to only 26% of those who stopped treatment completely.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Long-term intermittent treatment with mometasone furoate cream was effective for chronic hand eczema. Using the cream 3 times per week was more effective than using it 2 times per week or stopping treatment, with 83% of patients having no recurrence when using it 3 times weekly.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Severity: chronic hand eczemaAge: not availableThree-times-weekly maintenance therapy was most effective at preventing recurrence The effectiveness of mometasone can be enhanced when combined with other treatments. For example, using it with wet wrap dressings or skin repair masks showed better results than using mometasone alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsCombination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores 📄Both mometasone and fluticasone ointments were effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children. Using wet wrap dressings after 2 weeks of treatment provided additional improvement in symptoms.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: children (age range not specified)Both treatments were effective, with additional benefits when wet wraps were added Mometasone furoate cream is effective in treating atopic dermatitis, with success rates ranging from 80% to 90%. It can be used once daily, making it convenient for patients.
Summary:Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsResults:Combination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores
The treatment is generally safe, especially in children. In studies, it showed minimal side effects and didn't affect children's growth when used as directed. Morning cortisol levels remained normal in most cases, indicating minimal impact on the body's hormone system.
Summary:In children with mild to moderate eczema, neither mometasone furoate 0.1% nor tacrolimus 0.1% affected their short-term growth rates. This suggests these treatments are safe to use in children without concerns about growth suppression.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to moderateAge: 5-12 yearsResults:No statistically significant effect on growth rate was observed with either treatment
Long-term intermittent use (2-3 times per week) can help prevent disease recurrence. In one study, 83% of patients using it three times per week had no recurrences, compared to only 26% of those who stopped treatment completely.
Summary:Long-term intermittent treatment with mometasone furoate cream was effective for chronic hand eczema. Using the cream 3 times per week was more effective than using it 2 times per week or stopping treatment, with 83% of patients having no recurrence when using it 3 times weekly.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Severity: chronic hand eczemaAge: not availableResults:Three-times-weekly maintenance therapy was most effective at preventing recurrence
The effectiveness of mometasone can be enhanced when combined with other treatments. For example, using it with wet wrap dressings or skin repair masks showed better results than using mometasone alone.
Summary:Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsResults:Combination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores
Summary:Both mometasone and fluticasone ointments were effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children. Using wet wrap dressings after 2 weeks of treatment provided additional improvement in symptoms.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Both treatments were effective, with additional benefits when wet wraps were added
-
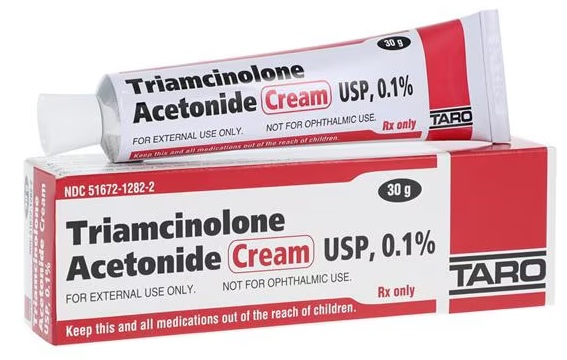 Triamcinolone acetonide(Triamcinolone acetonide)If you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidIf you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidTopical dailyMedium
Triamcinolone acetonide(Triamcinolone acetonide)If you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidIf you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Local reactions skin irritation $30/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSTriamcinolone acetonide is effective at reducing inflammation and improving symptoms of atopic dermatitis, with significant improvements seen within 2-4 weeks of treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 150TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control 📄Adding tetracycline to triamcinolone acetonide (a steroid) cream did not improve eczema symptoms more than using triamcinolone acetonide alone. However, the combination did reduce bacterial skin infection better than the steroid alone.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 44The medication is equally effective whether used as a cream or ointment with wet wraps, so patients can choose the form they prefer. While ointments were harder to apply, patients often preferred them for future useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both cream and ointment forms of triamcinolone acetonide were equally effective when used with wet wraps for treating atopic dermatitis in children. While patients found the ointment more difficult to apply, they preferred it for future treatments.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 39Severity: not availableAge: pediatricNo significant difference in effectiveness between cream and ointment formulations Triamcinolone acetonide appears to be safe, with only minor local reactions reported in a small number of patients (around 4-6% of users)Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 150TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control Surprisingly, even very low doses of triamcinolone acetonide (40 times lower than typical commercial products) can be effective at reducing inflammation in mild to moderate atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A low-dose steroid cream (triamcinolone acetonide) at 25 microg/g concentration was effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. The low-dose steroid showed significant improvement compared to the cream without steroid after just one week of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 14Low-dose steroid cream showed significant improvement in SCORAD scores starting from week 1, while the plain cream showed no improvement Triamcinolone acetonide is effective at reducing inflammation and improving symptoms of atopic dermatitis, with significant improvements seen within 2-4 weeks of treatment
Summary:A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 150Results:TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control
Summary:Adding tetracycline to triamcinolone acetonide (a steroid) cream did not improve eczema symptoms more than using triamcinolone acetonide alone. However, the combination did reduce bacterial skin infection better than the steroid alone.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 44Results:
The medication is equally effective whether used as a cream or ointment with wet wraps, so patients can choose the form they prefer. While ointments were harder to apply, patients often preferred them for future use
Summary:Both cream and ointment forms of triamcinolone acetonide were equally effective when used with wet wraps for treating atopic dermatitis in children. While patients found the ointment more difficult to apply, they preferred it for future treatments.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 39Severity: not availableAge: pediatricResults:No significant difference in effectiveness between cream and ointment formulations
Triamcinolone acetonide appears to be safe, with only minor local reactions reported in a small number of patients (around 4-6% of users)
Summary:A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 150Results:TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control
Surprisingly, even very low doses of triamcinolone acetonide (40 times lower than typical commercial products) can be effective at reducing inflammation in mild to moderate atopic dermatitis
Summary:A low-dose steroid cream (triamcinolone acetonide) at 25 microg/g concentration was effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. The low-dose steroid showed significant improvement compared to the cream without steroid after just one week of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 14Results:Low-dose steroid cream showed significant improvement in SCORAD scores starting from week 1, while the plain cream showed no improvement
-
 Hydrocortisone cream(Hydrocortisone)For temporary relief of itch and rashesFor temporary relief of itch and rashesTopical dailyMedium
Hydrocortisone cream(Hydrocortisone)For temporary relief of itch and rashesFor temporary relief of itch and rashesTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Adrenal suppression 8% Burning sensation 2% Cutaneous reactions Skin burning $25/monthNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTopical corticosteroids are effective as a first-line treatment for atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms within weeks of proper useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsStrong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period 📄A spray form of the steroid desoximetasone was tested in adults with atopic dermatitis. The spray significantly reduced itch and improved symptoms within 1 week, and these improvements lasted throughout the 4-week study. No side effects were reported.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: 18+Skin appearance improved within 1 week and stayed better for 4 weeks 📄The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness Potent (stronger) topical corticosteroids may be more effective than mild ones for moderate flare-ups, showing better symptom improvement and quality of life scores over 24 weeksStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsStrong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period The method of applying topical steroids (whether to wet or dry skin) does not significantly affect treatment outcomes, suggesting flexibility in application methodsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness Topical corticosteroids are effective as a first-line treatment for atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms within weeks of proper use
Summary:Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsResults:Strong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period
Summary:A spray form of the steroid desoximetasone was tested in adults with atopic dermatitis. The spray significantly reduced itch and improved symptoms within 1 week, and these improvements lasted throughout the 4-week study. No side effects were reported.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Skin appearance improved within 1 week and stayed better for 4 weeks
Summary:The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Results:Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness
Potent (stronger) topical corticosteroids may be more effective than mild ones for moderate flare-ups, showing better symptom improvement and quality of life scores over 24 weeks
Summary:Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsResults:Strong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period
The method of applying topical steroids (whether to wet or dry skin) does not significantly affect treatment outcomes, suggesting flexibility in application methods
Summary:The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Results:Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness
-
 Fluocinonide(Fluocinonide)If you need a strong topical steroidIf you need a strong topical steroidTopical dailyMedium
Fluocinonide(Fluocinonide)If you need a strong topical steroidIf you need a strong topical steroidTopical dailyMediumSide Effect Affected mild drug-related effects 12% burning sensation 4% $30/monthKEY TAKEAWAYSFluocinonide cream is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like itching and rash severity within 2 weeks of treatment. In one study, itching decreased by 79% and overall severity decreased by 76%.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A 3-day treatment with fluocinonide cream showed high patient adherence (100%) and significant improvement in eczema symptoms. By day 14, patients experienced 79% reduction in itching and 76% improvement in eczema severity, with more than half of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableSignificant reduction in itching after treatment 📄A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 25Significant improvement in eczema severity Once-daily application of fluocinonide appears to be as effective as twice-daily use, with a lower risk of side effects. The medication is generally well-tolerated, though some patients may experience mild burning sensation during the first few days of use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 25Significant improvement in eczema severity 📄Fluocinonide cream 0.1% was found to be safe and effective when used once daily in children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Over 90% of patients showed improvement in their condition, and applying it once daily was as effective as twice daily with lower risk of side effects.Randomized Controlled Trial Treatment was highly effective with both once-daily and twice-daily application Short-term use (2-3 weeks) of fluocinonide actually helps improve the skin barrier function in people with atopic dermatitis, though long-term use should be avoided as it can cause skin thinning.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 25Significant improvement in eczema severity Studies show fluocinonide is more effective than some other topical steroids like halcinonide for treating atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Fluocinonide cream is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like itching and rash severity within 2 weeks of treatment. In one study, itching decreased by 79% and overall severity decreased by 76%.
Summary:A 3-day treatment with fluocinonide cream showed high patient adherence (100%) and significant improvement in eczema symptoms. By day 14, patients experienced 79% reduction in itching and 76% improvement in eczema severity, with more than half of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableResults:Significant reduction in itching after treatment
Summary:A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 25Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Once-daily application of fluocinonide appears to be as effective as twice-daily use, with a lower risk of side effects. The medication is generally well-tolerated, though some patients may experience mild burning sensation during the first few days of use.
Summary:A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 25Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Fluocinonide cream 0.1% was found to be safe and effective when used once daily in children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Over 90% of patients showed improvement in their condition, and applying it once daily was as effective as twice daily with lower risk of side effects.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Results:Treatment was highly effective with both once-daily and twice-daily application
Short-term use (2-3 weeks) of fluocinonide actually helps improve the skin barrier function in people with atopic dermatitis, though long-term use should be avoided as it can cause skin thinning.
Summary:A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 25Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Studies show fluocinonide is more effective than some other topical steroids like halcinonide for treating atopic dermatitis.
-
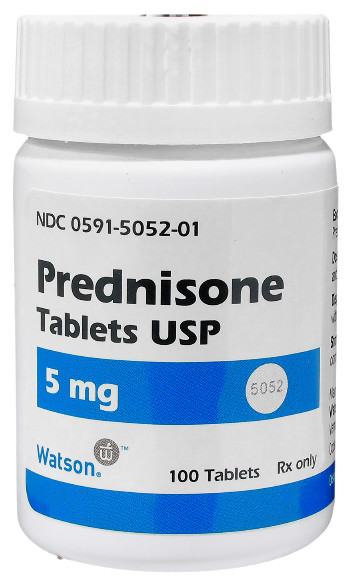 Prednisone(Prednisone)If you're open to steroids and growth suppression is not a concernIf you're open to steroids and topical treatments haven't worked for youOral dailyMedium
Prednisone(Prednisone)If you're open to steroids and growth suppression is not a concernIf you're open to steroids and topical treatments haven't worked for youOral dailyMediumSide Effect Affected Sodium retention 9999% Congestive heart failure 9999% Muscle weakness 9999% Osteoporosis 9999% $25/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSOral prednisolone is not recommended as a first-line treatment for severe adult eczema. In a direct comparison study, ciclosporin was found to be significantly more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ciclosporin was found to be more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults. Only 1 out of 21 patients on prednisolone achieved stable improvement compared to 6 out of 17 patients on ciclosporin. The study was stopped early due to many patients on prednisolone experiencing significant worsening of their eczema.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 38Ciclosporin was significantly more effective than prednisolone Topical forms of prednisolone (like methylprednisolone aceponate) can be effective for treating eczema flares and preventing relapses. When used twice weekly along with moisturizers, it reduced the risk of flares by 87% over 16 weeks.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using methylprednisolone aceponate cream twice weekly along with moisturizer was more effective at preventing eczema flares than using moisturizer alone. After 16 weeks, 87.1% of patients using the steroid cream remained free from flares compared to 65.8% using just moisturizer.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 249Patients using the steroid cream were 3.5 times less likely to experience a relapse Topical methylprednisolone aceponate provides fast itch relief, with patients experiencing significant reduction in itching within 1-2 days of starting treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a study of experimental eczema caused by nickel allergy, methylprednisolone aceponate (a topical corticosteroid) provided fast itch relief. On average, significant itch relief was achieved within 1 day of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 16Severity: not availableAge: not availableTreatment provided fast and effective itch relief In children and adolescents with severe eczema, topical methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% was found to be as effective as tacrolimus 0.03% for overall improvement, and better for reducing itch and improving sleep. It also had fewer side effects and lower cost.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% ointment and tacrolimus 0.03% ointment were effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Methylprednisolone showed better results for reducing itch and improving sleep, and was more cost-effective.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 265Severity: severe to very severeAge: children and adolescentsBoth treatments were equally effective in achieving clear or almost clear skin Oral prednisolone is not recommended as a first-line treatment for severe adult eczema. In a direct comparison study, ciclosporin was found to be significantly more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults.
Summary:Ciclosporin was found to be more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults. Only 1 out of 21 patients on prednisolone achieved stable improvement compared to 6 out of 17 patients on ciclosporin. The study was stopped early due to many patients on prednisolone experiencing significant worsening of their eczema.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 38Results:Ciclosporin was significantly more effective than prednisolone
Topical forms of prednisolone (like methylprednisolone aceponate) can be effective for treating eczema flares and preventing relapses. When used twice weekly along with moisturizers, it reduced the risk of flares by 87% over 16 weeks.
Summary:Using methylprednisolone aceponate cream twice weekly along with moisturizer was more effective at preventing eczema flares than using moisturizer alone. After 16 weeks, 87.1% of patients using the steroid cream remained free from flares compared to 65.8% using just moisturizer.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 249Results:Patients using the steroid cream were 3.5 times less likely to experience a relapse
Topical methylprednisolone aceponate provides fast itch relief, with patients experiencing significant reduction in itching within 1-2 days of starting treatment.
Summary:In a study of experimental eczema caused by nickel allergy, methylprednisolone aceponate (a topical corticosteroid) provided fast itch relief. On average, significant itch relief was achieved within 1 day of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 16Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Treatment provided fast and effective itch relief
In children and adolescents with severe eczema, topical methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% was found to be as effective as tacrolimus 0.03% for overall improvement, and better for reducing itch and improving sleep. It also had fewer side effects and lower cost.
Summary:Both methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% ointment and tacrolimus 0.03% ointment were effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Methylprednisolone showed better results for reducing itch and improving sleep, and was more cost-effective.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 265Severity: severe to very severeAge: children and adolescentsResults:Both treatments were equally effective in achieving clear or almost clear skin
-
 Halobetasol (Halobetasol propionate)Who is this for?:If you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidIf you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$40/monthDelivery:Topical 1-2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $40/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSHalobetasol is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates between 88-94% across multiple studies. Most patients see significant improvement or complete healing of their eczema.
Halobetasol (Halobetasol propionate)Who is this for?:If you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidIf you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$40/monthDelivery:Topical 1-2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $40/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSHalobetasol is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates between 88-94% across multiple studies. Most patients see significant improvement or complete healing of their eczema.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedAll three treatments showed similar high success rates 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate The medication works quickly, with many patients seeing improvements within the first 3 days of treatment. This fast action makes it particularly useful for quick relief of symptoms.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate 📄Halobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment was significantly more effective than vehicle (placebo) in treating eczema. After 2 weeks of treatment, 83% of patients using halobetasol showed complete or marked improvement compared to 28% using vehicle. The medication was well-tolerated with no skin thinning reported.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 224Halobetasol was significantly more effective than vehicle in treating chronic eczema Halobetasol is generally safe and well-tolerated. Side effects are uncommon (occurring in only 2-5% of patients) and usually mild, mainly including skin dryness, itching, or burning sensations at the application site.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedAll three treatments showed similar high success rates 📄Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The cream improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 111Severity: ChronicAge: Not specifiedSignificant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle (p<0.001) The medication is available in both cream and ointment forms, and can be effective in both adults and children. In pediatric patients, it showed excellent results with 100% success rate for eczema treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedAll three treatments showed similar high success rates Halobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates (defined as 'healed' or 'marked improvement') ranging from 88% to 94% in various studies. It starts working quickly, with many patients seeing improvement within 3 days of starting treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableAll three treatments showed similar high effectiveness 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate The medication is generally well-tolerated with a low rate of side effects (2-5% of patients). The most common side effects are skin dryness, itching, or burning at the application site.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableAll three treatments showed similar high effectiveness 📄Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The medication improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 111Significant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle by day 7 and day 14 (p<0.001) In children with severe eczema, the combination of halobetasol propionate cream during the day and ointment at night was extremely effective, with a 100% success rate. However, careful monitoring is needed as one case of mild skin thinning was reported.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results The medication performs as well as or better than other strong topical steroids like clobetasol propionate and betamethasone dipropionate, making it a reliable option for treating severe eczema.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableAll three treatments showed similar high effectiveness 📄Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate Halobetasol is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates between 88-94% across multiple studies. Most patients see significant improvement or complete healing of their eczema.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedResults:All three treatments showed similar high success rates
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
The medication works quickly, with many patients seeing improvements within the first 3 days of treatment. This fast action makes it particularly useful for quick relief of symptoms.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
Summary:Halobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment was significantly more effective than vehicle (placebo) in treating eczema. After 2 weeks of treatment, 83% of patients using halobetasol showed complete or marked improvement compared to 28% using vehicle. The medication was well-tolerated with no skin thinning reported.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 224Results:Halobetasol was significantly more effective than vehicle in treating chronic eczema
Halobetasol is generally safe and well-tolerated. Side effects are uncommon (occurring in only 2-5% of patients) and usually mild, mainly including skin dryness, itching, or burning sensations at the application site.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedResults:All three treatments showed similar high success rates
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The cream improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 111Severity: ChronicAge: Not specifiedResults:Significant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle (p<0.001)
The medication is available in both cream and ointment forms, and can be effective in both adults and children. In pediatric patients, it showed excellent results with 100% success rate for eczema treatment.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-93% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not specifiedResults:All three treatments showed similar high success rates
Halobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates (defined as 'healed' or 'marked improvement') ranging from 88% to 94% in various studies. It starts working quickly, with many patients seeing improvement within 3 days of starting treatment.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableResults:All three treatments showed similar high effectiveness
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
The medication is generally well-tolerated with a low rate of side effects (2-5% of patients). The most common side effects are skin dryness, itching, or burning at the application site.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableResults:All three treatments showed similar high effectiveness
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was significantly more effective than placebo in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms when applied twice daily for 14 days. The medication improved itching, redness, scaling, and thickened skin, with benefits seen within 7 days of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 111Results:Significant improvement in all symptoms compared to vehicle by day 7 and day 14 (p<0.001)
In children with severe eczema, the combination of halobetasol propionate cream during the day and ointment at night was extremely effective, with a 100% success rate. However, careful monitoring is needed as one case of mild skin thinning was reported.
The medication performs as well as or better than other strong topical steroids like clobetasol propionate and betamethasone dipropionate, making it a reliable option for treating severe eczema.
Summary:Halobetasol propionate cream was found to be as effective as two other steroid creams (clobetasol and betamethasone) in treating severe atopic dermatitis. About 88-90% of patients showed significant improvement, with effects starting within 3 days for about 40% of patients.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 264Severity: severeAge: Not availableResults:All three treatments showed similar high effectiveness
Summary:Halobetasol propionate ointment was more effective than diflucortolone valerate ointment in treating severe atopic dermatitis, with 91.5% of patients showing significant improvement compared to 83.6%. It also worked faster, with 70% of patients seeing improvements within 3 days, and had fewer side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Results:Halobetasol propionate showed better overall success rate
-
 Desonide (Desonide)Who is this for?:If you need a low-potency steroid treatmentIf you need a low-potency steroid treatmentEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$35/monthDelivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $35/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSDesonide is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvements in symptoms like itching and inflammation. When combined with moisturizers, it shows even better results with up to 100% effectiveness compared to 60% with desonide alone.
Desonide (Desonide)Who is this for?:If you need a low-potency steroid treatmentIf you need a low-potency steroid treatmentEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$35/monthDelivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $35/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSDesonide is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvements in symptoms like itching and inflammation. When combined with moisturizers, it shows even better results with up to 100% effectiveness compared to 60% with desonide alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Desonide is particularly safe for children, including infants. Studies show it rarely affects the body's natural hormone (cortisol) production, making it safer than stronger steroids like betamethasone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both desonide 0.05% ointment and hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment were found to be safe for children with atopic dermatitis when used for 4 weeks. Neither medication affected the body's natural cortisol production system.Clinical Trial Both medications were safe for use in children and did not affect their natural cortisol production system 📄Desonide hydrogel 0.05%, a low-potency steroid, was found to be safe and effective in treating children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The treatment showed good results in improving symptoms while having minimal impact on the body's hormone system.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-6 yearsTreatment was generally safe with minimal impact on the body's hormone system 📄Both desonide cream 0.1% and betamethasone cream were equally effective in treating childhood atopic dermatitis. However, desonide had less impact on the body's cortisol levels, making it potentially safer for children.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 29Severity: Not specifiedAge: mean 13.8 monthsBoth treatments showed similar clinical effectiveness The hydrogel form of desonide helps improve skin moisture and barrier function, with significant improvements seen in as little as 1-2 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Desonide hydrogel 0.05% was found to be safe and effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children aged 3 months to 18 years. The treatment was well-tolerated and showed significant improvements compared to the vehicle (gel without medication).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 582The medication showed significant improvement compared to the vehicle alone When used with moisturizers, desonide can help prevent disease recurrence. Studies show this combination can extend the time before symptoms return to about 69 days compared to 49 days with desonide alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Desonide is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvements in symptoms like itching and inflammation. When combined with moisturizers, it shows even better results with up to 100% effectiveness compared to 60% with desonide alone.
Desonide is particularly safe for children, including infants. Studies show it rarely affects the body's natural hormone (cortisol) production, making it safer than stronger steroids like betamethasone.
Summary:Both desonide 0.05% ointment and hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment were found to be safe for children with atopic dermatitis when used for 4 weeks. Neither medication affected the body's natural cortisol production system.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Results:Both medications were safe for use in children and did not affect their natural cortisol production system
Summary:Desonide hydrogel 0.05%, a low-potency steroid, was found to be safe and effective in treating children aged 6 months to 6 years with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The treatment showed good results in improving symptoms while having minimal impact on the body's hormone system.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-6 yearsResults:Treatment was generally safe with minimal impact on the body's hormone system
Summary:Both desonide cream 0.1% and betamethasone cream were equally effective in treating childhood atopic dermatitis. However, desonide had less impact on the body's cortisol levels, making it potentially safer for children.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 29Severity: Not specifiedAge: mean 13.8 monthsResults:Both treatments showed similar clinical effectiveness
The hydrogel form of desonide helps improve skin moisture and barrier function, with significant improvements seen in as little as 1-2 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Desonide hydrogel 0.05% was found to be safe and effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children aged 3 months to 18 years. The treatment was well-tolerated and showed significant improvements compared to the vehicle (gel without medication).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 582Results:The medication showed significant improvement compared to the vehicle alone
When used with moisturizers, desonide can help prevent disease recurrence. Studies show this combination can extend the time before symptoms return to about 69 days compared to 49 days with desonide alone.
-
 Clobetasol (Clobetasol propionate)Who is this for?:If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)Effectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Topical 2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSClobetasol propionate is a highly effective treatment for eczema, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like redness, itching, and inflammation within 2-4 weeks of treatment
Clobetasol (Clobetasol propionate)Who is this for?:If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)If you need a super-high potency corticosteroid treatment (but should not be used for more than 2 weeks)Effectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Topical 2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSClobetasol propionate is a highly effective treatment for eczema, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like redness, itching, and inflammation within 2-4 weeks of treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultClobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week 📄Clobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was tested against a vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 81The medication can be safely used with minimal side effects when used as directed. Side effects, when they occur, are generally mild and affect about 4% of patientsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultClobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week 📄Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 55Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden Using clobetasol propionate twice weekly as maintenance therapy can help prevent relapses in chronic eczema, with studies showing it kept 70% of patients free from relapses during the observation periodStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 55Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden The medication comes in different forms (cream, lotion, ointment) with similar effectiveness, though the lotion form may provide better long-term results after stopping treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Clobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates of over 90% in multiple studies. It typically starts working within a few days and can clear symptoms within 2-4 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsnot available When used twice weekly for maintenance therapy, clobetasol can help prevent eczema from coming back. In one study, 70% of patients remained free from relapses using this approach.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol propionate (a very strong steroid) was more effective than flupredniden acetate (a medium-strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 55Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses when used twice weekly While generally safe for short-term use, side effects can occur in about 4% of patients. These are usually mild but can include skin thinning and temporary changes in cortisol levels. Regular monitoring by a doctor is recommended for long-term use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultClobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week 📄Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsnot available Different formulations (cream, lotion, emollient) appear to be similarly effective, though some studies suggest the lotion form may provide better long-term results than the cream version.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Clobetasol propionate is a highly effective treatment for eczema, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like redness, itching, and inflammation within 2-4 weeks of treatment
Summary:Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultResults:Clobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week
Summary:Clobetasol propionate cream 0.05% was tested against a vehicle (cream without active ingredient) in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 81Results:
The medication can be safely used with minimal side effects when used as directed. Side effects, when they occur, are generally mild and affect about 4% of patients
Summary:Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultResults:Clobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week
Summary:Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 55Results:Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden
Using clobetasol propionate twice weekly as maintenance therapy can help prevent relapses in chronic eczema, with studies showing it kept 70% of patients free from relapses during the observation period
Summary:Clobetasol propionate, a very strong topical steroid, was more effective than flupredniden acetate (medium strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 55Results:Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses than flupredniden
The medication comes in different forms (cream, lotion, ointment) with similar effectiveness, though the lotion form may provide better long-term results after stopping treatment
Clobetasol propionate is highly effective at treating eczema, with success rates of over 90% in multiple studies. It typically starts working within a few days and can clear symptoms within 2-4 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsResults:not available
When used twice weekly for maintenance therapy, clobetasol can help prevent eczema from coming back. In one study, 70% of patients remained free from relapses using this approach.
Summary:Clobetasol propionate (a very strong steroid) was more effective than flupredniden acetate (a medium-strength steroid) in preventing hand eczema from coming back. When using clobetasol twice weekly, 70% of patients remained free from eczema flares compared to 30% with flupredniden.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 55Results:Clobetasol was more effective at preventing relapses when used twice weekly
While generally safe for short-term use, side effects can occur in about 4% of patients. These are usually mild but can include skin thinning and temporary changes in cortisol levels. Regular monitoring by a doctor is recommended for long-term use.
Summary:Clobetasol cream was more effective than fluocinonide cream in treating eczema when applied three times daily for 2 weeks. Clobetasol showed faster healing and fewer side effects (4%) compared to fluocinonide (12%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 113Severity: not availableAge: adolescent and adultResults:Clobetasol showed faster healing and maintained efficacy, while fluocinonide's healing rate slowed after first week
Summary:Clobetasol propionate emollient cream 0.05% was tested against a placebo cream in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The study lasted 4 weeks with twice daily application.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 81Severity: moderate to severeAge: ≥12 yearsResults:not available
Different formulations (cream, lotion, emollient) appear to be similarly effective, though some studies suggest the lotion form may provide better long-term results than the cream version.
-
 Betamethasone (Betamethasone)Who is this for?:If you respond to corticosteroidsIf you are 13 or older and responds to corticosteroidsEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$35/monthDelivery:Topical 1-2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $35/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSBetamethasone is effective at reducing inflammation and symptoms of eczema, with studies showing 76-94% of patients experiencing significant improvement within 2-3 weeks of treatment.
Betamethasone (Betamethasone)Who is this for?:If you respond to corticosteroidsIf you are 13 or older and responds to corticosteroidsEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$35/monthDelivery:Topical 1-2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $35/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSBetamethasone is effective at reducing inflammation and symptoms of eczema, with studies showing 76-94% of patients experiencing significant improvement within 2-3 weeks of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both betamethasone and tacrolimus treatments effectively reduced eczema severity and inflammation. Betamethasone was better at reducing inflammation, while tacrolimus was better at improving skin hydration.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 36Severity: moderateAge: 18+Both treatments effectively reduced disease severity While betamethasone provides quick relief, long-term use may damage the skin barrier and cause skin thinning. It's better suited for short-term treatment of severe flares rather than long-term maintenance therapy.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Betamethasone was more effective at reducing inflammation compared to pimecrolimus in atopic dermatitis skin samples. However, betamethasone may impair skin barrier repair, while pimecrolimus helps maintain it, suggesting pimecrolimus might be better for long-term treatment.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not available📄Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableBetamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms 📄In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health When combined with antibacterial agents like fusidic acid, betamethasone is more effective at treating infected eczema, eliminating 67% of bacteria compared to 51% with betamethasone alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A new cream containing fusidic acid and betamethasone (Fucicort Lipid cream) was found to be as effective as the existing cream formulation in treating infected atopic dermatitis. Both creams reduced severity scores by about 83% and cleared bacterial infection in about 90% of patients after 2 weeks of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 629Severity: Not specifiedAge: Not specifiedBoth Fucicort formulations showed similar effectiveness, significantly better than vehicle Alternative treatments like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be better for long-term use as they improve skin barrier function without causing the skin thinning associated with betamethasone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both tacrolimus and betamethasone improved skin barrier function during treatment. However, after stopping treatment, the benefits lasted longer with tacrolimus while the improvement from betamethasone partially wore off.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 21Severity: moderateAge: not availableBoth treatments improved skin barrier function, but tacrolimus benefits lasted longer after stopping treatment 📄Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableBetamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms 📄In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health Betamethasone is effective at reducing inflammation and symptoms of eczema, with studies showing 76-94% of patients experiencing significant improvement within 2-3 weeks of treatment.
Summary:Both betamethasone and tacrolimus treatments effectively reduced eczema severity and inflammation. Betamethasone was better at reducing inflammation, while tacrolimus was better at improving skin hydration.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 36Severity: moderateAge: 18+Results:Both treatments effectively reduced disease severity
While betamethasone provides quick relief, long-term use may damage the skin barrier and cause skin thinning. It's better suited for short-term treatment of severe flares rather than long-term maintenance therapy.
Summary:Betamethasone was more effective at reducing inflammation compared to pimecrolimus in atopic dermatitis skin samples. However, betamethasone may impair skin barrier repair, while pimecrolimus helps maintain it, suggesting pimecrolimus might be better for long-term treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:
Summary:Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Betamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms
Summary:In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health
When combined with antibacterial agents like fusidic acid, betamethasone is more effective at treating infected eczema, eliminating 67% of bacteria compared to 51% with betamethasone alone.
Summary:A new cream containing fusidic acid and betamethasone (Fucicort Lipid cream) was found to be as effective as the existing cream formulation in treating infected atopic dermatitis. Both creams reduced severity scores by about 83% and cleared bacterial infection in about 90% of patients after 2 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 629Severity: Not specifiedAge: Not specifiedResults:Both Fucicort formulations showed similar effectiveness, significantly better than vehicle
Alternative treatments like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be better for long-term use as they improve skin barrier function without causing the skin thinning associated with betamethasone.
Summary:Both tacrolimus and betamethasone improved skin barrier function during treatment. However, after stopping treatment, the benefits lasted longer with tacrolimus while the improvement from betamethasone partially wore off.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 21Severity: moderateAge: not availableResults:Both treatments improved skin barrier function, but tacrolimus benefits lasted longer after stopping treatment
Summary:Both betamethasone and pimecrolimus improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in atopic dermatitis. While betamethasone was better at reducing symptoms, it caused skin thinning, making pimecrolimus potentially better for long-term use.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 15Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Betamethasone was more effective at reducing clinical symptoms
Summary:In people with controlled atopic dermatitis, betamethasone cream damaged the skin barrier after 4 weeks of use, while tacrolimus ointment improved skin barrier function. Tacrolimus was better at maintaining skin hydration and natural moisturizing factors.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:Tacrolimus was superior to betamethasone for maintaining skin barrier health
-
 Mometasone (Mometasone furoate)Who is this for?:If you respond to corticosteroidsIf you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$35/monthDelivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $35/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSMometasone furoate cream is effective in treating atopic dermatitis, with success rates ranging from 80% to 90%. It can be used once daily, making it convenient for patients.
Mometasone (Mometasone furoate)Who is this for?:If you respond to corticosteroidsIf you respond to corticosteroids and need short-term relief through a very strong steroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$35/monthDelivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $35/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSMometasone furoate cream is effective in treating atopic dermatitis, with success rates ranging from 80% to 90%. It can be used once daily, making it convenient for patients.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsCombination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores The treatment is generally safe, especially in children. In studies, it showed minimal side effects and didn't affect children's growth when used as directed. Morning cortisol levels remained normal in most cases, indicating minimal impact on the body's hormone system.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children with mild to moderate eczema, neither mometasone furoate 0.1% nor tacrolimus 0.1% affected their short-term growth rates. This suggests these treatments are safe to use in children without concerns about growth suppression.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to moderateAge: 5-12 yearsNo statistically significant effect on growth rate was observed with either treatment Long-term intermittent use (2-3 times per week) can help prevent disease recurrence. In one study, 83% of patients using it three times per week had no recurrences, compared to only 26% of those who stopped treatment completely.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Long-term intermittent treatment with mometasone furoate cream was effective for chronic hand eczema. Using the cream 3 times per week was more effective than using it 2 times per week or stopping treatment, with 83% of patients having no recurrence when using it 3 times weekly.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 120Severity: chronic hand eczemaAge: not availableThree-times-weekly maintenance therapy was most effective at preventing recurrence The effectiveness of mometasone can be enhanced when combined with other treatments. For example, using it with wet wrap dressings or skin repair masks showed better results than using mometasone alone.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsCombination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores 📄Both mometasone and fluticasone ointments were effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children. Using wet wrap dressings after 2 weeks of treatment provided additional improvement in symptoms.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: children (age range not specified)Both treatments were effective, with additional benefits when wet wraps were added Mometasone furoate cream is effective in treating atopic dermatitis, with success rates ranging from 80% to 90%. It can be used once daily, making it convenient for patients.
Summary:Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsResults:Combination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores
The treatment is generally safe, especially in children. In studies, it showed minimal side effects and didn't affect children's growth when used as directed. Morning cortisol levels remained normal in most cases, indicating minimal impact on the body's hormone system.
Summary:In children with mild to moderate eczema, neither mometasone furoate 0.1% nor tacrolimus 0.1% affected their short-term growth rates. This suggests these treatments are safe to use in children without concerns about growth suppression.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to moderateAge: 5-12 yearsResults:No statistically significant effect on growth rate was observed with either treatment
Long-term intermittent use (2-3 times per week) can help prevent disease recurrence. In one study, 83% of patients using it three times per week had no recurrences, compared to only 26% of those who stopped treatment completely.
Summary:Long-term intermittent treatment with mometasone furoate cream was effective for chronic hand eczema. Using the cream 3 times per week was more effective than using it 2 times per week or stopping treatment, with 83% of patients having no recurrence when using it 3 times weekly.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 120Severity: chronic hand eczemaAge: not availableResults:Three-times-weekly maintenance therapy was most effective at preventing recurrence
The effectiveness of mometasone can be enhanced when combined with other treatments. For example, using it with wet wrap dressings or skin repair masks showed better results than using mometasone alone.
Summary:Using mometasone cream together with an Alginate Skin Repair Mask was more effective than using mometasone cream alone for treating atopic dermatitis. The combination treatment showed better results with 97.5% effectiveness compared to 80% for cream alone, and had fewer side effects and disease recurrences.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 80Severity: Not specifiedAge: 20-47 yearsResults:Combination therapy resulted in significantly lower SCORAD scores
Summary:Both mometasone and fluticasone ointments were effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children. Using wet wrap dressings after 2 weeks of treatment provided additional improvement in symptoms.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Both treatments were effective, with additional benefits when wet wraps were added
-
 Triamcinolone acetonide (Triamcinolone acetonide)Who is this for?:If you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidIf you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$30/monthDelivery:Topical 1-2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $30/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSTriamcinolone acetonide is effective at reducing inflammation and improving symptoms of atopic dermatitis, with significant improvements seen within 2-4 weeks of treatment
Triamcinolone acetonide (Triamcinolone acetonide)Who is this for?:If you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidIf you are looking for short-term relief through a potent topical corticosteroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$30/monthDelivery:Topical 1-2 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $30/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSTriamcinolone acetonide is effective at reducing inflammation and improving symptoms of atopic dermatitis, with significant improvements seen within 2-4 weeks of treatmentStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 150TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control 📄Adding tetracycline to triamcinolone acetonide (a steroid) cream did not improve eczema symptoms more than using triamcinolone acetonide alone. However, the combination did reduce bacterial skin infection better than the steroid alone.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 44The medication is equally effective whether used as a cream or ointment with wet wraps, so patients can choose the form they prefer. While ointments were harder to apply, patients often preferred them for future useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both cream and ointment forms of triamcinolone acetonide were equally effective when used with wet wraps for treating atopic dermatitis in children. While patients found the ointment more difficult to apply, they preferred it for future treatments.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 39Severity: not availableAge: pediatricNo significant difference in effectiveness between cream and ointment formulations Triamcinolone acetonide appears to be safe, with only minor local reactions reported in a small number of patients (around 4-6% of users)Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 150TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control Surprisingly, even very low doses of triamcinolone acetonide (40 times lower than typical commercial products) can be effective at reducing inflammation in mild to moderate atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A low-dose steroid cream (triamcinolone acetonide) at 25 microg/g concentration was effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. The low-dose steroid showed significant improvement compared to the cream without steroid after just one week of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 14Low-dose steroid cream showed significant improvement in SCORAD scores starting from week 1, while the plain cream showed no improvement Triamcinolone acetonide is effective at reducing inflammation and improving symptoms of atopic dermatitis, with significant improvements seen within 2-4 weeks of treatment
Summary:A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 150Results:TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control
Summary:Adding tetracycline to triamcinolone acetonide (a steroid) cream did not improve eczema symptoms more than using triamcinolone acetonide alone. However, the combination did reduce bacterial skin infection better than the steroid alone.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 44Results:
The medication is equally effective whether used as a cream or ointment with wet wraps, so patients can choose the form they prefer. While ointments were harder to apply, patients often preferred them for future use
Summary:Both cream and ointment forms of triamcinolone acetonide were equally effective when used with wet wraps for treating atopic dermatitis in children. While patients found the ointment more difficult to apply, they preferred it for future treatments.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 39Severity: not availableAge: pediatricResults:No significant difference in effectiveness between cream and ointment formulations
Triamcinolone acetonide appears to be safe, with only minor local reactions reported in a small number of patients (around 4-6% of users)
Summary:A cream containing triamcinolone acetonide combined with laurocapram was more effective at treating atopic dermatitis compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone or vehicle control. The combination improved redness, skin thickness, and itching with minimal side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 150Results:TNX showed significantly higher improvement in signs and symptoms compared to both TN and vehicle control
Surprisingly, even very low doses of triamcinolone acetonide (40 times lower than typical commercial products) can be effective at reducing inflammation in mild to moderate atopic dermatitis
Summary:A low-dose steroid cream (triamcinolone acetonide) at 25 microg/g concentration was effective in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. The low-dose steroid showed significant improvement compared to the cream without steroid after just one week of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 14Results:Low-dose steroid cream showed significant improvement in SCORAD scores starting from week 1, while the plain cream showed no improvement
-
 Hydrocortisone cream (Hydrocortisone)Who is this for?:For temporary relief of itch and rashesFor temporary relief of itch and rashesEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Topical 1-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Hydrocortisone creamNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTopical corticosteroids are effective as a first-line treatment for atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms within weeks of proper use
Hydrocortisone cream (Hydrocortisone)Who is this for?:For temporary relief of itch and rashesFor temporary relief of itch and rashesEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Topical 1-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Hydrocortisone creamNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSTopical corticosteroids are effective as a first-line treatment for atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms within weeks of proper useStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsStrong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period 📄A spray form of the steroid desoximetasone was tested in adults with atopic dermatitis. The spray significantly reduced itch and improved symptoms within 1 week, and these improvements lasted throughout the 4-week study. No side effects were reported.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: 18+Skin appearance improved within 1 week and stayed better for 4 weeks 📄The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness Potent (stronger) topical corticosteroids may be more effective than mild ones for moderate flare-ups, showing better symptom improvement and quality of life scores over 24 weeksStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsStrong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period The method of applying topical steroids (whether to wet or dry skin) does not significantly affect treatment outcomes, suggesting flexibility in application methodsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness Topical corticosteroids are effective as a first-line treatment for atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms within weeks of proper use
Summary:Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsResults:Strong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period
Summary:A spray form of the steroid desoximetasone was tested in adults with atopic dermatitis. The spray significantly reduced itch and improved symptoms within 1 week, and these improvements lasted throughout the 4-week study. No side effects were reported.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Skin appearance improved within 1 week and stayed better for 4 weeks
Summary:The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Results:Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness
Potent (stronger) topical corticosteroids may be more effective than mild ones for moderate flare-ups, showing better symptom improvement and quality of life scores over 24 weeks
Summary:Using a strong steroid cream (fluticasone) worked better than a mild steroid cream (hydrocortisone) for treating moderate eczema flare-ups in children. Children using the stronger steroid had better symptom improvement and quality of life over 24 weeks.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 32Severity: moderateAge: 3 months-17 yearsResults:Strong steroid showed significantly better symptom control throughout the study period
The method of applying topical steroids (whether to wet or dry skin) does not significantly affect treatment outcomes, suggesting flexibility in application methods
Summary:The study compared two ways of applying steroid cream in children with eczema - either on wet skin after a bath (soak and smear) or on dry skin. Both methods worked equally well, improving eczema by about 80-85%.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 45Severity: not availableAge: children (specific range not available)Results:Both methods of applying topical corticosteroids (wet vs. dry skin) showed similar effectiveness
-
 Fluocinonide (Fluocinonide)Who is this for?:If you need a strong topical steroidIf you need a strong topical steroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$30/monthDelivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSFluocinonide cream is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like itching and rash severity within 2 weeks of treatment. In one study, itching decreased by 79% and overall severity decreased by 76%.
Fluocinonide (Fluocinonide)Who is this for?:If you need a strong topical steroidIf you need a strong topical steroidEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$30/monthDelivery:Topical dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSFluocinonide cream is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like itching and rash severity within 2 weeks of treatment. In one study, itching decreased by 79% and overall severity decreased by 76%.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A 3-day treatment with fluocinonide cream showed high patient adherence (100%) and significant improvement in eczema symptoms. By day 14, patients experienced 79% reduction in itching and 76% improvement in eczema severity, with more than half of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableSignificant reduction in itching after treatment 📄A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 25Significant improvement in eczema severity Once-daily application of fluocinonide appears to be as effective as twice-daily use, with a lower risk of side effects. The medication is generally well-tolerated, though some patients may experience mild burning sensation during the first few days of use.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 25Significant improvement in eczema severity 📄Fluocinonide cream 0.1% was found to be safe and effective when used once daily in children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Over 90% of patients showed improvement in their condition, and applying it once daily was as effective as twice daily with lower risk of side effects.Randomized Controlled Trial Treatment was highly effective with both once-daily and twice-daily application Short-term use (2-3 weeks) of fluocinonide actually helps improve the skin barrier function in people with atopic dermatitis, though long-term use should be avoided as it can cause skin thinning.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 25Significant improvement in eczema severity Studies show fluocinonide is more effective than some other topical steroids like halcinonide for treating atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results Fluocinonide cream is effective at treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing significant improvement in symptoms like itching and rash severity within 2 weeks of treatment. In one study, itching decreased by 79% and overall severity decreased by 76%.
Summary:A 3-day treatment with fluocinonide cream showed high patient adherence (100%) and significant improvement in eczema symptoms. By day 14, patients experienced 79% reduction in itching and 76% improvement in eczema severity, with more than half of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableResults:Significant reduction in itching after treatment
Summary:A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 25Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Once-daily application of fluocinonide appears to be as effective as twice-daily use, with a lower risk of side effects. The medication is generally well-tolerated, though some patients may experience mild burning sensation during the first few days of use.
Summary:A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 25Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Fluocinonide cream 0.1% was found to be safe and effective when used once daily in children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Over 90% of patients showed improvement in their condition, and applying it once daily was as effective as twice daily with lower risk of side effects.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Results:Treatment was highly effective with both once-daily and twice-daily application
Short-term use (2-3 weeks) of fluocinonide actually helps improve the skin barrier function in people with atopic dermatitis, though long-term use should be avoided as it can cause skin thinning.
Summary:A two-week treatment with fluocinonide 0.1% cream improved skin barrier function and reduced symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. 28% of patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 25Results:Significant improvement in eczema severity
Studies show fluocinonide is more effective than some other topical steroids like halcinonide for treating atopic dermatitis.
-
 Prednisone (Prednisone)Who is this for?:If you're open to steroids and topical treatments haven't worked for youIf you're open to steroids and growth suppression is not a concernEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSOral prednisolone is not recommended as a first-line treatment for severe adult eczema. In a direct comparison study, ciclosporin was found to be significantly more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults.
Prednisone (Prednisone)Who is this for?:If you're open to steroids and topical treatments haven't worked for youIf you're open to steroids and growth suppression is not a concernEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSOral prednisolone is not recommended as a first-line treatment for severe adult eczema. In a direct comparison study, ciclosporin was found to be significantly more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Ciclosporin was found to be more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults. Only 1 out of 21 patients on prednisolone achieved stable improvement compared to 6 out of 17 patients on ciclosporin. The study was stopped early due to many patients on prednisolone experiencing significant worsening of their eczema.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 38Ciclosporin was significantly more effective than prednisolone Topical forms of prednisolone (like methylprednisolone aceponate) can be effective for treating eczema flares and preventing relapses. When used twice weekly along with moisturizers, it reduced the risk of flares by 87% over 16 weeks.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Using methylprednisolone aceponate cream twice weekly along with moisturizer was more effective at preventing eczema flares than using moisturizer alone. After 16 weeks, 87.1% of patients using the steroid cream remained free from flares compared to 65.8% using just moisturizer.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 249Patients using the steroid cream were 3.5 times less likely to experience a relapse Topical methylprednisolone aceponate provides fast itch relief, with patients experiencing significant reduction in itching within 1-2 days of starting treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In a study of experimental eczema caused by nickel allergy, methylprednisolone aceponate (a topical corticosteroid) provided fast itch relief. On average, significant itch relief was achieved within 1 day of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 16Severity: not availableAge: not availableTreatment provided fast and effective itch relief In children and adolescents with severe eczema, topical methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% was found to be as effective as tacrolimus 0.03% for overall improvement, and better for reducing itch and improving sleep. It also had fewer side effects and lower cost.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% ointment and tacrolimus 0.03% ointment were effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Methylprednisolone showed better results for reducing itch and improving sleep, and was more cost-effective.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 265Severity: severe to very severeAge: children and adolescentsBoth treatments were equally effective in achieving clear or almost clear skin Oral prednisolone is not recommended as a first-line treatment for severe adult eczema. In a direct comparison study, ciclosporin was found to be significantly more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults.
Summary:Ciclosporin was found to be more effective than prednisolone for treating severe eczema in adults. Only 1 out of 21 patients on prednisolone achieved stable improvement compared to 6 out of 17 patients on ciclosporin. The study was stopped early due to many patients on prednisolone experiencing significant worsening of their eczema.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 38Results:Ciclosporin was significantly more effective than prednisolone
Topical forms of prednisolone (like methylprednisolone aceponate) can be effective for treating eczema flares and preventing relapses. When used twice weekly along with moisturizers, it reduced the risk of flares by 87% over 16 weeks.
Summary:Using methylprednisolone aceponate cream twice weekly along with moisturizer was more effective at preventing eczema flares than using moisturizer alone. After 16 weeks, 87.1% of patients using the steroid cream remained free from flares compared to 65.8% using just moisturizer.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 249Results:Patients using the steroid cream were 3.5 times less likely to experience a relapse
Topical methylprednisolone aceponate provides fast itch relief, with patients experiencing significant reduction in itching within 1-2 days of starting treatment.
Summary:In a study of experimental eczema caused by nickel allergy, methylprednisolone aceponate (a topical corticosteroid) provided fast itch relief. On average, significant itch relief was achieved within 1 day of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 16Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Treatment provided fast and effective itch relief
In children and adolescents with severe eczema, topical methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% was found to be as effective as tacrolimus 0.03% for overall improvement, and better for reducing itch and improving sleep. It also had fewer side effects and lower cost.
Summary:Both methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% ointment and tacrolimus 0.03% ointment were effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Methylprednisolone showed better results for reducing itch and improving sleep, and was more cost-effective.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 265Severity: severe to very severeAge: children and adolescentsResults:Both treatments were equally effective in achieving clear or almost clear skin
Off-label
-
 Cyclosporine(Cyclosporine)NoneIf other treatments don't work for you and you are looking for relief within 1-2 weeksOral dailyMedium
Cyclosporine(Cyclosporine)NoneIf other treatments don't work for you and you are looking for relief within 1-2 weeksOral dailyMedium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Liver and kidney toxicity Thrombotic Microangiopathy Serious infections
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$25/monthKEY TAKEAWAYSCyclosporine works quickly (within 2-3 weeks) and is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children, but is not recommended for use over one yearStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Observational Study Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Common side effects include kidney problems (nephrotoxicity), high blood pressure, increased risk of infections, gastrointestinal upset, and abnormal lab results. Children generally tolerate the medication better than adults.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Observational Study Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Studies show cyclosporine and dupilumab (a newer medication) are both effective treatments, with cyclosporine showing faster initial response but dupilumab potentially providing better long-term controlStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: dupilumab and cyclosporine. Dupilumab showed better results than cyclosporine in reducing eczema severity, both in the short term (12-16 weeks) and longer term (24-30 weeks). About 75-80% of patients on dupilumab had significant improvement compared to 40-56% on cyclosporine.Comparative Study Total Patients: 163Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Dupilumab showed consistently better results than cyclosporine in achieving 50% improvement in eczema severity 📄Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsDrug survival (how long patients stay on the medication) is about 1 year for cyclosporine, with most discontinuations due to either side effects or loss of effectivenessStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment for about 1 year on average. This duration was longer than in patients with psoriasis, who stayed on the medication for about 4.4 months.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 130Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availablePatients with atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment longer than patients with psoriasis Cyclosporine works quickly (within 2-3 weeks) and is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children, but is not recommended for use over one year
Summary:Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)Results:
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Common side effects include kidney problems (nephrotoxicity), high blood pressure, increased risk of infections, gastrointestinal upset, and abnormal lab results. Children generally tolerate the medication better than adults.
Summary:Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)Results:
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Studies show cyclosporine and dupilumab (a newer medication) are both effective treatments, with cyclosporine showing faster initial response but dupilumab potentially providing better long-term control
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: dupilumab and cyclosporine. Dupilumab showed better results than cyclosporine in reducing eczema severity, both in the short term (12-16 weeks) and longer term (24-30 weeks). About 75-80% of patients on dupilumab had significant improvement compared to 40-56% on cyclosporine.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 163Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Dupilumab showed consistently better results than cyclosporine in achieving 50% improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsResults:
Drug survival (how long patients stay on the medication) is about 1 year for cyclosporine, with most discontinuations due to either side effects or loss of effectiveness
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment for about 1 year on average. This duration was longer than in patients with psoriasis, who stayed on the medication for about 4.4 months.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 130Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Patients with atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment longer than patients with psoriasis
-
 CellCept(Mycophenolate mofetil)If your child has have widespread severe flareups and topicals don't workIf you have widespread flareups and topicals don't work for youOral dailyHigh
CellCept(Mycophenolate mofetil)If your child has have widespread severe flareups and topicals don't workIf you have widespread flareups and topicals don't work for youOral dailyHigh⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Diarrhea 45% Leukopenia 36% Bacterial infections 34% Viral infections 31%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.KEY TAKEAWAYSMycophenolate mofetil has shown good efficacy for treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing that about 78% of patients achieve partial or full remission of symptoms. It works by suppressing the immune system and typically takes 6-8 weeks to show effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+The medication is generally considered safe but requires monitoring. Common side effects include headaches, herpes infections, stomach upset, liver function abnormalities, and reduced blood cell counts. There is also a small risk of developing infections or cancer due to the immune suppression.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+📄This real-world study looked at side effects of various medications used to treat atopic dermatitis, including dupilumab and other immunomodulating drugs. The study found some side effects occurred more frequently than expected, particularly eye-related issues and facial redness with dupilumab, and fatigue with methotrexate.Observational Study Total Patients: 266Severity: not availableAge: adults and pediatric patientsIn rare cases, serious complications can occur. One reported case showed development of Candida infection in the esophagus after 22 months of treatment. Another case reported development of lung disease, though this resolved after stopping the medication.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A patient with severe atopic dermatitis was treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and developed lung problems (interstitial lung disease) as a side effect. After stopping MMF and receiving steroid treatment, the patient's lung condition improved.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 37 yearsMMF showed good clinical effect but had to be discontinued due to serious side effects 📄A patient treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) for atopic dermatitis developed a fungal infection in their esophagus after 22 months of treatment. This is a rare complication that hasn't been reported before with MMF treatment.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: not availableAge: 59When compared to other treatments, mycophenolate mofetil appears to have lower effectiveness than newer medications like dupilumab. However, it may still be a useful option for some patients, particularly when other treatments have failed or aren't suitable.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Comparative Study Mycophenolate mofetil has shown good efficacy for treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing that about 78% of patients achieve partial or full remission of symptoms. It works by suppressing the immune system and typically takes 6-8 weeks to show effects.
Summary:This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication is generally considered safe but requires monitoring. Common side effects include headaches, herpes infections, stomach upset, liver function abnormalities, and reduced blood cell counts. There is also a small risk of developing infections or cancer due to the immune suppression.
Summary:This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This real-world study looked at side effects of various medications used to treat atopic dermatitis, including dupilumab and other immunomodulating drugs. The study found some side effects occurred more frequently than expected, particularly eye-related issues and facial redness with dupilumab, and fatigue with methotrexate.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 266Severity: not availableAge: adults and pediatric patientsResults:
In rare cases, serious complications can occur. One reported case showed development of Candida infection in the esophagus after 22 months of treatment. Another case reported development of lung disease, though this resolved after stopping the medication.
Summary:A patient with severe atopic dermatitis was treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and developed lung problems (interstitial lung disease) as a side effect. After stopping MMF and receiving steroid treatment, the patient's lung condition improved.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 37 yearsResults:MMF showed good clinical effect but had to be discontinued due to serious side effects
Summary:A patient treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) for atopic dermatitis developed a fungal infection in their esophagus after 22 months of treatment. This is a rare complication that hasn't been reported before with MMF treatment.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: not availableAge: 59Results:
When compared to other treatments, mycophenolate mofetil appears to have lower effectiveness than newer medications like dupilumab. However, it may still be a useful option for some patients, particularly when other treatments have failed or aren't suitable.
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
-
 Methotrexate(Methotrexate)NoneIf you have severe eczema that affects a large part of your body and doesn't respond well to steroidsOral or injection dailyHigh
Methotrexate(Methotrexate)NoneIf you have severe eczema that affects a large part of your body and doesn't respond well to steroidsOral or injection dailyHigh⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Elevated liver tests 15% Nausea/vomiting 10% Stomatitis 3% Thrombocytopenia 3%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$25/monthKEY TAKEAWAYSMethotrexate is slower to work but can be effective for long-term control of atopic dermatitis. It typically takes at least 6 weeks to see effects. The medication works by decreasing inflammation through inhibiting cell division and lymphocyte proliferation.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 97Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. More serious but rare side effects include liver toxicity and low blood counts, which requires regular blood test monitoring. Taking folic acid supplements helps reduce these side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. When compared to other treatments, methotrexate shows lower effectiveness than cyclosporine and dupilumab in the short term (8 weeks), but may have better long-term outcomes. In children, methotrexate shows better drug survival rates than cyclosporine but lower than dupilumab.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared how long children with severe eczema stayed on different medications (dupilumab, methotrexate, and cyclosporine). Dupilumab showed the best long-term results, with 84% of patients still using it after 1 year, compared to 61% for methotrexate and 44% for cyclosporine. The main reasons patients stopped treatments were because they weren't working well enough or because of side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 362Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-17 yearsDupilumab showed consistently better long-term continuation rates compared to methotrexate and cyclosporine 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 97Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks The medication can be used as a maintenance therapy for longer-term control of atopic dermatitis, unlike cyclosporine which is typically limited to one year of use due to side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. 📄Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsMethotrexate is slower to work but can be effective for long-term control of atopic dermatitis. It typically takes at least 6 weeks to see effects. The medication works by decreasing inflammation through inhibiting cell division and lymphocyte proliferation.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 97Results:Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. More serious but rare side effects include liver toxicity and low blood counts, which requires regular blood test monitoring. Taking folic acid supplements helps reduce these side effects.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
When compared to other treatments, methotrexate shows lower effectiveness than cyclosporine and dupilumab in the short term (8 weeks), but may have better long-term outcomes. In children, methotrexate shows better drug survival rates than cyclosporine but lower than dupilumab.
Summary:This study compared how long children with severe eczema stayed on different medications (dupilumab, methotrexate, and cyclosporine). Dupilumab showed the best long-term results, with 84% of patients still using it after 1 year, compared to 61% for methotrexate and 44% for cyclosporine. The main reasons patients stopped treatments were because they weren't working well enough or because of side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 362Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-17 yearsResults:Dupilumab showed consistently better long-term continuation rates compared to methotrexate and cyclosporine
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 97Results:Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks
The medication can be used as a maintenance therapy for longer-term control of atopic dermatitis, unlike cyclosporine which is typically limited to one year of use due to side effects.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Summary:Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsResults:
-
 Olumiant(Baricitinib)If your child is over 2 years old, needs strong and fast relieve, and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateIf you need strong and fast relieve and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateOral once dailyMedium
Olumiant(Baricitinib)If your child is over 2 years old, needs strong and fast relieve, and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateIf you need strong and fast relieve and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateOral once dailyMedium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Nasopharyngitis 12% Upper respiratory tract infection 8% Folliculitis 6% Pulmonary embolism 1%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSBaricitinib 4mg combined with topical corticosteroids (TCS) is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with about 31% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment. The medication starts working quickly, with improvements in itch seen as early as 2-4 days after starting treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib, whether used alone or with topical steroids, quickly improved all four main signs of eczema (excoriation, swelling/bumps, redness, and skin thickening). The medication worked particularly well for reducing scratching damage, with improvements seen as early as the first week of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: adultsBaricitinib improved all signs of eczema, with particularly rapid effects on scratching damage 📄Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 329The benefits of baricitinib can be maintained long-term (up to 52-68 weeks) in patients who respond to treatment. Some patients can even reduce their dose while maintaining benefits, though others may need to continue the original dose.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults. Clinical trials showed that it can significantly improve skin clearance and reduce itch, with about 30-40% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Baricitinib 4mg showed the best results for skin clearance 📄This study looked at what happens when patients who responded well to baricitinib either continued their dose, reduced their dose, or stopped treatment completely. Most patients who reduced their dose maintained improvement in their eczema, and those who lost improvement usually got better again when restarting their original dose.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 526Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableMost patients who lost response regained improvement after restarting their original dose 📄Baricitinib combined with topical steroids showed long-term effectiveness in treating moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 68 weeks. About 40-60% of patients saw significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, and around 40-50% experienced meaningful itch reduction.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 155Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Long-term improvement in eczema severity was maintained across both doses Common side effects include nasopharyngitis (common cold), herpes simplex infections, upper respiratory infections, and headache. While the medication is generally well-tolerated, patients need to be monitored for infections and other potential side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib combined with topical steroids was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in patients who couldn't use or didn't respond to ciclosporin. After 16 weeks, 32% of patients on the highest dose (4mg) had their eczema improve by 75% or more, compared to 17% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for up to one year.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 463Severity: moderate to severeAge: not available📄Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 329In real-world clinical practice, about 43% of patients may discontinue treatment due to lack of effectiveness or side effects. However, the medication can be effective even in patients who didn't respond to other treatments like dupilumab.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib showed some effectiveness in treating difficult-to-treat eczema patients, including those who didn't respond to dupilumab. However, about 43% of patients stopped treatment due to either lack of effectiveness or side effects. The most common side effects were nausea, urinary tract infections, and herpes simplex infections.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 51Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+About 3 in 10 patients achieved low disease activity after 16 weeks Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical corticosteroids (TCS) is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with about 31% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment. The medication starts working quickly, with improvements in itch seen as early as 2-4 days after starting treatment.
Summary:Baricitinib, whether used alone or with topical steroids, quickly improved all four main signs of eczema (excoriation, swelling/bumps, redness, and skin thickening). The medication worked particularly well for reducing scratching damage, with improvements seen as early as the first week of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: adultsResults:Baricitinib improved all signs of eczema, with particularly rapid effects on scratching damage
Summary:Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 329Results:
The benefits of baricitinib can be maintained long-term (up to 52-68 weeks) in patients who respond to treatment. Some patients can even reduce their dose while maintaining benefits, though others may need to continue the original dose.
Summary:Baricitinib is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults. Clinical trials showed that it can significantly improve skin clearance and reduce itch, with about 30-40% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Baricitinib 4mg showed the best results for skin clearance
Summary:This study looked at what happens when patients who responded well to baricitinib either continued their dose, reduced their dose, or stopped treatment completely. Most patients who reduced their dose maintained improvement in their eczema, and those who lost improvement usually got better again when restarting their original dose.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 526Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Most patients who lost response regained improvement after restarting their original dose
Summary:Baricitinib combined with topical steroids showed long-term effectiveness in treating moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 68 weeks. About 40-60% of patients saw significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, and around 40-50% experienced meaningful itch reduction.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 155Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Long-term improvement in eczema severity was maintained across both doses
Common side effects include nasopharyngitis (common cold), herpes simplex infections, upper respiratory infections, and headache. While the medication is generally well-tolerated, patients need to be monitored for infections and other potential side effects.
Summary:Baricitinib combined with topical steroids was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in patients who couldn't use or didn't respond to ciclosporin. After 16 weeks, 32% of patients on the highest dose (4mg) had their eczema improve by 75% or more, compared to 17% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for up to one year.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 463Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:
Summary:Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 329Results:
In real-world clinical practice, about 43% of patients may discontinue treatment due to lack of effectiveness or side effects. However, the medication can be effective even in patients who didn't respond to other treatments like dupilumab.
Summary:Baricitinib showed some effectiveness in treating difficult-to-treat eczema patients, including those who didn't respond to dupilumab. However, about 43% of patients stopped treatment due to either lack of effectiveness or side effects. The most common side effects were nausea, urinary tract infections, and herpes simplex infections.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 51Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:About 3 in 10 patients achieved low disease activity after 16 weeks
-
 Imuran(Azathioprine)NoneIf you have severe eczema but can wait 2-3 months for a responseOral dailyHigh
Imuran(Azathioprine)NoneIf you have severe eczema but can wait 2-3 months for a responseOral dailyHigh⚠️ Boxed Warning
Side Effect Affected Leukopenia (any degree) 28% Severe Leukopenia (<2,500 cells/mm3) 5% Infections 1% Nausea and vomiting 12%
This medication carries a boxed warning. This is the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) most stringent warning for prescription drugs, indicating a serious or life-threatening risk associated with the medication.$22/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSAzathioprine has shown lower effectiveness compared to newer treatments like dupilumab and high-dose cyclosporine for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Azathioprine has a slow onset of action (taking weeks to months to work) and requires regular blood test monitoring due to potential side effects on bone marrow and liver.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Common side effects include stomach upset, increased risk of infections and cancers, bone marrow suppression, liver toxicity, and rare allergic reactions. Due to these risks, recent medical guidelines recommend against using azathioprine for atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. 📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Treatment discontinuation rates are high with azathioprine, mainly due to side effects and lack of effectiveness. Studies show it has a higher rate of discontinuation compared to other treatments like dupilumab.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Azathioprine has shown lower effectiveness compared to newer treatments like dupilumab and high-dose cyclosporine for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Azathioprine has a slow onset of action (taking weeks to months to work) and requires regular blood test monitoring due to potential side effects on bone marrow and liver.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Common side effects include stomach upset, increased risk of infections and cancers, bone marrow suppression, liver toxicity, and rare allergic reactions. Due to these risks, recent medical guidelines recommend against using azathioprine for atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Treatment discontinuation rates are high with azathioprine, mainly due to side effects and lack of effectiveness. Studies show it has a higher rate of discontinuation compared to other treatments like dupilumab.
Summary:This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
-
 Cyclosporine (Cyclosporine)Who is this for?:If other treatments don't work for you and you are looking for relief within 1-2 weeksNoneEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium
Cyclosporine (Cyclosporine)Who is this for?:If other treatments don't work for you and you are looking for relief within 1-2 weeksNoneEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$25/monthDelivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceNot currently available through Lemma HealthKEY TAKEAWAYSCyclosporine works quickly (within 2-3 weeks) and is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children, but is not recommended for use over one yearStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Observational Study Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Common side effects include kidney problems (nephrotoxicity), high blood pressure, increased risk of infections, gastrointestinal upset, and abnormal lab results. Children generally tolerate the medication better than adults.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Observational Study Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Studies show cyclosporine and dupilumab (a newer medication) are both effective treatments, with cyclosporine showing faster initial response but dupilumab potentially providing better long-term controlStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: dupilumab and cyclosporine. Dupilumab showed better results than cyclosporine in reducing eczema severity, both in the short term (12-16 weeks) and longer term (24-30 weeks). About 75-80% of patients on dupilumab had significant improvement compared to 40-56% on cyclosporine.Comparative Study Total Patients: 163Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Dupilumab showed consistently better results than cyclosporine in achieving 50% improvement in eczema severity 📄Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsDrug survival (how long patients stay on the medication) is about 1 year for cyclosporine, with most discontinuations due to either side effects or loss of effectivenessStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄Patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment for about 1 year on average. This duration was longer than in patients with psoriasis, who stayed on the medication for about 4.4 months.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 130Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availablePatients with atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment longer than patients with psoriasis Cyclosporine works quickly (within 2-3 weeks) and is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis in both adults and children, but is not recommended for use over one year
Summary:Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)Results:
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Common side effects include kidney problems (nephrotoxicity), high blood pressure, increased risk of infections, gastrointestinal upset, and abnormal lab results. Children generally tolerate the medication better than adults.
Summary:Cyclosporine A was effective in treating severe atopic dermatitis in children, with 64% of patients showing good or excellent response after 4 weeks. Side effects were common but mild, and 20% of patients maintained improvement for more than 6 months after treatment.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 63Severity: severeAge: children (mean 8.4 years)Results:
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Studies show cyclosporine and dupilumab (a newer medication) are both effective treatments, with cyclosporine showing faster initial response but dupilumab potentially providing better long-term control
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: dupilumab and cyclosporine. Dupilumab showed better results than cyclosporine in reducing eczema severity, both in the short term (12-16 weeks) and longer term (24-30 weeks). About 75-80% of patients on dupilumab had significant improvement compared to 40-56% on cyclosporine.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 163Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Dupilumab showed consistently better results than cyclosporine in achieving 50% improvement in eczema severity
Summary:Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsResults:
Drug survival (how long patients stay on the medication) is about 1 year for cyclosporine, with most discontinuations due to either side effects or loss of effectiveness
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:Patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment for about 1 year on average. This duration was longer than in patients with psoriasis, who stayed on the medication for about 4.4 months.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 130Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Patients with atopic dermatitis stayed on cyclosporine treatment longer than patients with psoriasis
-
 CellCept (Mycophenolate mofetil)Who is this for?:If you have widespread flareups and topicals don't work for youIf your child has have widespread severe flareups and topicals don't workEffectiveness:Side Effects:High
CellCept (Mycophenolate mofetil)Who is this for?:If you have widespread flareups and topicals don't work for youIf your child has have widespread severe flareups and topicals don't workEffectiveness:Side Effects:High⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceNot currently available through Lemma HealthKEY TAKEAWAYSMycophenolate mofetil has shown good efficacy for treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing that about 78% of patients achieve partial or full remission of symptoms. It works by suppressing the immune system and typically takes 6-8 weeks to show effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+The medication is generally considered safe but requires monitoring. Common side effects include headaches, herpes infections, stomach upset, liver function abnormalities, and reduced blood cell counts. There is also a small risk of developing infections or cancer due to the immune suppression.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+📄This real-world study looked at side effects of various medications used to treat atopic dermatitis, including dupilumab and other immunomodulating drugs. The study found some side effects occurred more frequently than expected, particularly eye-related issues and facial redness with dupilumab, and fatigue with methotrexate.Observational Study Total Patients: 266Severity: not availableAge: adults and pediatric patientsIn rare cases, serious complications can occur. One reported case showed development of Candida infection in the esophagus after 22 months of treatment. Another case reported development of lung disease, though this resolved after stopping the medication.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A patient with severe atopic dermatitis was treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and developed lung problems (interstitial lung disease) as a side effect. After stopping MMF and receiving steroid treatment, the patient's lung condition improved.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 37 yearsMMF showed good clinical effect but had to be discontinued due to serious side effects 📄A patient treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) for atopic dermatitis developed a fungal infection in their esophagus after 22 months of treatment. This is a rare complication that hasn't been reported before with MMF treatment.Case Reports Total Patients: 1Severity: not availableAge: 59When compared to other treatments, mycophenolate mofetil appears to have lower effectiveness than newer medications like dupilumab. However, it may still be a useful option for some patients, particularly when other treatments have failed or aren't suitable.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+📄This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Comparative Study Mycophenolate mofetil has shown good efficacy for treating atopic dermatitis, with studies showing that about 78% of patients achieve partial or full remission of symptoms. It works by suppressing the immune system and typically takes 6-8 weeks to show effects.
Summary:This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:
The medication is generally considered safe but requires monitoring. Common side effects include headaches, herpes infections, stomach upset, liver function abnormalities, and reduced blood cell counts. There is also a small risk of developing infections or cancer due to the immune suppression.
Summary:This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This real-world study looked at side effects of various medications used to treat atopic dermatitis, including dupilumab and other immunomodulating drugs. The study found some side effects occurred more frequently than expected, particularly eye-related issues and facial redness with dupilumab, and fatigue with methotrexate.Study Type:Observational StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 266Severity: not availableAge: adults and pediatric patientsResults:
In rare cases, serious complications can occur. One reported case showed development of Candida infection in the esophagus after 22 months of treatment. Another case reported development of lung disease, though this resolved after stopping the medication.
Summary:A patient with severe atopic dermatitis was treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and developed lung problems (interstitial lung disease) as a side effect. After stopping MMF and receiving steroid treatment, the patient's lung condition improved.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: severeAge: 37 yearsResults:MMF showed good clinical effect but had to be discontinued due to serious side effects
Summary:A patient treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) for atopic dermatitis developed a fungal infection in their esophagus after 22 months of treatment. This is a rare complication that hasn't been reported before with MMF treatment.Study Type:Case ReportsStudied Population:Total Patients: 1Severity: not availableAge: 59Results:
When compared to other treatments, mycophenolate mofetil appears to have lower effectiveness than newer medications like dupilumab. However, it may still be a useful option for some patients, particularly when other treatments have failed or aren't suitable.
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This real-world study compared the safety of dupilumab to conventional systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis over 5 years. Dupilumab showed fewer side effects related to circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems, and infections compared to other treatments. However, it did have a higher risk of eye inflammation (conjunctivitis) compared to some other medications.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
-
 Methotrexate (Methotrexate)Who is this for?:If you have severe eczema that affects a large part of your body and doesn't respond well to steroidsNoneEffectiveness:Side Effects:High
Methotrexate (Methotrexate)Who is this for?:If you have severe eczema that affects a large part of your body and doesn't respond well to steroidsNoneEffectiveness:Side Effects:High⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$25/monthDelivery:Oral or injection dailySee EvidenceNot currently available through Lemma HealthKEY TAKEAWAYSMethotrexate is slower to work but can be effective for long-term control of atopic dermatitis. It typically takes at least 6 weeks to see effects. The medication works by decreasing inflammation through inhibiting cell division and lymphocyte proliferation.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 97Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. More serious but rare side effects include liver toxicity and low blood counts, which requires regular blood test monitoring. Taking folic acid supplements helps reduce these side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. When compared to other treatments, methotrexate shows lower effectiveness than cyclosporine and dupilumab in the short term (8 weeks), but may have better long-term outcomes. In children, methotrexate shows better drug survival rates than cyclosporine but lower than dupilumab.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study compared how long children with severe eczema stayed on different medications (dupilumab, methotrexate, and cyclosporine). Dupilumab showed the best long-term results, with 84% of patients still using it after 1 year, compared to 61% for methotrexate and 44% for cyclosporine. The main reasons patients stopped treatments were because they weren't working well enough or because of side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 362Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-17 yearsDupilumab showed consistently better long-term continuation rates compared to methotrexate and cyclosporine 📄This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 97Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks The medication can be used as a maintenance therapy for longer-term control of atopic dermatitis, unlike cyclosporine which is typically limited to one year of use due to side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. 📄Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsMethotrexate is slower to work but can be effective for long-term control of atopic dermatitis. It typically takes at least 6 weeks to see effects. The medication works by decreasing inflammation through inhibiting cell division and lymphocyte proliferation.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 97Results:Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. More serious but rare side effects include liver toxicity and low blood counts, which requires regular blood test monitoring. Taking folic acid supplements helps reduce these side effects.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
When compared to other treatments, methotrexate shows lower effectiveness than cyclosporine and dupilumab in the short term (8 weeks), but may have better long-term outcomes. In children, methotrexate shows better drug survival rates than cyclosporine but lower than dupilumab.
Summary:This study compared how long children with severe eczema stayed on different medications (dupilumab, methotrexate, and cyclosporine). Dupilumab showed the best long-term results, with 84% of patients still using it after 1 year, compared to 61% for methotrexate and 44% for cyclosporine. The main reasons patients stopped treatments were because they weren't working well enough or because of side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 362Severity: moderate to severeAge: 2-17 yearsResults:Dupilumab showed consistently better long-term continuation rates compared to methotrexate and cyclosporine
Summary:This study compared two medications for moderate-to-severe eczema: methotrexate and cyclosporine. While cyclosporine worked better at 8 weeks, increasing the dose of methotrexate led to similar effectiveness by 20 weeks. Cyclosporine had more side effects than methotrexate.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 97Results:Cyclosporine was more effective than methotrexate at 8 weeks
The medication can be used as a maintenance therapy for longer-term control of atopic dermatitis, unlike cyclosporine which is typically limited to one year of use due to side effects.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Summary:Both cyclosporine and methotrexate were effective in treating severe eczema in children and young people. Cyclosporine worked faster, but methotrexate's effects lasted longer after stopping treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 103Severity: severeAge: 2-16 yearsResults:
-
 Olumiant (Baricitinib)Who is this for?:If you need strong and fast relieve and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateIf your child is over 2 years old, needs strong and fast relieve, and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium
Olumiant (Baricitinib)Who is this for?:If you need strong and fast relieve and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateIf your child is over 2 years old, needs strong and fast relieve, and treatments applied to the skin are not sufficient or appropriateEffectiveness:Side Effects:Medium⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:Delivery:Oral once dailySee EvidenceGet Prescription$45 one-time consultation; you'll pay your pharmacy's price for the medicationKEY TAKEAWAYSBaricitinib 4mg combined with topical corticosteroids (TCS) is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with about 31% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment. The medication starts working quickly, with improvements in itch seen as early as 2-4 days after starting treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib, whether used alone or with topical steroids, quickly improved all four main signs of eczema (excoriation, swelling/bumps, redness, and skin thickening). The medication worked particularly well for reducing scratching damage, with improvements seen as early as the first week of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: adultsBaricitinib improved all signs of eczema, with particularly rapid effects on scratching damage 📄Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 329The benefits of baricitinib can be maintained long-term (up to 52-68 weeks) in patients who respond to treatment. Some patients can even reduce their dose while maintaining benefits, though others may need to continue the original dose.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults. Clinical trials showed that it can significantly improve skin clearance and reduce itch, with about 30-40% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment.Randomized Controlled Trial Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Baricitinib 4mg showed the best results for skin clearance 📄This study looked at what happens when patients who responded well to baricitinib either continued their dose, reduced their dose, or stopped treatment completely. Most patients who reduced their dose maintained improvement in their eczema, and those who lost improvement usually got better again when restarting their original dose.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 526Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableMost patients who lost response regained improvement after restarting their original dose 📄Baricitinib combined with topical steroids showed long-term effectiveness in treating moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 68 weeks. About 40-60% of patients saw significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, and around 40-50% experienced meaningful itch reduction.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 155Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Long-term improvement in eczema severity was maintained across both doses Common side effects include nasopharyngitis (common cold), herpes simplex infections, upper respiratory infections, and headache. While the medication is generally well-tolerated, patients need to be monitored for infections and other potential side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib combined with topical steroids was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in patients who couldn't use or didn't respond to ciclosporin. After 16 weeks, 32% of patients on the highest dose (4mg) had their eczema improve by 75% or more, compared to 17% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for up to one year.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 463Severity: moderate to severeAge: not available📄Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 329In real-world clinical practice, about 43% of patients may discontinue treatment due to lack of effectiveness or side effects. However, the medication can be effective even in patients who didn't respond to other treatments like dupilumab.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Baricitinib showed some effectiveness in treating difficult-to-treat eczema patients, including those who didn't respond to dupilumab. However, about 43% of patients stopped treatment due to either lack of effectiveness or side effects. The most common side effects were nausea, urinary tract infections, and herpes simplex infections.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 51Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+About 3 in 10 patients achieved low disease activity after 16 weeks Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical corticosteroids (TCS) is effective for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, with about 31% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment. The medication starts working quickly, with improvements in itch seen as early as 2-4 days after starting treatment.
Summary:Baricitinib, whether used alone or with topical steroids, quickly improved all four main signs of eczema (excoriation, swelling/bumps, redness, and skin thickening). The medication worked particularly well for reducing scratching damage, with improvements seen as early as the first week of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: adultsResults:Baricitinib improved all signs of eczema, with particularly rapid effects on scratching damage
Summary:Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 329Results:
The benefits of baricitinib can be maintained long-term (up to 52-68 weeks) in patients who respond to treatment. Some patients can even reduce their dose while maintaining benefits, though others may need to continue the original dose.
Summary:Baricitinib is effective in treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults. Clinical trials showed that it can significantly improve skin clearance and reduce itch, with about 30-40% of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Baricitinib 4mg showed the best results for skin clearance
Summary:This study looked at what happens when patients who responded well to baricitinib either continued their dose, reduced their dose, or stopped treatment completely. Most patients who reduced their dose maintained improvement in their eczema, and those who lost improvement usually got better again when restarting their original dose.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 526Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Most patients who lost response regained improvement after restarting their original dose
Summary:Baricitinib combined with topical steroids showed long-term effectiveness in treating moderate-to-severe eczema for up to 68 weeks. About 40-60% of patients saw significant improvement in their eczema symptoms, and around 40-50% experienced meaningful itch reduction.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 155Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:Long-term improvement in eczema severity was maintained across both doses
Common side effects include nasopharyngitis (common cold), herpes simplex infections, upper respiratory infections, and headache. While the medication is generally well-tolerated, patients need to be monitored for infections and other potential side effects.
Summary:Baricitinib combined with topical steroids was effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema in patients who couldn't use or didn't respond to ciclosporin. After 16 weeks, 32% of patients on the highest dose (4mg) had their eczema improve by 75% or more, compared to 17% on placebo, and these improvements lasted for up to one year.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 463Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:
Summary:Baricitinib 4mg combined with topical steroids helped improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults after 16 weeks of treatment. About 48% of patients on 4mg baricitinib achieved a 75% improvement in their eczema severity score (EASI-75), compared to 23% on placebo. The medication also helped reduce itch quickly, with improvements seen as early as 2 days after starting treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 329Results:
In real-world clinical practice, about 43% of patients may discontinue treatment due to lack of effectiveness or side effects. However, the medication can be effective even in patients who didn't respond to other treatments like dupilumab.
Summary:Baricitinib showed some effectiveness in treating difficult-to-treat eczema patients, including those who didn't respond to dupilumab. However, about 43% of patients stopped treatment due to either lack of effectiveness or side effects. The most common side effects were nausea, urinary tract infections, and herpes simplex infections.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 51Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:About 3 in 10 patients achieved low disease activity after 16 weeks
-
 Imuran (Azathioprine)Who is this for?:If you have severe eczema but can wait 2-3 months for a responseNoneEffectiveness:Side Effects:High
Imuran (Azathioprine)Who is this for?:If you have severe eczema but can wait 2-3 months for a responseNoneEffectiveness:Side Effects:High⚠️ Boxed Warning
Cost:$22/monthDelivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $22/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSAzathioprine has shown lower effectiveness compared to newer treatments like dupilumab and high-dose cyclosporine for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Azathioprine has a slow onset of action (taking weeks to months to work) and requires regular blood test monitoring due to potential side effects on bone marrow and liver.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. Common side effects include stomach upset, increased risk of infections and cancers, bone marrow suppression, liver toxicity, and rare allergic reactions. Due to these risks, recent medical guidelines recommend against using azathioprine for atopic dermatitis.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Review Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableHigh dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events. 📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Treatment discontinuation rates are high with azathioprine, mainly due to side effects and lack of effectiveness. Studies show it has a higher rate of discontinuation compared to other treatments like dupilumab.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+📄This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Comparative Study Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Azathioprine has shown lower effectiveness compared to newer treatments like dupilumab and high-dose cyclosporine for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Azathioprine has a slow onset of action (taking weeks to months to work) and requires regular blood test monitoring due to potential side effects on bone marrow and liver.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Common side effects include stomach upset, increased risk of infections and cancers, bone marrow suppression, liver toxicity, and rare allergic reactions. Due to these risks, recent medical guidelines recommend against using azathioprine for atopic dermatitis.
Summary:Newer treatments for atopic dermatitis (like dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, and JAK inhibitors) are showing better results with fewer side effects compared to older medications. High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab work better than methotrexate and azathioprine. While high-dose upadacitinib was most effective, it had more side effects.Study Type:ReviewStudied Population:Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:High dose cyclosporine and dupilumab showed superior efficacy compared to methotrexate and azathioprine. High-dose upadacitinib showed highest efficacy but with more adverse events.
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Treatment discontinuation rates are high with azathioprine, mainly due to side effects and lack of effectiveness. Studies show it has a higher rate of discontinuation compared to other treatments like dupilumab.
Summary:This study looked at 10 years of data on oral immunosuppressive treatments for severe atopic dermatitis in two hospitals. Cyclosporine A was the most commonly used medication (80% of patients), followed by mycophenolate mofetil (31%). Treatment was often stopped due to either the disease being controlled, the medication not working, or side effects.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 334Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:
Summary:This study compared how long patients stayed on different medications for atopic dermatitis and why they stopped taking them. Dupilumab had the highest continuation rate, with only one patient stopping treatment. Other medications like cyclosporine, azathioprine, and methotrexate were often stopped due to side effects.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 94Severity: moderate to severeAge: 18+Results:
Procedure
-
 Phototherapy(UV-A, Narrowband UV-B)If your child wishes to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsIf you wish to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsLight exposure 2-3 times per weekMedium
Phototherapy(UV-A, Narrowband UV-B)If your child wishes to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsIf you wish to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsLight exposure 2-3 times per weekMediumSide Effect Affected Skin redness Skin dryness $325 per monthKEY TAKEAWAYSPhototherapy is effective at reducing eczema symptoms and severity in both children and adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. Studies show significant improvements in itching, sleep quality, and overall disease severity scores.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsTreatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years 📄Narrowband UVB light therapy improved symptoms and quality of life for atopic dermatitis patients, with benefits lasting up to 3 months after treatment. The treatment caused only mild side effects like slight redness and burning.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 144Severity: not availableAge: not availablePO-SCORAD scores showed significant improvement that lasted for at least 3 months 📄Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not available70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment Phototherapy helps reduce the need for topical steroid creams. One large study found that 70% of patients needed significantly less topical steroids in the 12 months after phototherapy treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not available70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment Phototherapy is generally safe with minimal side effects. The most common side effect is dry skin. However, some patients may experience mild redness or burning. People with certain conditions like skin cancer history should not receive phototherapy.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsTreatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years 📄Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableBoth types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity Different types of phototherapy (NB-UVB and UVA-1) appear to have similar effectiveness, though some studies suggest higher doses may work better for people with darker skin types.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableBoth types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity 📄UVA1 phototherapy is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis. High-dose UVA1 treatment works better than medium-dose for patients with darker skin, while both doses work equally well for patients with fair skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 27Severity: severeAge: 18+Both doses improved SCORAD scores, with high dose being significantly more effective in darker skin types (p<0.0001) Phototherapy is effective at reducing eczema symptoms and severity in both children and adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. Studies show significant improvements in itching, sleep quality, and overall disease severity scores.
Summary:Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsResults:Treatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years
Summary:Narrowband UVB light therapy improved symptoms and quality of life for atopic dermatitis patients, with benefits lasting up to 3 months after treatment. The treatment caused only mild side effects like slight redness and burning.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 144Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:PO-SCORAD scores showed significant improvement that lasted for at least 3 months
Summary:Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment
Phototherapy helps reduce the need for topical steroid creams. One large study found that 70% of patients needed significantly less topical steroids in the 12 months after phototherapy treatment.
Summary:Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment
Phototherapy is generally safe with minimal side effects. The most common side effect is dry skin. However, some patients may experience mild redness or burning. People with certain conditions like skin cancer history should not receive phototherapy.
Summary:Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsResults:Treatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years
Summary:Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Both types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity
Different types of phototherapy (NB-UVB and UVA-1) appear to have similar effectiveness, though some studies suggest higher doses may work better for people with darker skin types.
Summary:Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Both types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity
Summary:UVA1 phototherapy is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis. High-dose UVA1 treatment works better than medium-dose for patients with darker skin, while both doses work equally well for patients with fair skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 27Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:Both doses improved SCORAD scores, with high dose being significantly more effective in darker skin types (p<0.0001)
-
 Elimination diet(Elimination diet)If your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsIf your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsProcedure dailyLow
Elimination diet(Elimination diet)If your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsIf your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsProcedure dailyLowSide Effect Affected KEY TAKEAWAYSElimination diets can be effective for some patients with atopic dermatitis, with about 60% of patients showing improvement in their skin condition when certain foods are removed from their dietStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Comparative Study Total Patients: 31More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet When food-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis follow an elimination diet, their allergic responses (measured by IgE antibodies) to problematic foods like eggs or milk decrease over timeStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableElimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms While elimination diets may help some patients, it's difficult to predict who will respond well to the diet just based on standard allergy tests (like skin prick tests or blood tests)Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Comparative Study 📄In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Comparative Study Total Patients: 31More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet Patients who show improvement with elimination diets often experience a reduction in both skin symptoms and internal immune responsesStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Comparative Study 📄Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableElimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms Elimination diets can be effective for some patients with atopic dermatitis, with about 60% of patients showing improvement in their skin condition when certain foods are removed from their diet
Summary:In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 31Results:More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet
When food-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis follow an elimination diet, their allergic responses (measured by IgE antibodies) to problematic foods like eggs or milk decrease over time
Summary:Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Elimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms
While elimination diets may help some patients, it's difficult to predict who will respond well to the diet just based on standard allergy tests (like skin prick tests or blood tests)
Summary:There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
Summary:In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 31Results:More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet
Patients who show improvement with elimination diets often experience a reduction in both skin symptoms and internal immune responses
Summary:There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
Summary:Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Elimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms
-
 Allergen-specific immunotherapy(AIT)If your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedIf your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedInjection weeklyMedium
Allergen-specific immunotherapy(AIT)If your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedIf your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedInjection weeklyMediumSide Effect Affected slight adverse events Nausea Abdominal pain Rhinitis aggravation KEY TAKEAWAYS -
 Acupuncture(Acupuncture)If you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenIf you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenProcedure weeklyLow
Acupuncture(Acupuncture)If you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenIf you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenProcedure weeklyLowSide Effect Affected $400 per month($500 - $300)KEY TAKEAWAYSAcupuncture appears to be effective at reducing itch intensity and symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with twice-weekly treatments for 4 weeks showing significant improvements compared to sham (placebo) acupunctureStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 30Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture Acupuncture can help reduce both immediate itch symptoms (when applied during an itch episode) and prevent future itch episodes, with immediate treatment showing stronger effects for reducing itch intensityStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect 📄Acupuncture at specific points significantly reduced itch in patients with atopic eczema compared to placebo acupuncture or no treatment. The treatment also reduced skin reactions to allergens when given preventively.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 30Severity: not availableAge: not availableTrue acupuncture significantly reduced itch intensity both immediately and preventively Acupuncture appears to be as effective as antihistamine medications (like cetirizine) for reducing itch, but without causing drowsiness or reduced attention that are common side effects of antihistaminesStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect Acupuncture treatment is generally safe, with only mild and rare side effects reported like temporary numbness or mild discomfortStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 30Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture Acupuncture appears to be effective at reducing itch intensity and symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with twice-weekly treatments for 4 weeks showing significant improvements compared to sham (placebo) acupuncture
Summary:Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 30Results:Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture
Acupuncture can help reduce both immediate itch symptoms (when applied during an itch episode) and prevent future itch episodes, with immediate treatment showing stronger effects for reducing itch intensity
Summary:Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect
Summary:Acupuncture at specific points significantly reduced itch in patients with atopic eczema compared to placebo acupuncture or no treatment. The treatment also reduced skin reactions to allergens when given preventively.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 30Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:True acupuncture significantly reduced itch intensity both immediately and preventively
Acupuncture appears to be as effective as antihistamine medications (like cetirizine) for reducing itch, but without causing drowsiness or reduced attention that are common side effects of antihistamines
Summary:Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect
Acupuncture treatment is generally safe, with only mild and rare side effects reported like temporary numbness or mild discomfort
Summary:Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 30Results:Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture
-
 Bleach baths(Sodium hypochlorite)Add-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsAdd-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsProcedure weeklyLow
Bleach baths(Sodium hypochlorite)Add-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsAdd-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsProcedure weeklyLowSide Effect Affected Stinging and burning Itching ($15 - $60)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of bleach baths for treating eczema shows mixed results. While some studies show improvement in symptoms, others found bleach baths were not more effective than plain water baths in reducing bacteria or improving eczema severity.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableWater baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area 📄The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria Bleach body wash (0.006% sodium hypochlorite) may be a more convenient alternative to bleach baths. Studies showed the body wash improved symptoms and reduced the need for topical steroids, with patients preferring it over traditional bleach baths.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsPatients showed improvement in overall eczema severity Bleach treatments appear to work through multiple mechanisms beyond just killing bacteria. They may have direct anti-inflammatory effects on the skin.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsPatients showed improvement in overall eczema severity 📄The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria Bleach treatments are generally well-tolerated and safe, with no significant adverse effects on skin barrier function reported.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsPatients showed improvement in overall eczema severity 📄Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableWater baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area The effectiveness of bleach baths for treating eczema shows mixed results. While some studies show improvement in symptoms, others found bleach baths were not more effective than plain water baths in reducing bacteria or improving eczema severity.
Summary:Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Water baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area
Summary:The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria
Bleach body wash (0.006% sodium hypochlorite) may be a more convenient alternative to bleach baths. Studies showed the body wash improved symptoms and reduced the need for topical steroids, with patients preferring it over traditional bleach baths.
Summary:A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsResults:Patients showed improvement in overall eczema severity
Bleach treatments appear to work through multiple mechanisms beyond just killing bacteria. They may have direct anti-inflammatory effects on the skin.
Summary:A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsResults:Patients showed improvement in overall eczema severity
Summary:The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria
Bleach treatments are generally well-tolerated and safe, with no significant adverse effects on skin barrier function reported.
Summary:A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsResults:Patients showed improvement in overall eczema severity
Summary:Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Water baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area
-
 Phototherapy (UV-A, Narrowband UV-B)Who is this for?:If you wish to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsIf your child wishes to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$325 per monthDelivery:Light exposure 2-3 times per weekSee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSPhototherapy is effective at reducing eczema symptoms and severity in both children and adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. Studies show significant improvements in itching, sleep quality, and overall disease severity scores.
Phototherapy (UV-A, Narrowband UV-B)Who is this for?:If you wish to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsIf your child wishes to avoid or reduce reliance on topical and drug treatmentsEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$325 per monthDelivery:Light exposure 2-3 times per weekSee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSPhototherapy is effective at reducing eczema symptoms and severity in both children and adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. Studies show significant improvements in itching, sleep quality, and overall disease severity scores.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsTreatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years 📄Narrowband UVB light therapy improved symptoms and quality of life for atopic dermatitis patients, with benefits lasting up to 3 months after treatment. The treatment caused only mild side effects like slight redness and burning.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 144Severity: not availableAge: not availablePO-SCORAD scores showed significant improvement that lasted for at least 3 months 📄Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not available70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment Phototherapy helps reduce the need for topical steroid creams. One large study found that 70% of patients needed significantly less topical steroids in the 12 months after phototherapy treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not available70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment Phototherapy is generally safe with minimal side effects. The most common side effect is dry skin. However, some patients may experience mild redness or burning. People with certain conditions like skin cancer history should not receive phototherapy.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsTreatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years 📄Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableBoth types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity Different types of phototherapy (NB-UVB and UVA-1) appear to have similar effectiveness, though some studies suggest higher doses may work better for people with darker skin types.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableBoth types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity 📄UVA1 phototherapy is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis. High-dose UVA1 treatment works better than medium-dose for patients with darker skin, while both doses work equally well for patients with fair skin.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 27Severity: severeAge: 18+Both doses improved SCORAD scores, with high dose being significantly more effective in darker skin types (p<0.0001) Phototherapy is effective at reducing eczema symptoms and severity in both children and adults with moderate-to-severe eczema. Studies show significant improvements in itching, sleep quality, and overall disease severity scores.
Summary:Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsResults:Treatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years
Summary:Narrowband UVB light therapy improved symptoms and quality of life for atopic dermatitis patients, with benefits lasting up to 3 months after treatment. The treatment caused only mild side effects like slight redness and burning.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 144Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:PO-SCORAD scores showed significant improvement that lasted for at least 3 months
Summary:Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment
Phototherapy helps reduce the need for topical steroid creams. One large study found that 70% of patients needed significantly less topical steroids in the 12 months after phototherapy treatment.
Summary:Narrowband UVB light therapy helped reduce the need for steroid creams in 70% of eczema patients. About half of the patients achieved clear or almost clear skin after treatment. The therapy also reduced the need for oral steroids and antihistamines.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 844Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:70% of patients needed less topical steroids after treatment
Phototherapy is generally safe with minimal side effects. The most common side effect is dry skin. However, some patients may experience mild redness or burning. People with certain conditions like skin cancer history should not receive phototherapy.
Summary:Narrow-band UVB light therapy was found to be effective and safe for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children aged 4-14 years. The treatment improved symptoms significantly, and these improvements lasted for up to 2 years after treatment ended.Study Type:Studied Population:Total Patients: 30Severity: moderate to severeAge: 4-14 yearsResults:Treatment improved AD symptoms significantly and maintained improvement for 2 years
Summary:Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Both types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity
Different types of phototherapy (NB-UVB and UVA-1) appear to have similar effectiveness, though some studies suggest higher doses may work better for people with darker skin types.
Summary:Both types of light therapy (narrowband UVB alone or combined with UVA) were equally effective in treating chronic atopic dermatitis. The main difference was that patients receiving only narrowband UVB experienced more skin dryness.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 19Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Both types of light therapy were effective in improving eczema severity
Summary:UVA1 phototherapy is effective for treating severe atopic dermatitis. High-dose UVA1 treatment works better than medium-dose for patients with darker skin, while both doses work equally well for patients with fair skin.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 27Severity: severeAge: 18+Results:Both doses improved SCORAD scores, with high dose being significantly more effective in darker skin types (p<0.0001)
-
 Elimination diet (Elimination diet)Who is this for?:If your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsIf your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Procedure None dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSElimination diets can be effective for some patients with atopic dermatitis, with about 60% of patients showing improvement in their skin condition when certain foods are removed from their diet
Elimination diet (Elimination diet)Who is this for?:If your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsIf your AD is triggered by certain food ingredientsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Procedure None dailySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSElimination diets can be effective for some patients with atopic dermatitis, with about 60% of patients showing improvement in their skin condition when certain foods are removed from their dietStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Comparative Study Total Patients: 31More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet When food-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis follow an elimination diet, their allergic responses (measured by IgE antibodies) to problematic foods like eggs or milk decrease over timeStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableElimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms While elimination diets may help some patients, it's difficult to predict who will respond well to the diet just based on standard allergy tests (like skin prick tests or blood tests)Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Comparative Study 📄In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Comparative Study Total Patients: 31More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet Patients who show improvement with elimination diets often experience a reduction in both skin symptoms and internal immune responsesStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Comparative Study 📄Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: not availableElimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms Elimination diets can be effective for some patients with atopic dermatitis, with about 60% of patients showing improvement in their skin condition when certain foods are removed from their diet
Summary:In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 31Results:More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet
When food-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis follow an elimination diet, their allergic responses (measured by IgE antibodies) to problematic foods like eggs or milk decrease over time
Summary:Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Elimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms
While elimination diets may help some patients, it's difficult to predict who will respond well to the diet just based on standard allergy tests (like skin prick tests or blood tests)
Summary:There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
Summary:In children with severe eczema and gut symptoms, 61% showed improvement when following an elimination diet. The presence of certain immune cells (IgE-positive cells) in the gut could help predict which children would not respond to an elimination diet.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 31Results:More than half of the children showed improvement with elimination diet
Patients who show improvement with elimination diets often experience a reduction in both skin symptoms and internal immune responses
Summary:There is limited scientific evidence that elimination diets help with atopic dermatitis, except in cases where specific food allergies have been confirmed. Food elimination should only be done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.Study Type:Comparative StudyStudied Population:Results:
Summary:Elimination diets helped improve symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who were sensitive to egg or milk. During the elimination diet, both antibodies to these foods and immune cell responses decreased, suggesting the diet was effective.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Elimination diet led to improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms
-
 Allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedIf your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Injection weeklySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYS
Allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedIf your AD is related to allergies and other treatment-options are exhaustedEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:Delivery:Injection weeklySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYS -
 Acupuncture (Acupuncture)Who is this for?:If you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenIf you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$400 per monthDelivery:Procedure weeklySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSAcupuncture appears to be effective at reducing itch intensity and symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with twice-weekly treatments for 4 weeks showing significant improvements compared to sham (placebo) acupuncture
Acupuncture (Acupuncture)Who is this for?:If you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenIf you are looking to add an alternative treatment to your regimenEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$400 per monthDelivery:Procedure weeklySee EvidenceDiscuss with a DermatologistKEY TAKEAWAYSAcupuncture appears to be effective at reducing itch intensity and symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with twice-weekly treatments for 4 weeks showing significant improvements compared to sham (placebo) acupunctureStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 30Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture Acupuncture can help reduce both immediate itch symptoms (when applied during an itch episode) and prevent future itch episodes, with immediate treatment showing stronger effects for reducing itch intensityStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect 📄Acupuncture at specific points significantly reduced itch in patients with atopic eczema compared to placebo acupuncture or no treatment. The treatment also reduced skin reactions to allergens when given preventively.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 30Severity: not availableAge: not availableTrue acupuncture significantly reduced itch intensity both immediately and preventively Acupuncture appears to be as effective as antihistamine medications (like cetirizine) for reducing itch, but without causing drowsiness or reduced attention that are common side effects of antihistaminesStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 20All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect Acupuncture treatment is generally safe, with only mild and rare side effects reported like temporary numbness or mild discomfortStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 30Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture Acupuncture appears to be effective at reducing itch intensity and symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, with twice-weekly treatments for 4 weeks showing significant improvements compared to sham (placebo) acupuncture
Summary:Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 30Results:Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture
Acupuncture can help reduce both immediate itch symptoms (when applied during an itch episode) and prevent future itch episodes, with immediate treatment showing stronger effects for reducing itch intensity
Summary:Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect
Summary:Acupuncture at specific points significantly reduced itch in patients with atopic eczema compared to placebo acupuncture or no treatment. The treatment also reduced skin reactions to allergens when given preventively.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 30Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:True acupuncture significantly reduced itch intensity both immediately and preventively
Acupuncture appears to be as effective as antihistamine medications (like cetirizine) for reducing itch, but without causing drowsiness or reduced attention that are common side effects of antihistamines
Summary:Acupuncture was effective at reducing itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acupuncture given during an itch episode (abortive) worked better than both preventive acupuncture and the antihistamine cetirizine. Unlike cetirizine, acupuncture did not cause drowsiness or reduced attention.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 20Results:All active treatments significantly reduced itch compared to no intervention, with abortive acupuncture showing the strongest effect
Acupuncture treatment is generally safe, with only mild and rare side effects reported like temporary numbness or mild discomfort
Summary:Acupuncture treatment performed 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks improved symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Both itch and sleep improved with real acupuncture compared to sham acupuncture.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 30Results:Both twice-weekly and thrice-weekly acupuncture improved symptoms compared to sham acupuncture
-
 Bleach baths (Sodium hypochlorite)Who is this for?:Add-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsAdd-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Procedure weeklySee EvidenceBuy Bleach bathsNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of bleach baths for treating eczema shows mixed results. While some studies show improvement in symptoms, others found bleach baths were not more effective than plain water baths in reducing bacteria or improving eczema severity.
Bleach baths (Sodium hypochlorite)Who is this for?:Add-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsAdd-on to other treatments if you experience frequent skin infectionsEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Procedure weeklySee EvidenceBuy Bleach bathsNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSThe effectiveness of bleach baths for treating eczema shows mixed results. While some studies show improvement in symptoms, others found bleach baths were not more effective than plain water baths in reducing bacteria or improving eczema severity.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableWater baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area 📄The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria Bleach body wash (0.006% sodium hypochlorite) may be a more convenient alternative to bleach baths. Studies showed the body wash improved symptoms and reduced the need for topical steroids, with patients preferring it over traditional bleach baths.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsPatients showed improvement in overall eczema severity Bleach treatments appear to work through multiple mechanisms beyond just killing bacteria. They may have direct anti-inflammatory effects on the skin.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsPatients showed improvement in overall eczema severity 📄The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria Bleach treatments are generally well-tolerated and safe, with no significant adverse effects on skin barrier function reported.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Multicenter Study Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsPatients showed improvement in overall eczema severity 📄Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableWater baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area The effectiveness of bleach baths for treating eczema shows mixed results. While some studies show improvement in symptoms, others found bleach baths were not more effective than plain water baths in reducing bacteria or improving eczema severity.
Summary:Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Water baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area
Summary:The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria
Bleach body wash (0.006% sodium hypochlorite) may be a more convenient alternative to bleach baths. Studies showed the body wash improved symptoms and reduced the need for topical steroids, with patients preferring it over traditional bleach baths.
Summary:A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsResults:Patients showed improvement in overall eczema severity
Bleach treatments appear to work through multiple mechanisms beyond just killing bacteria. They may have direct anti-inflammatory effects on the skin.
Summary:A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsResults:Patients showed improvement in overall eczema severity
Summary:The study found that using steroid cream alone was enough to normalize the bacteria on eczema-affected skin. Adding bleach baths to the treatment didn't provide additional benefits for changing the skin bacteria composition.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 35Severity: not availableAge: children (age range not specified)Results:Adding bleach baths to steroid cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for normalizing skin bacteria
Bleach treatments are generally well-tolerated and safe, with no significant adverse effects on skin barrier function reported.
Summary:A body wash containing diluted bleach (sodium hypochlorite) improved eczema symptoms in children with moderate-to-severe eczema who had Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on their skin. Patients preferred using the body wash over traditional bleach baths, and they needed to use less steroid cream during the study.Study Type:Multicenter StudyStudied Population:Total Patients: 50Severity: moderate to severeAge: 6 months-17 yearsResults:Patients showed improvement in overall eczema severity
Summary:Bleach baths taken twice weekly for 4 weeks were not more effective than regular water baths in treating moderate-to-severe eczema. While bleach baths did reduce the need for topical steroids and antibiotics, water baths actually showed better improvement in the affected skin area.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 40Severity: moderate to severeAge: not availableResults:Water baths were more effective than bleach baths in reducing affected area
Supportive & Adjunct Medications
-
 Zyrtec(Cetirizine)If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesOral dailyLow
Zyrtec(Cetirizine)If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected Urticaria (skin rash) 5% ($2 - $20)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSCetirizine is effective at reducing itching and other skin symptoms in both children and adults with atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cetirizine helped reduce itching and other symptoms of atopic dermatitis in adults, with better results at higher doses (40mg). The medication was most effective at reducing itching, redness, and skin thickening compared to placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 178Severity: not availableAge: 18+Higher doses of cetirizine were more effective at improving symptoms, with 40mg showing the best results Long-term use of cetirizine is safe, even in young children. Studies showed no negative effects on behavior, thinking ability, or physical development when used for up to 18 monthsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cetirizine was found to be safe for long-term use in young children with atopic dermatitis. The medication showed similar or fewer side effects compared to placebo over 18 months of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 817Severity: not availableAge: 12-24 monthsThis was primarily a safety study Cetirizine can help reduce the need for strong topical steroids in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Long-term use of cetirizine in infants with atopic dermatitis helped reduce the need for stronger topical steroids, especially in patients with more severe disease. The medication also significantly reduced the occurrence of hives compared to placebo (5.8% vs 16.2%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 817Severity: not specifiedAge: 12-24 monthsIn children with atopic dermatitis who are allergic to grass pollen or dust mites, cetirizine may help prevent or delay the development of asthmaStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In infants with atopic dermatitis who were allergic to grass pollen or house dust mites, cetirizine treatment for 18 months helped prevent or delay the development of asthma. This protective effect was particularly strong and lasted for 36 months in children allergic to grass pollen.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: 1-2 yearsCetirizine prevented/delayed asthma development in sensitized infants Cetirizine is effective at reducing itching and other skin symptoms in both children and adults with atopic dermatitis
Summary:Cetirizine helped reduce itching and other symptoms of atopic dermatitis in adults, with better results at higher doses (40mg). The medication was most effective at reducing itching, redness, and skin thickening compared to placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 178Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Higher doses of cetirizine were more effective at improving symptoms, with 40mg showing the best results
Long-term use of cetirizine is safe, even in young children. Studies showed no negative effects on behavior, thinking ability, or physical development when used for up to 18 months
Summary:Cetirizine was found to be safe for long-term use in young children with atopic dermatitis. The medication showed similar or fewer side effects compared to placebo over 18 months of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 817Severity: not availableAge: 12-24 monthsResults:This was primarily a safety study
Cetirizine can help reduce the need for strong topical steroids in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
Summary:Long-term use of cetirizine in infants with atopic dermatitis helped reduce the need for stronger topical steroids, especially in patients with more severe disease. The medication also significantly reduced the occurrence of hives compared to placebo (5.8% vs 16.2%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 817Severity: not specifiedAge: 12-24 monthsResults:
In children with atopic dermatitis who are allergic to grass pollen or dust mites, cetirizine may help prevent or delay the development of asthma
Summary:In infants with atopic dermatitis who were allergic to grass pollen or house dust mites, cetirizine treatment for 18 months helped prevent or delay the development of asthma. This protective effect was particularly strong and lasted for 36 months in children allergic to grass pollen.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: 1-2 yearsResults:Cetirizine prevented/delayed asthma development in sensitized infants
-
 Allegra(Fexofenadine)If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesOral dailyLow
Allegra(Fexofenadine)If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected ($9 - $16)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSWhen combined with topical corticosteroids, fexofenadine significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis. The improvement in itching can be noticed after just 1 day of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week Fexofenadine helps reduce itching both during the day and at night, and can decrease the area of skin affected by itching.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week Fexofenadine is generally safe to use, with side effects similar to those experienced by people taking a placebo (sugar pill).Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week When combined with topical corticosteroids, fexofenadine significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis. The improvement in itching can be noticed after just 1 day of treatment.
Summary:Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week
Fexofenadine helps reduce itching both during the day and at night, and can decrease the area of skin affected by itching.
Summary:Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week
Fexofenadine is generally safe to use, with side effects similar to those experienced by people taking a placebo (sugar pill).
Summary:Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week
-
 Mupirocin(Mupirocin)If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)Topical dailyLow
Mupirocin(Mupirocin)If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)Topical dailyLowSide Effect Affected diarrhea nausea $25/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSMupirocin combined with steroid creams (like hydrocortisone or fluticasone) is effective and safe for treating atopic dermatitis, especially when there might be bacterial infection present. In one study, 74% of patients improved with this combination treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A combination ointment containing fluticasone propionate and mupirocin was effective in treating atopic dermatitis with suspected bacterial infection. After 2 weeks of treatment, the majority of patients (67.2%) had only mild disease, and patient comfort improved from 33.65% to 78.60%.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 122Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableSignificant improvement in disease severity with majority of patients achieving mild disease status 📄Using hydrocortisone cream combined with mupirocin was more effective (74% success) than hydrocortisone alone (65% success) or moisturizer (36% success) in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in infants. The combination treatment was safe and helped address potential bacterial infection.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 83Combined treatment with hydrocortisone and mupirocin was most effective, followed by hydrocortisone alone, both significantly better than emollient Mupirocin cream is as effective as oral antibiotics (like cephalexin) for treating infected eczema, with fewer side effects. It's also preferred by patients because it's applied directly to the skin rather than taken as pills.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableMupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin While mupirocin can effectively reduce bacteria (particularly Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin during treatment, bacteria levels may return to normal after stopping treatment. However, this doesn't necessarily mean symptoms will get worse.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableMupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts Short-term use of mupirocin appears to be safe, with minimal side effects. The most common side effects reported were mild and included diarrhea and nausea.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableMupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin 📄Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableMupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts Mupirocin combined with steroid creams (like hydrocortisone or fluticasone) is effective and safe for treating atopic dermatitis, especially when there might be bacterial infection present. In one study, 74% of patients improved with this combination treatment.
Summary:A combination ointment containing fluticasone propionate and mupirocin was effective in treating atopic dermatitis with suspected bacterial infection. After 2 weeks of treatment, the majority of patients (67.2%) had only mild disease, and patient comfort improved from 33.65% to 78.60%.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 122Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableResults:Significant improvement in disease severity with majority of patients achieving mild disease status
Summary:Using hydrocortisone cream combined with mupirocin was more effective (74% success) than hydrocortisone alone (65% success) or moisturizer (36% success) in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in infants. The combination treatment was safe and helped address potential bacterial infection.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 83Results:Combined treatment with hydrocortisone and mupirocin was most effective, followed by hydrocortisone alone, both significantly better than emollient
Mupirocin cream is as effective as oral antibiotics (like cephalexin) for treating infected eczema, with fewer side effects. It's also preferred by patients because it's applied directly to the skin rather than taken as pills.
Summary:Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin
While mupirocin can effectively reduce bacteria (particularly Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin during treatment, bacteria levels may return to normal after stopping treatment. However, this doesn't necessarily mean symptoms will get worse.
Summary:Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts
Short-term use of mupirocin appears to be safe, with minimal side effects. The most common side effects reported were mild and included diarrhea and nausea.
Summary:Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin
Summary:Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts
-
 Claritin(Loratadine)If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesOral dailyLow
Claritin(Loratadine)If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesOral dailyLowSide Effect Affected somnolence/sedation ($3 - $16)No prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSLoratadine can help reduce itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis, both during the day and night. More than half of patients showed positive response to the treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Loratadine significantly reduced itching (pruritus) in patients with atopic dermatitis compared to placebo, both during day and night. At least 9 out of 16 patients responded positively to the treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 16Majority of patients (at least 56%) responded positively to loratadine treatment 📄Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo Loratadine is as effective as hydroxyzine (another antihistamine) for treating symptoms, but causes much less drowsiness. Only 5% of patients on loratadine reported feeling sleepy compared to 40% of those taking hydroxyzine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo When used alongside strong topical steroids (like mometasone cream), loratadine may not provide additional benefits, though it remains safe to use with no serious side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The study found that adding loratadine (an antihistamine) to mometasone cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for children with atopic dermatitis. The mometasone cream alone was very effective in treating the condition.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 48Severity: not availableAge: mean age 73.67 months (approximately 6 years)Both groups showed significant improvement, with no difference between loratadine and placebo groups (p = 0.99) A newer version of loratadine (desloratadine) combined with other medications may be effective for treating eczema and reducing inflammation.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The combination of desloratadine citrate and compound glycyrrhizin was more effective in treating subacute eczema compared to compound glycyrrhizin alone. The combination therapy showed lower inflammation markers and fewer side effects.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: subacuteAge: not availableThe combination therapy was more effective in reducing inflammation Loratadine can help reduce itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis, both during the day and night. More than half of patients showed positive response to the treatment.
Summary:Loratadine significantly reduced itching (pruritus) in patients with atopic dermatitis compared to placebo, both during day and night. At least 9 out of 16 patients responded positively to the treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 16Results:Majority of patients (at least 56%) responded positively to loratadine treatment
Summary:Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo
Loratadine is as effective as hydroxyzine (another antihistamine) for treating symptoms, but causes much less drowsiness. Only 5% of patients on loratadine reported feeling sleepy compared to 40% of those taking hydroxyzine.
Summary:Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo
When used alongside strong topical steroids (like mometasone cream), loratadine may not provide additional benefits, though it remains safe to use with no serious side effects.
Summary:The study found that adding loratadine (an antihistamine) to mometasone cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for children with atopic dermatitis. The mometasone cream alone was very effective in treating the condition.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 48Severity: not availableAge: mean age 73.67 months (approximately 6 years)Results:Both groups showed significant improvement, with no difference between loratadine and placebo groups (p = 0.99)
A newer version of loratadine (desloratadine) combined with other medications may be effective for treating eczema and reducing inflammation.
Summary:The combination of desloratadine citrate and compound glycyrrhizin was more effective in treating subacute eczema compared to compound glycyrrhizin alone. The combination therapy showed lower inflammation markers and fewer side effects.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: subacuteAge: not availableResults:The combination therapy was more effective in reducing inflammation
-
 Hydroxyzine(Hydroxyzine)If you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareIf you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareOral dailyMedium
Hydroxyzine(Hydroxyzine)If you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareIf you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareOral dailyMediumSide Effect Affected somnolence/sedation sedation $25/monthPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSHydroxyzine is effective at reducing itching (pruritus) in atopic dermatitis, with significant itch suppression lasting up to 24 hours after taking the medication. The best itch control (over 85% reduction) occurs between 2-12 hours after taking the medicine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation The medication can reduce daily symptoms of atopic dermatitis by about 38%, which is similar to other antihistamines like loratadine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy The main side effect is drowsiness/sedation, which is more common with hydroxyzine compared to newer antihistamines. In one study, 40% of patients on hydroxyzine reported feeling sleepy, compared to only 5% on loratadine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy 📄Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation For children with atopic dermatitis, a lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) can be just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg three times daily) while causing less drowsiness.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation Hydroxyzine is effective at reducing itching (pruritus) in atopic dermatitis, with significant itch suppression lasting up to 24 hours after taking the medication. The best itch control (over 85% reduction) occurs between 2-12 hours after taking the medicine.
Summary:Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Results:Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation
The medication can reduce daily symptoms of atopic dermatitis by about 38%, which is similar to other antihistamines like loratadine.
Summary:Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy
The main side effect is drowsiness/sedation, which is more common with hydroxyzine compared to newer antihistamines. In one study, 40% of patients on hydroxyzine reported feeling sleepy, compared to only 5% on loratadine.
Summary:Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy
Summary:Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Results:Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation
For children with atopic dermatitis, a lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) can be just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg three times daily) while causing less drowsiness.
Summary:Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Results:Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation
-
 Zyrtec (Cetirizine)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy ZyrtecNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSCetirizine is effective at reducing itching and other skin symptoms in both children and adults with atopic dermatitis
Zyrtec (Cetirizine)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy ZyrtecNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSCetirizine is effective at reducing itching and other skin symptoms in both children and adults with atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cetirizine helped reduce itching and other symptoms of atopic dermatitis in adults, with better results at higher doses (40mg). The medication was most effective at reducing itching, redness, and skin thickening compared to placebo.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 178Severity: not availableAge: 18+Higher doses of cetirizine were more effective at improving symptoms, with 40mg showing the best results Long-term use of cetirizine is safe, even in young children. Studies showed no negative effects on behavior, thinking ability, or physical development when used for up to 18 monthsStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Cetirizine was found to be safe for long-term use in young children with atopic dermatitis. The medication showed similar or fewer side effects compared to placebo over 18 months of treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 817Severity: not availableAge: 12-24 monthsThis was primarily a safety study Cetirizine can help reduce the need for strong topical steroids in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitisStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Long-term use of cetirizine in infants with atopic dermatitis helped reduce the need for stronger topical steroids, especially in patients with more severe disease. The medication also significantly reduced the occurrence of hives compared to placebo (5.8% vs 16.2%).Clinical Trial Total Patients: 817Severity: not specifiedAge: 12-24 monthsIn children with atopic dermatitis who are allergic to grass pollen or dust mites, cetirizine may help prevent or delay the development of asthmaStudy Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄In infants with atopic dermatitis who were allergic to grass pollen or house dust mites, cetirizine treatment for 18 months helped prevent or delay the development of asthma. This protective effect was particularly strong and lasted for 36 months in children allergic to grass pollen.Clinical Trial Severity: not availableAge: 1-2 yearsCetirizine prevented/delayed asthma development in sensitized infants Cetirizine is effective at reducing itching and other skin symptoms in both children and adults with atopic dermatitis
Summary:Cetirizine helped reduce itching and other symptoms of atopic dermatitis in adults, with better results at higher doses (40mg). The medication was most effective at reducing itching, redness, and skin thickening compared to placebo.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 178Severity: not availableAge: 18+Results:Higher doses of cetirizine were more effective at improving symptoms, with 40mg showing the best results
Long-term use of cetirizine is safe, even in young children. Studies showed no negative effects on behavior, thinking ability, or physical development when used for up to 18 months
Summary:Cetirizine was found to be safe for long-term use in young children with atopic dermatitis. The medication showed similar or fewer side effects compared to placebo over 18 months of treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 817Severity: not availableAge: 12-24 monthsResults:This was primarily a safety study
Cetirizine can help reduce the need for strong topical steroids in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
Summary:Long-term use of cetirizine in infants with atopic dermatitis helped reduce the need for stronger topical steroids, especially in patients with more severe disease. The medication also significantly reduced the occurrence of hives compared to placebo (5.8% vs 16.2%).Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 817Severity: not specifiedAge: 12-24 monthsResults:
In children with atopic dermatitis who are allergic to grass pollen or dust mites, cetirizine may help prevent or delay the development of asthma
Summary:In infants with atopic dermatitis who were allergic to grass pollen or house dust mites, cetirizine treatment for 18 months helped prevent or delay the development of asthma. This protective effect was particularly strong and lasted for 36 months in children allergic to grass pollen.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Severity: not availableAge: 1-2 yearsResults:Cetirizine prevented/delayed asthma development in sensitized infants
-
 Allegra (Fexofenadine)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy AllegraNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSWhen combined with topical corticosteroids, fexofenadine significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis. The improvement in itching can be noticed after just 1 day of treatment.
Allegra (Fexofenadine)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy AllegraNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSWhen combined with topical corticosteroids, fexofenadine significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis. The improvement in itching can be noticed after just 1 day of treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week Fexofenadine helps reduce itching both during the day and at night, and can decrease the area of skin affected by itching.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week Fexofenadine is generally safe to use, with side effects similar to those experienced by people taking a placebo (sugar pill).Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week When combined with topical corticosteroids, fexofenadine significantly reduces itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis. The improvement in itching can be noticed after just 1 day of treatment.
Summary:Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week
Fexofenadine helps reduce itching both during the day and at night, and can decrease the area of skin affected by itching.
Summary:Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week
Fexofenadine is generally safe to use, with side effects similar to those experienced by people taking a placebo (sugar pill).
Summary:Adding fexofenadine (an antihistamine) to topical hydrocortisone helped reduce itching in patients with atopic dermatitis more effectively than hydrocortisone alone. The improvement in itching was seen after just 1 day of treatment and continued throughout the study week.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 400Severity: not availableAge: 16+Results:Fexofenadine significantly reduced itching compared to placebo, with improvements seen after 1 day and maintained throughout the week
-
 Mupirocin (Mupirocin)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)Effectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$25/monthDelivery:Topical 3-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSMupirocin combined with steroid creams (like hydrocortisone or fluticasone) is effective and safe for treating atopic dermatitis, especially when there might be bacterial infection present. In one study, 74% of patients improved with this combination treatment.
Mupirocin (Mupirocin)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)If your AD is related to a bacterial infection (staphylococcus aureus)Effectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:$25/monthDelivery:Topical 3-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSMupirocin combined with steroid creams (like hydrocortisone or fluticasone) is effective and safe for treating atopic dermatitis, especially when there might be bacterial infection present. In one study, 74% of patients improved with this combination treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄A combination ointment containing fluticasone propionate and mupirocin was effective in treating atopic dermatitis with suspected bacterial infection. After 2 weeks of treatment, the majority of patients (67.2%) had only mild disease, and patient comfort improved from 33.65% to 78.60%.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 122Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableSignificant improvement in disease severity with majority of patients achieving mild disease status 📄Using hydrocortisone cream combined with mupirocin was more effective (74% success) than hydrocortisone alone (65% success) or moisturizer (36% success) in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in infants. The combination treatment was safe and helped address potential bacterial infection.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 83Combined treatment with hydrocortisone and mupirocin was most effective, followed by hydrocortisone alone, both significantly better than emollient Mupirocin cream is as effective as oral antibiotics (like cephalexin) for treating infected eczema, with fewer side effects. It's also preferred by patients because it's applied directly to the skin rather than taken as pills.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableMupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin While mupirocin can effectively reduce bacteria (particularly Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin during treatment, bacteria levels may return to normal after stopping treatment. However, this doesn't necessarily mean symptoms will get worse.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableMupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts Short-term use of mupirocin appears to be safe, with minimal side effects. The most common side effects reported were mild and included diarrhea and nausea.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableMupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin 📄Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableMupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts Mupirocin combined with steroid creams (like hydrocortisone or fluticasone) is effective and safe for treating atopic dermatitis, especially when there might be bacterial infection present. In one study, 74% of patients improved with this combination treatment.
Summary:A combination ointment containing fluticasone propionate and mupirocin was effective in treating atopic dermatitis with suspected bacterial infection. After 2 weeks of treatment, the majority of patients (67.2%) had only mild disease, and patient comfort improved from 33.65% to 78.60%.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 122Severity: mild to severeAge: not availableResults:Significant improvement in disease severity with majority of patients achieving mild disease status
Summary:Using hydrocortisone cream combined with mupirocin was more effective (74% success) than hydrocortisone alone (65% success) or moisturizer (36% success) in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in infants. The combination treatment was safe and helped address potential bacterial infection.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 83Results:Combined treatment with hydrocortisone and mupirocin was most effective, followed by hydrocortisone alone, both significantly better than emollient
Mupirocin cream is as effective as oral antibiotics (like cephalexin) for treating infected eczema, with fewer side effects. It's also preferred by patients because it's applied directly to the skin rather than taken as pills.
Summary:Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin
While mupirocin can effectively reduce bacteria (particularly Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin during treatment, bacteria levels may return to normal after stopping treatment. However, this doesn't necessarily mean symptoms will get worse.
Summary:Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts
Short-term use of mupirocin appears to be safe, with minimal side effects. The most common side effects reported were mild and included diarrhea and nausea.
Summary:Mupirocin cream was found to be as effective as oral cephalexin (an antibiotic) for treating infected eczema. The cream worked better at killing bacteria and was preferred by patients over taking oral medication.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 159Severity: secondarily infected eczemaAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin cream was similarly effective to oral cephalexin
Summary:Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, significantly reduced Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and improved their symptoms. Although bacteria returned after stopping treatment, patients' symptoms didn't get worse during the study period.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 49Severity: not availableAge: not availableResults:Mupirocin significantly reduced bacterial counts
-
 Claritin (Loratadine)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy ClaritinNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSLoratadine can help reduce itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis, both during the day and night. More than half of patients showed positive response to the treatment.
Claritin (Loratadine)Who is this for?:If your AD is related to allergiesIf your AD is related to allergiesEffectiveness:Side Effects:LowCost:Delivery:Oral dailySee EvidenceBuy ClaritinNo prescription neededKEY TAKEAWAYSLoratadine can help reduce itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis, both during the day and night. More than half of patients showed positive response to the treatment.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Loratadine significantly reduced itching (pruritus) in patients with atopic dermatitis compared to placebo, both during day and night. At least 9 out of 16 patients responded positively to the treatment.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 16Majority of patients (at least 56%) responded positively to loratadine treatment 📄Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo Loratadine is as effective as hydroxyzine (another antihistamine) for treating symptoms, but causes much less drowsiness. Only 5% of patients on loratadine reported feeling sleepy compared to 40% of those taking hydroxyzine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo When used alongside strong topical steroids (like mometasone cream), loratadine may not provide additional benefits, though it remains safe to use with no serious side effects.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The study found that adding loratadine (an antihistamine) to mometasone cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for children with atopic dermatitis. The mometasone cream alone was very effective in treating the condition.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 48Severity: not availableAge: mean age 73.67 months (approximately 6 years)Both groups showed significant improvement, with no difference between loratadine and placebo groups (p = 0.99) A newer version of loratadine (desloratadine) combined with other medications may be effective for treating eczema and reducing inflammation.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄The combination of desloratadine citrate and compound glycyrrhizin was more effective in treating subacute eczema compared to compound glycyrrhizin alone. The combination therapy showed lower inflammation markers and fewer side effects.Randomized Controlled Trial Total Patients: 100Severity: subacuteAge: not availableThe combination therapy was more effective in reducing inflammation Loratadine can help reduce itching (pruritus) in people with atopic dermatitis, both during the day and night. More than half of patients showed positive response to the treatment.
Summary:Loratadine significantly reduced itching (pruritus) in patients with atopic dermatitis compared to placebo, both during day and night. At least 9 out of 16 patients responded positively to the treatment.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 16Results:Majority of patients (at least 56%) responded positively to loratadine treatment
Summary:Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo
Loratadine is as effective as hydroxyzine (another antihistamine) for treating symptoms, but causes much less drowsiness. Only 5% of patients on loratadine reported feeling sleepy compared to 40% of those taking hydroxyzine.
Summary:Loratadine was found to be as effective as hydroxyzine in treating atopic dermatitis symptoms, reducing symptoms by 57%. Importantly, loratadine caused much less drowsiness than hydroxyzine, with only one patient reporting sleepiness compared to eight patients on hydroxyzine.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Loratadine showed better symptom reduction than both hydroxyzine and placebo
When used alongside strong topical steroids (like mometasone cream), loratadine may not provide additional benefits, though it remains safe to use with no serious side effects.
Summary:The study found that adding loratadine (an antihistamine) to mometasone cream treatment did not provide additional benefits for children with atopic dermatitis. The mometasone cream alone was very effective in treating the condition.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 48Severity: not availableAge: mean age 73.67 months (approximately 6 years)Results:Both groups showed significant improvement, with no difference between loratadine and placebo groups (p = 0.99)
A newer version of loratadine (desloratadine) combined with other medications may be effective for treating eczema and reducing inflammation.
Summary:The combination of desloratadine citrate and compound glycyrrhizin was more effective in treating subacute eczema compared to compound glycyrrhizin alone. The combination therapy showed lower inflammation markers and fewer side effects.Study Type:Randomized Controlled TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 100Severity: subacuteAge: not availableResults:The combination therapy was more effective in reducing inflammation
-
 Hydroxyzine (Hydroxyzine)Who is this for?:If you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareIf you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Oral 3-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSHydroxyzine is effective at reducing itching (pruritus) in atopic dermatitis, with significant itch suppression lasting up to 24 hours after taking the medication. The best itch control (over 85% reduction) occurs between 2-12 hours after taking the medicine.
Hydroxyzine (Hydroxyzine)Who is this for?:If you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareIf you need support for managing sleep and anxiety that worsens your eczema flareEffectiveness:Side Effects:MediumCost:$25/monthDelivery:Oral 3-4 dailySee EvidenceBuy Now — $25/moPlus $45 one-time consultation feeKEY TAKEAWAYSHydroxyzine is effective at reducing itching (pruritus) in atopic dermatitis, with significant itch suppression lasting up to 24 hours after taking the medication. The best itch control (over 85% reduction) occurs between 2-12 hours after taking the medicine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation The medication can reduce daily symptoms of atopic dermatitis by about 38%, which is similar to other antihistamines like loratadine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy The main side effect is drowsiness/sedation, which is more common with hydroxyzine compared to newer antihistamines. In one study, 40% of patients on hydroxyzine reported feeling sleepy, compared to only 5% on loratadine.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy 📄Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation For children with atopic dermatitis, a lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) can be just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg three times daily) while causing less drowsiness.Study Summary Study Type Studied Population Results 📄Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Clinical Trial Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation Hydroxyzine is effective at reducing itching (pruritus) in atopic dermatitis, with significant itch suppression lasting up to 24 hours after taking the medication. The best itch control (over 85% reduction) occurs between 2-12 hours after taking the medicine.
Summary:Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Results:Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation
The medication can reduce daily symptoms of atopic dermatitis by about 38%, which is similar to other antihistamines like loratadine.
Summary:Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy
The main side effect is drowsiness/sedation, which is more common with hydroxyzine compared to newer antihistamines. In one study, 40% of patients on hydroxyzine reported feeling sleepy, compared to only 5% on loratadine.
Summary:Hydroxyzine reduced symptoms by 38% in patients with atopic dermatitis, but caused significant drowsiness in 40% of patients. The medication was as effective as loratadine but had more side effects.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 41Severity: not availableAge: 18-65Results:Both medications reduced symptoms more than placebo, with loratadine showing better efficacy
Summary:Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Results:Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation
For children with atopic dermatitis, a lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) can be just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg three times daily) while causing less drowsiness.
Summary:Hydroxyzine effectively reduced itching in children with severe eczema, with over 85% reduction in itching from 2-12 hours after taking the medicine. A lower dose (0.7 mg/kg three times daily) was just as effective as a higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) but caused less drowsiness.Study Type:Clinical TrialStudied Population:Total Patients: 12Severity: severeAge: children (mean 6.1 ± 4.6 years)Results:Lower dose (0.7 mg/kg) was as effective as higher dose (1.4 mg/kg) with less sedation